Embed presentation
Download to read offline

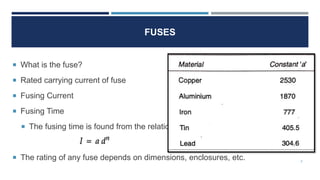
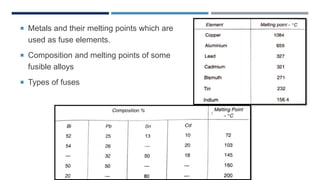

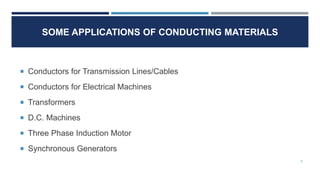

This document discusses different electrical engineering materials including fuses, resistors, and conducting materials. It explains what a fuse is and fuse ratings like rated carrying current and fusing time. It also lists different metal fuse elements and fusible alloy compositions and melting points. Resistors are described as integral circuit components, and materials used for precision and potentiometer resistors are covered. Conducting materials applications include transmission lines, electrical machines, transformers, DC machines, induction motors and synchronous generators.





