The document discusses power flow analysis, which determines the voltage, current, real power, and reactive power at points in an electrical network under normal operating conditions. It provides three key points:
1. Power flow analysis is important for planning, operations, and future expansion of power systems by studying the effects of new loads, generators, or transmission lines.
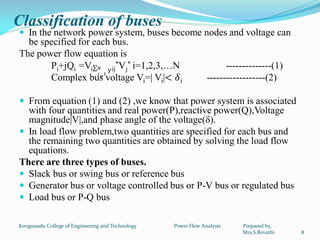
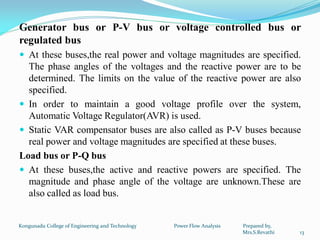
2. The analysis involves classifying buses as slack, generator, or load buses and formulating the network equations based on the bus admittance matrix.
3. Solving the load flow problem involves determining the complex voltages across all buses given the network configuration and bus demands. This provides critical information for monitoring overloads and voltage deviations.







![Description of load flow problem
In load flow analysis, the system is considered to be operating
under steady state balanced condition and per phase analysis is
used.
The network consists of a number of buses[Generator, load
buses]representing either generating station or bulk power sub
station, switching stations interconnected by means of
transmission lines or power transformers.
Each transmission line is characterized by its π equivalent
circuit.
The transformer with off-nominal tap ratio is characterized by
their π equivalent circuit.
Shunt compensating capacitors or reactors are represented as
shunt susceptance.
14
Kongunadu College of Engineering and Technology Power Flow Analysis Prepared by,
Mrs.S.Revathi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powerflowanalysis-181217110212/85/Power-flow-analysis-14-320.jpg)

![Ideal Load Flow Problem (or)Statement of Ideal load flow
problem:
Load Flow Problem is stated as follows:
Given: The network configuration[line impedance and half line
charging admittance] and all the bus power injections.
Pi=PG-PD
Where Pi=Bus power injection
PG =Bus generation
PD =Bus demand
To determine the complex voltage at all the buses:
The state vector X is defined as
X=[V1, V2,…… VN,δ1, δ2,……….. δN]T
Once the voltages at all the buses are known,then we can
compute slack bus power,power flows in the transmission lines
and power loss in the transmission lines.
16
Kongunadu College of Engineering and Technology Power Flow Analysis Prepared by,
Mrs.S.Revathi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powerflowanalysis-181217110212/85/Power-flow-analysis-16-320.jpg)
![Practical Load Flow problem or Statement of practical
power flow problem:
Practical load flow problem can be stated as follows:
Given: The network configuration, complex power
demands for all buses, real power generation Schedules
and voltage magnitudes of all the P-V buses and voltage
magnitude of slack bus
To determine:
Bus admittance matrix
Bus voltage phase angles of all buses except the slack bus
and bus voltage magnitudes of all the P-Q buses.
State vector X=[V1, V2,…… VN,δ1, δ2,……….. δN]T
17
Kongunadu College of Engineering and Technology Power Flow Analysis Prepared by,
Mrs.S.Revathi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powerflowanalysis-181217110212/85/Power-flow-analysis-17-320.jpg)
