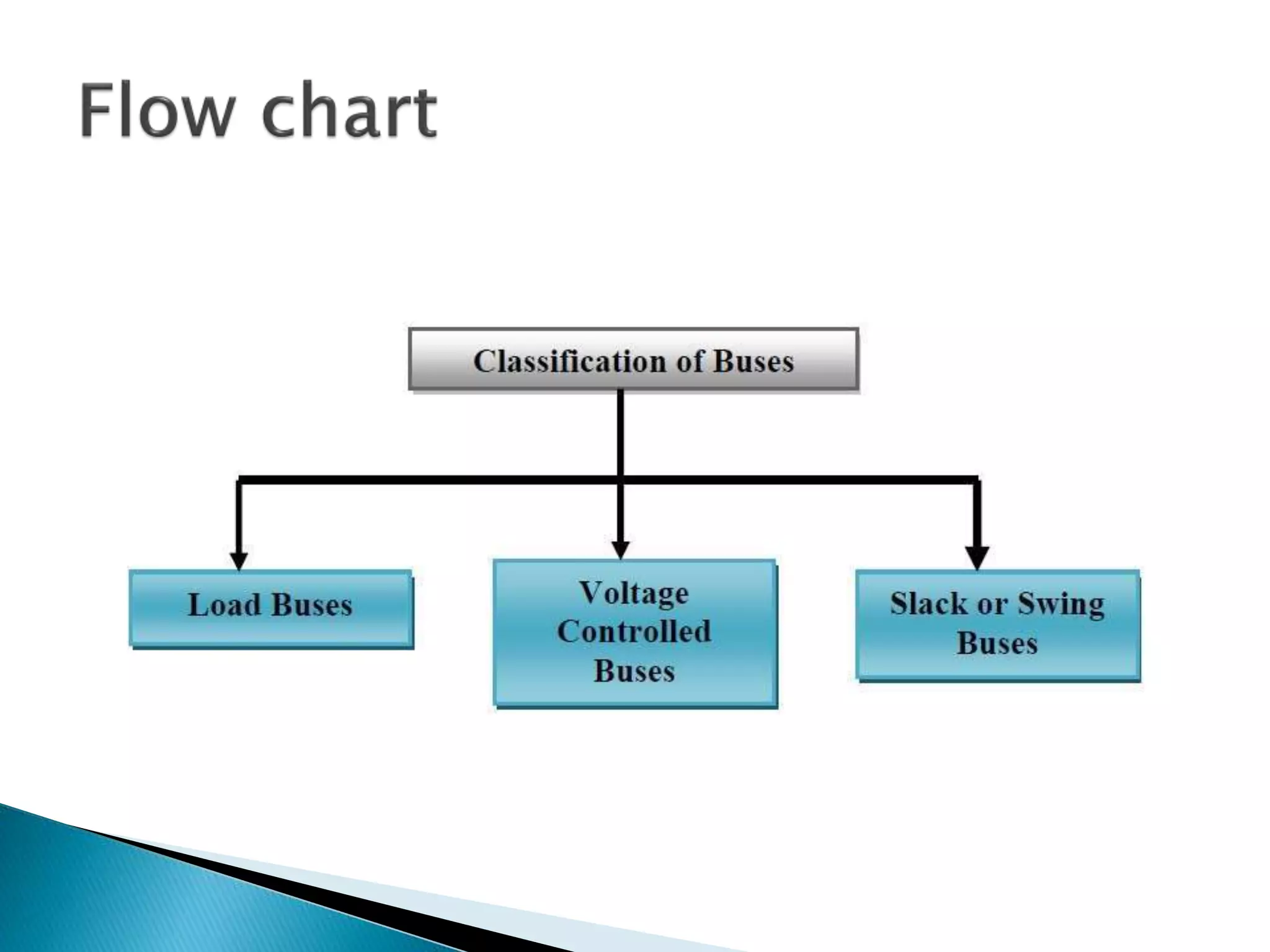
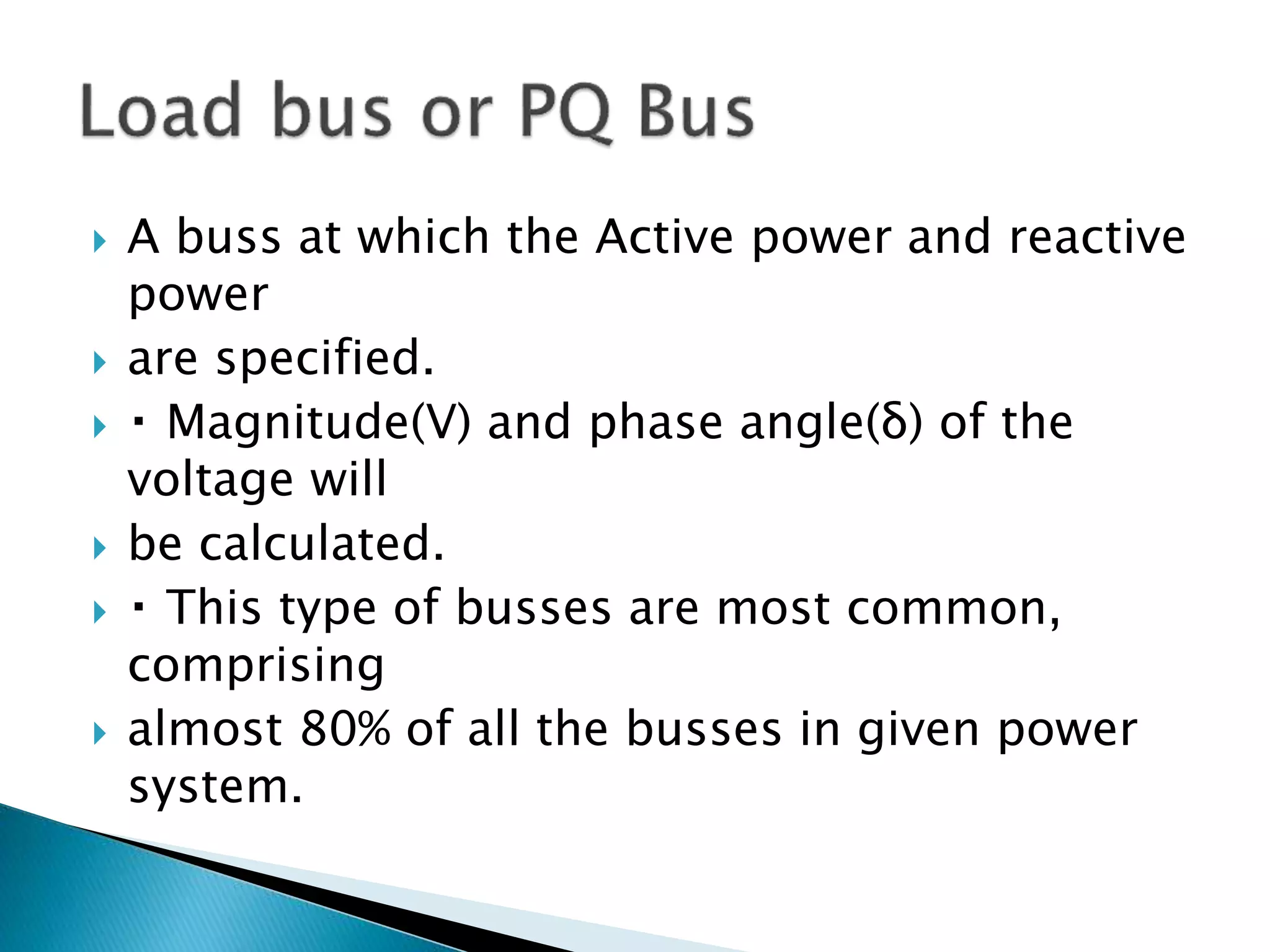
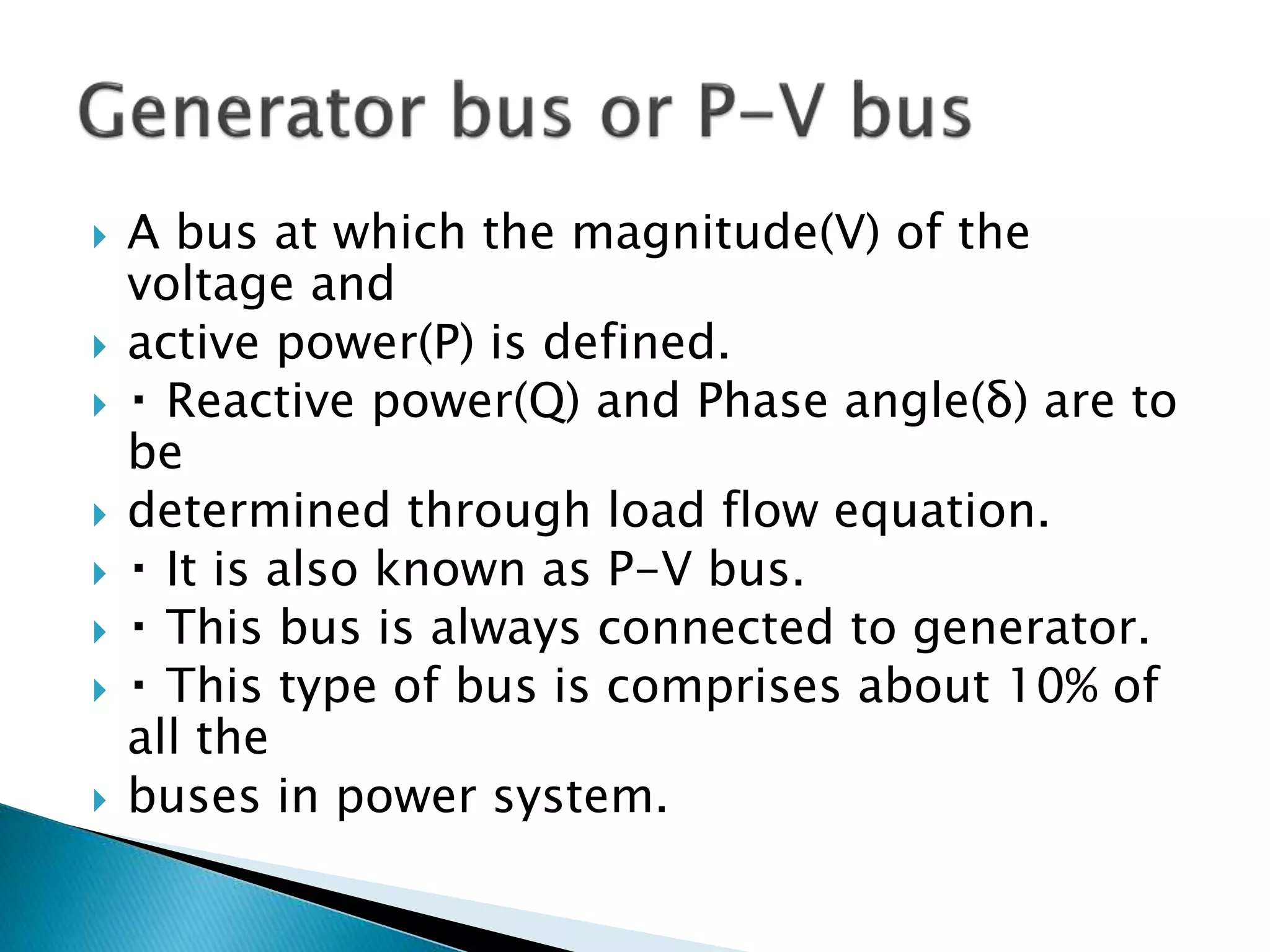
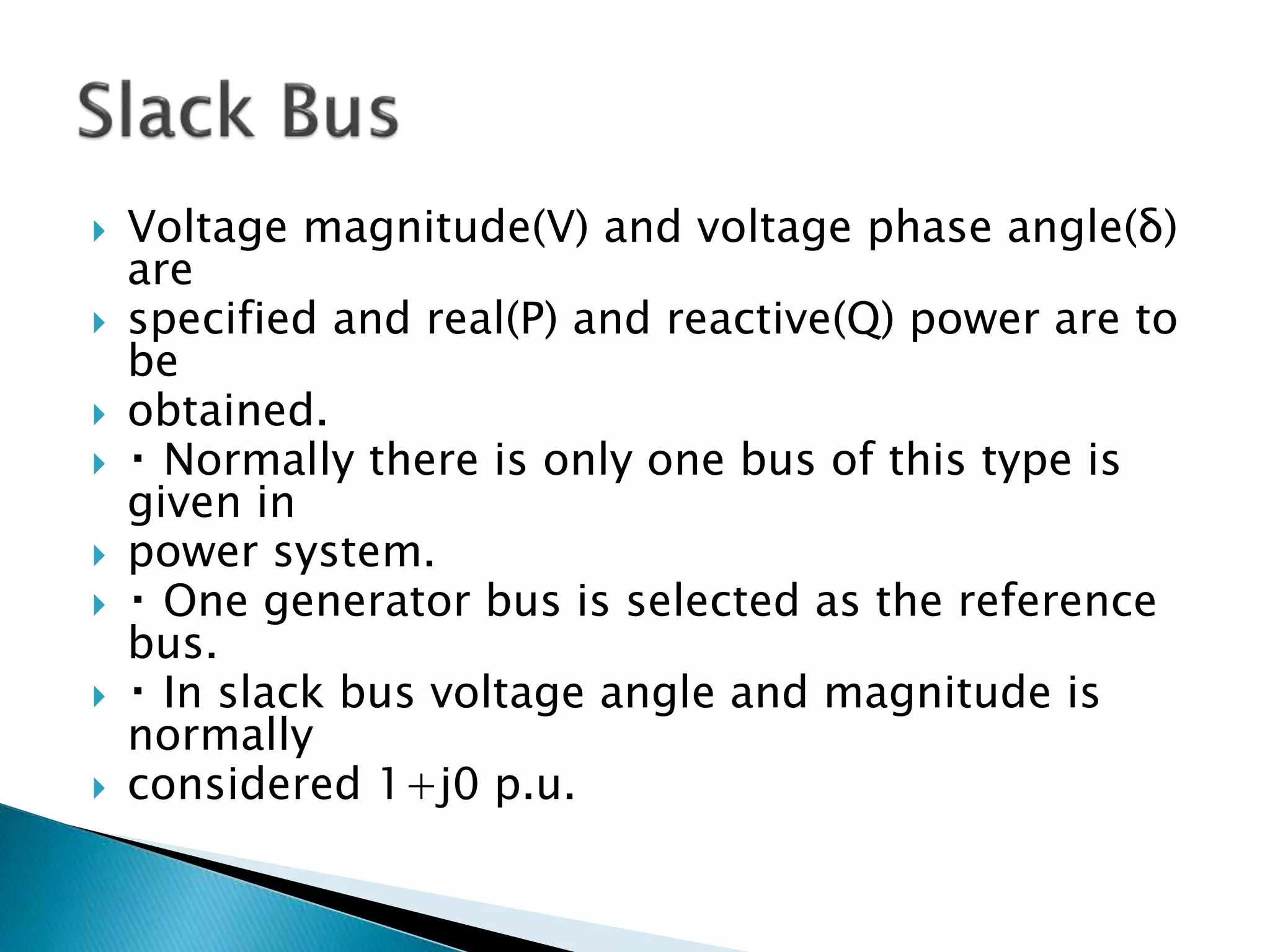
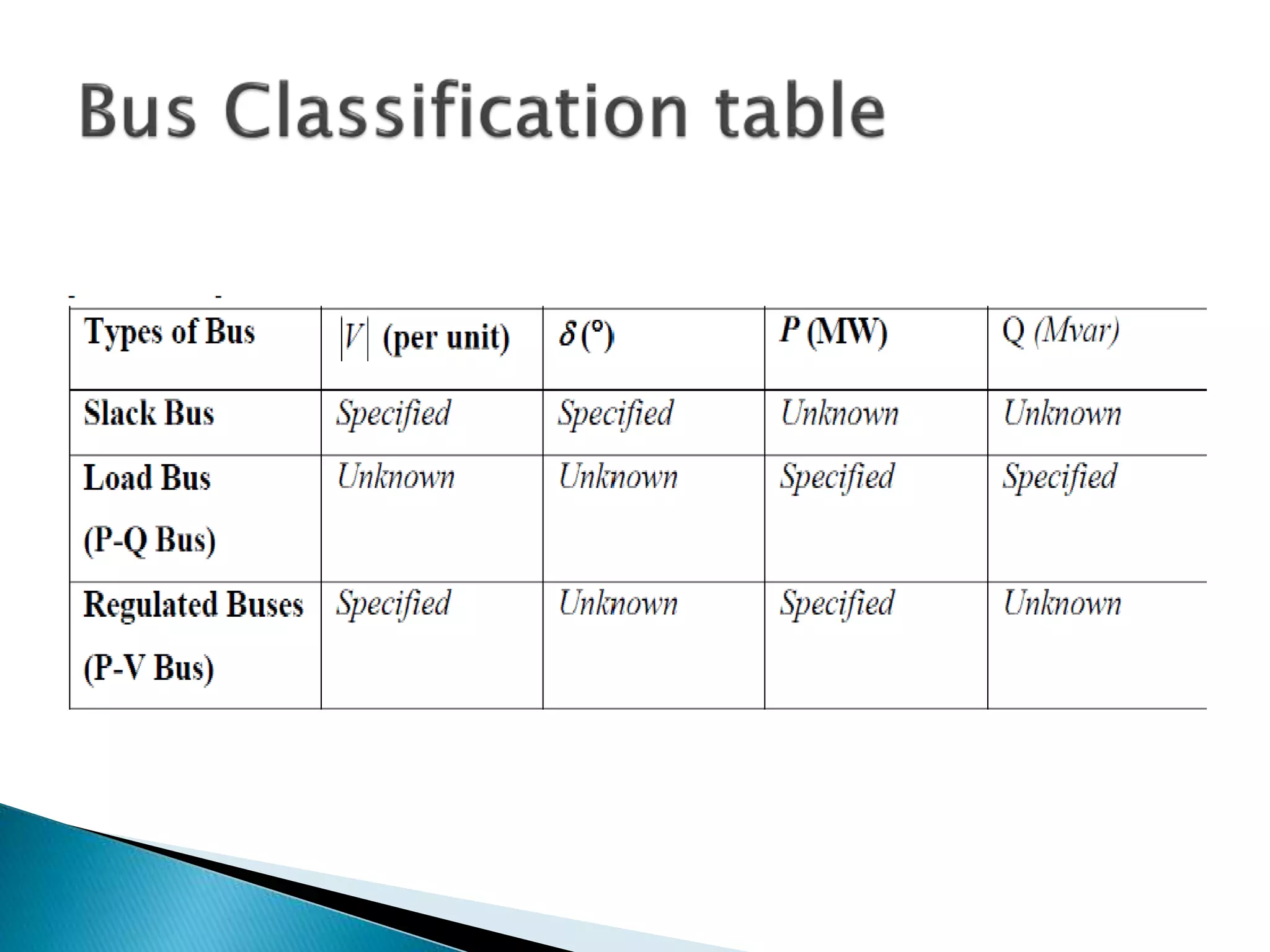
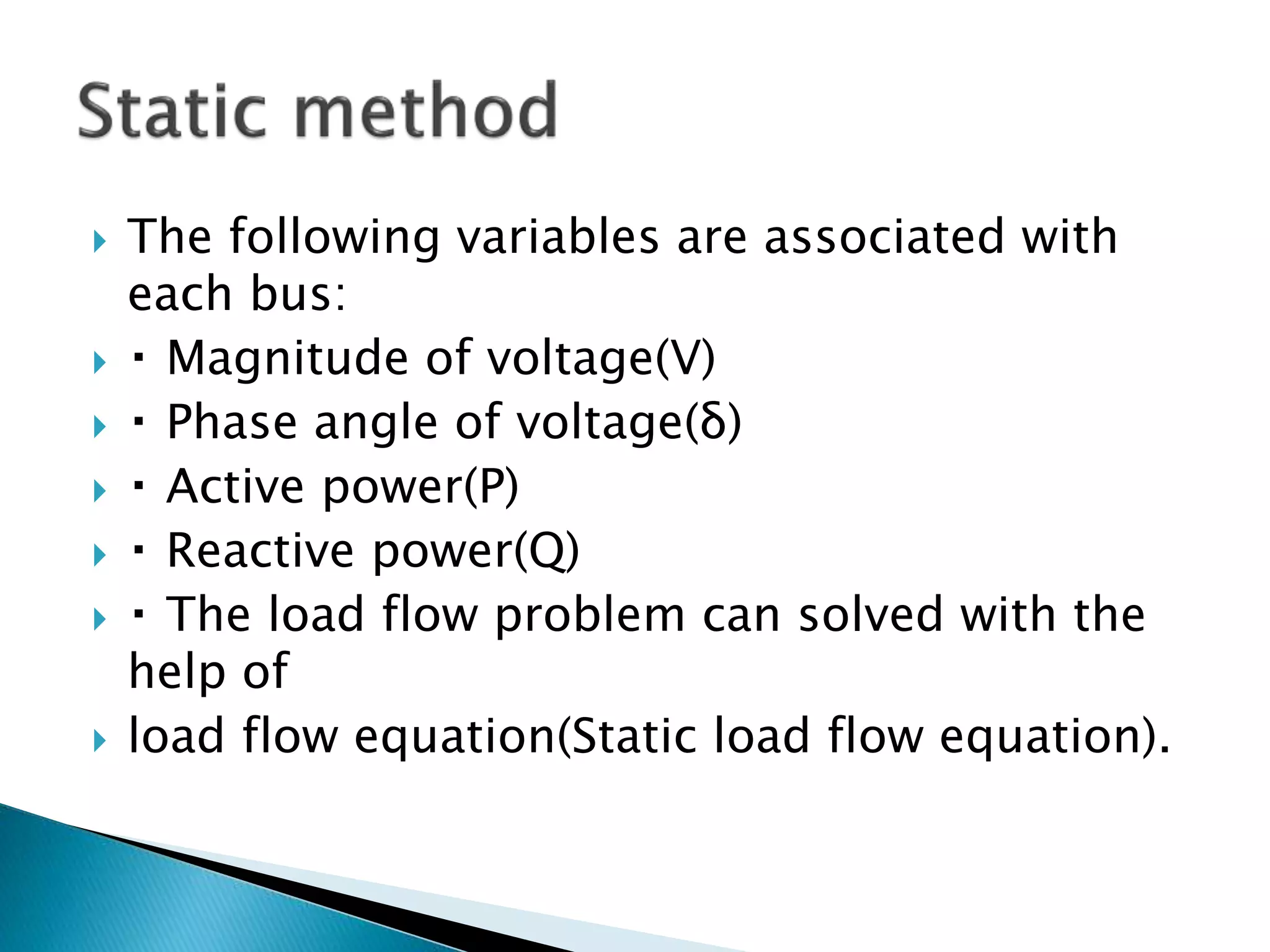
Load flow studies analyze the steady state operation of a power system by determining voltage magnitudes and angles, as well as active and reactive power flows. The key purposes of load flow analysis include designing, planning, and optimizing the operation of a power system. The analysis models each bus in the system where generators, transmission lines, and loads connect. Buses are classified based on which two of four parameters - voltage magnitude, voltage angle, active power, and reactive power - are specified as inputs. Load flow equations are then solved to calculate the unknown parameters.