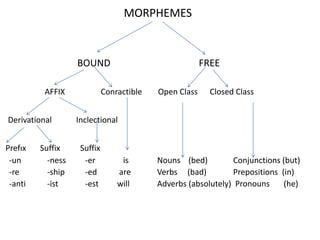
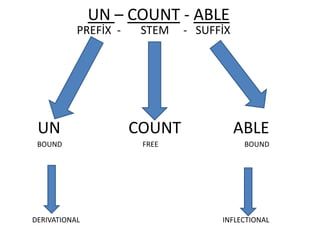
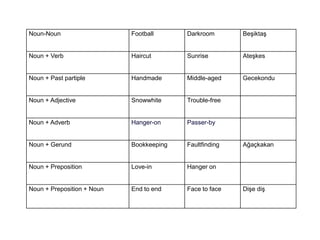
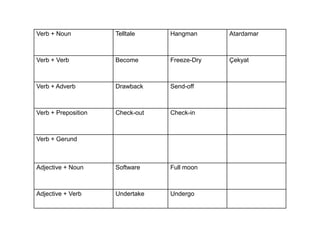
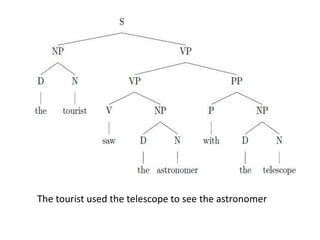
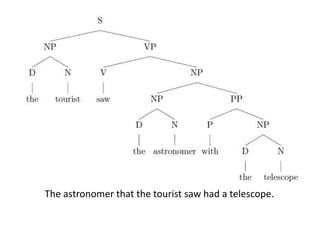
Morphology is the study of word forms and formation. It examines the different types of morphemes - the smallest units of meaning - that make up words, including free morphemes that can stand alone and bound morphemes like prefixes and suffixes. Morphemes are further classified as open or closed class, derivational or inflectional based on how they combine to form new words or modify existing words. Word formation techniques like coining, meaning change, and compounding are used to generate novel words.