Embed presentation
Download to read offline

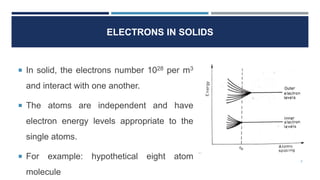



The document discusses electrons in solids and the fundamentals of bonding in solids. It notes that in solids, electrons interact with one another at high densities of 1028 per cubic meter. Atoms maintain their individual energy levels even when bonded together in solids and molecules. Bonding in solids involves interatomic binding forces called chemical bonds that hold atoms, ions, and molecules at different spacing levels, including primary and secondary bonds that are classified into four categories.




