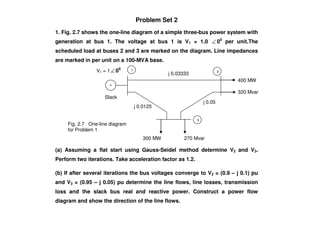
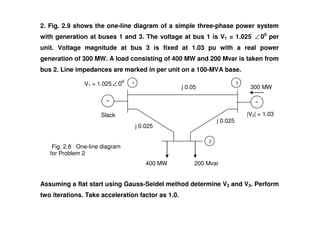
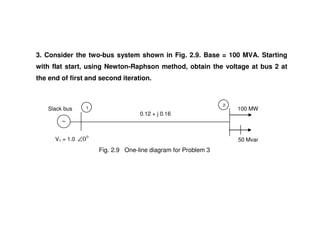
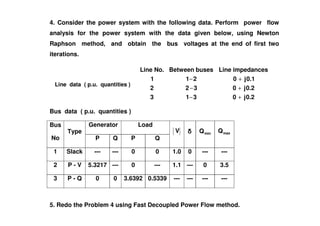
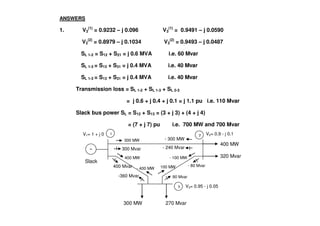
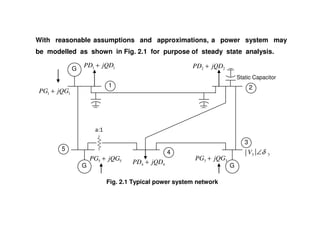
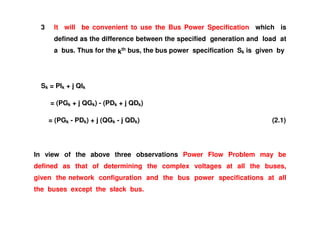
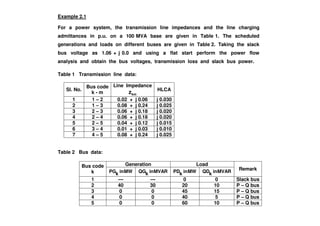
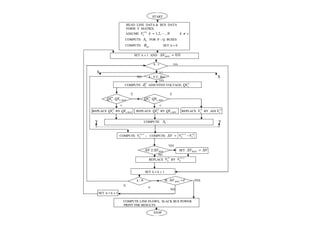
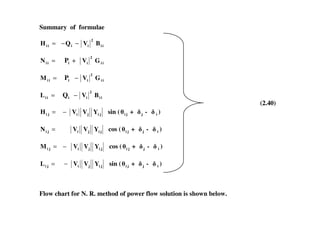
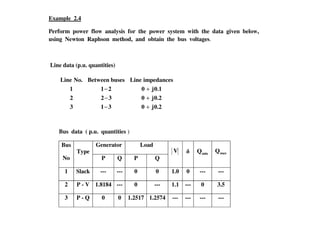
The document discusses power flow analysis, which determines bus voltages and power flows in a power system under normal steady-state operating conditions. It provides the mathematical formulation of the power flow problem as a set of nonlinear algebraic equations that must be solved iteratively. Buses are classified as slack, generator, or load buses depending on which two of four associated quantities - real power, reactive power, voltage magnitude, and voltage angle - are specified versus solved for. Solution methods like the Gauss-Seidel method are commonly used to iteratively solve the power flow equations until bus voltages converge.















![yk0
ikm
ym0
Line flow equations
Knowing the bus voltages, the power in the lines can be computed as
shown below.
k0kkmmkkm yVy)VV(Current +−=i
(2.18)
Power flow from bus k to bus mis *
kmkkm VS i= (2.19)
Fig. 2.3 Circuit for
line flow calculation
ykm
Substituting equation (2.18) in equation (2.19)
]yVy)VV([VS *
k0
*
k
*
km
*
m
*
kkkm +−= (2.20)
Similarly, power flow from bus m to bus k is
]yVy)VV([VS *
m0
*
m
*
km
*
k
*
mmmk +−= (2.21)
The line loss in the transmission line mk − is given by
mkkmmkL SSS +=− (2.22)
Total transmission loss in the system is
−
−=
linesthe
allover
ji
jiLL SS (2.23)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powerflowanalysis-180124144851/85/Power-flow-analysis-18-320.jpg)
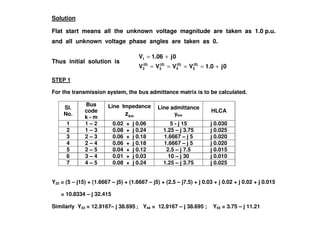





![Computation of line flows and transmission loss
Line flows can be computed from
)0.086j0.888(
]})0.03j0.0(0)j1.06({
)15j5(})0.05126j1.04623()0j1.06({[)0j(1.06
]yVy)VV([VS
]yVy)VV([VS
*
10
*
1
*
12
*
2
*
1112
*
k0
*
k
*
km
*
m
*
kkkm
−=
−−+
++−−+=
+−=
+−=
)0.086j0.888( −=
)0.062j0.874(
]})0.03j(0.0)0.05126j1.04623({
15)j5}()0j1.06(0.05126)j1.04623({[)0.05126j1.04623(
yVy)VV([VS
Similarly
*
20
*
2
*
12
*
1
*
2221
+−=
−++
+−−+−=
+−=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powerflowanalysis-180124144851/85/Power-flow-analysis-28-320.jpg)

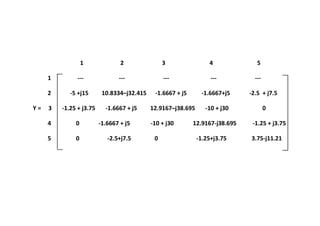
![S ds
Computation of slack bus power
Slack bus power can be determined by summing up the powers flowing
out in the lines connected at the slack bus and the load at the slack bus.
S13
S gs
S12
In this case, load at slack bus is zero and hence slack bus power is
1213gs SSS +=
)0.011j0.407(
]})0.025j0.0(0)j1.06({
)3.75j1.25(})0.08917j1.02036()0j1.06({[)0j(1.06
]yVy)VV([VS *
10
*
1
*
13
*
3
*
1113
+=
−−+
++−−+=
+−=
)0.075j1.295()0.086j0.888()0.011j0.407(SSS 1213gs −=−++=+=
Thus the power supplied by the slack bus:
Real power = 129.5 MW Reactive power = 7.5 MVAR (Capacitive )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powerflowanalysis-180124144851/85/Power-flow-analysis-30-320.jpg)



![Let the initial solution be (0)
n
(0)
2
(0)
1 x,,x,x
If 0)x,,x,(xfk (0)
n
(0)
2
(0)
111 −
0)x,,x,(xfk (0)
n
(0)
2
(0)
122 −
0)x,,x,(xfk (0)
n
(0)
2
(0)
1nn −
then the solution is reached. Let us say that the solution is not reached. Assume
n21 x,,x,x are the corrections required on (0)
n
(0)
2
(0)
1 x,,x,x respectively.
Then
1k)]x(x,),x(x),x[(xf n
(0)
n2
(0)
21
(0)
11 =+++
2n
(0)
n2
(0)
21
(0)
12 k)]x(x,),x(x),x[(xf =+++
(2.30)
nn
(0)
n2
(0)
21
(0)
1n k)]x(x,),x(x),x[(xf =+++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powerflowanalysis-180124144851/85/Power-flow-analysis-35-320.jpg)


![The above equation can be written in a compact form as
)X(FKX)X(F (0)(0)'
−= (2.33)
This set of linear equations need to be solved for the correction vector
=
n
2
1
x
x
x
X
)X(FKX)X(F (0)(0)'
−= (2.34)
In eqn.(1.50) )X(F (0)'
is called the JACOBIAN MATRIX and the vector
)X(FK (0)
− is called the ERROR VECTOR. The Jacobian matrix is also denoted as J.
Solving eqn. (2.34) for X
X = [ ] 1)0('
)X(F −
[ ])X(FK )(0
− (2.35)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powerflowanalysis-180124144851/85/Power-flow-analysis-38-320.jpg)
![Then the improved estimate is
XXX )0(1)(
+=
Generalizing this, for th
)1h( + iteration
XXX )h()1h(
+=+
where (2.36)XXX += where (2.36)
[ ] [ ])X(FK)X(FX )h(1)h('
−= −
(2.37)
i.e. X is the solution of )X(FKX)X(F )h()h('
−= (2.38)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powerflowanalysis-180124144851/85/Power-flow-analysis-39-320.jpg)

























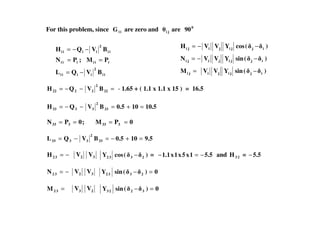
















![Reactive power at bus 3 is calculated as
−=3Q [{ 5 x 1.0 x 1.0 cos ( )}4.820
− +{ 5 x 1.0 x 1.1 cos ( )}9.530
− - ( 10 x 1.0 x 1.0)]
= 0.4064−
0.8510.40641.2574QQIQ 333 −=+−=−=
Thus
V
Q
VB"
= yields
10 3V = - 0.851 i.e. 3V = - 0.0851
This gives 0.91490.08511.0V )1(
3 =−=
At the end of first iteration, bus voltage
0
3
0
2
0
1
4.820.9149V
4.711.1V
01.0V
−∠=
∠=
∠=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powerflowanalysis-180124144851/85/Power-flow-analysis-92-320.jpg)

![On solving this
3
2
=
− 0.0015
0.004476
0)2(
2 4.97rad.0.086660.0044760.08218 ==+=
0)2(
3 4.90rad.0.085580.00150.08408 −=−=−−=
This gives 0
1 01.0V ∠= 0
2 4.971.1V ∠= 0
3 4.900.9149V −∠=
Reactive power at bus 3 is calculated as
−=3Q [{ 5 x 0.9149 x 1.0 cos ( )}4.900
− +{ 5 x 0.9149 x 1.1 cos ( )}9.870
−
(− 10 x 2
0.9149 )] = 1.1448−
0.1231
V
Q
;0.11261.14481.2574Q
3
3
3 −=−=+−=
Thus
V
Q
VB"
= yields 10 3V = - 0.1231 i.e. 3V = - 0.01231
This gives 0.90260.012310.9149V )2(
3 =−=
At the end of second iteration, bus voltages are
0
1 01.0V ∠= 0
2 4.971.1V ∠= 0
3 4.900.9026V −∠=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powerflowanalysis-180124144851/85/Power-flow-analysis-94-320.jpg)