Embed presentation
Download to read offline


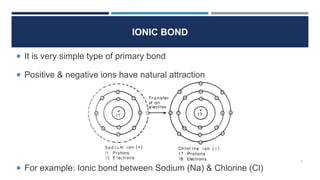



The document discusses the different types of bonds that can form between atoms in solids. It describes ionic bonds, which form between positive and negative ions through electrostatic attraction. Covalent bonds are formed through the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Metallic bonds result from the delocalization of electrons among positively charged metal ions. The four main types of bonds covered are ionic, covalent, metallic, and Van der Waals bonds, with ionic and covalent classified as primary bonds and metallic and Van der Waals as secondary bonds. Examples are given of properties associated with each bond type.





