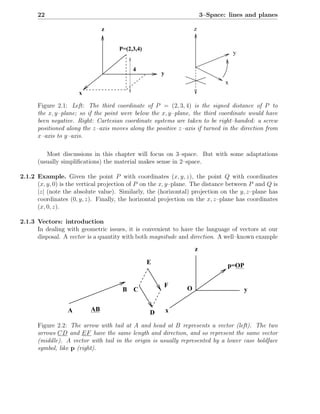
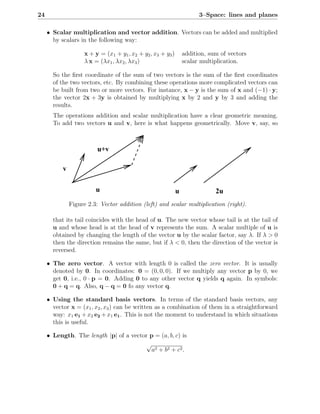
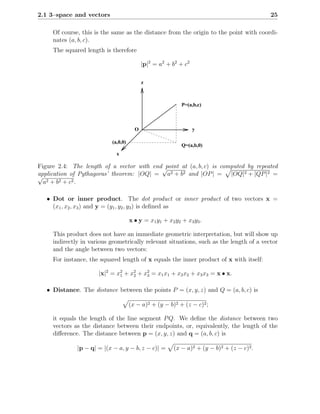
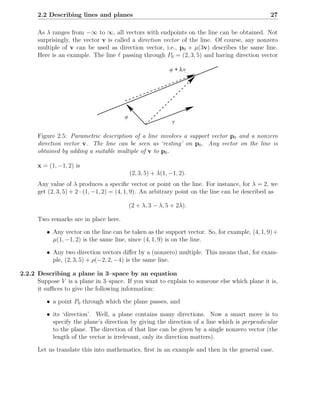
This chapter discusses describing and analyzing points, lines, and planes in 3-dimensional space. It introduces vectors as a way to represent geometric objects with both magnitude and direction. Key topics covered include defining lines and planes parametrically using a point and direction vector, vector arithmetic, perpendicular and parallel lines/planes, and computing lengths, angles, and intersections between lines and planes.

















![2.9 Tesselations of planes 47
image. In conclusion, the mirror image of P is obtained by adding −4 · (1, 1, 1) to (2, 3, 4),
i.e., P ′ has coordinates (2, 3, 4) − 4 · (1, 1, 1) = (−2, −1, 0).
To check the answer: see if ((2, 3, 4) + (−2, −1, 0))/2 is on the plane and check if the
difference (−2, −1, 0) − (2, 3, 4) = (−4, −4, −4) is perpendicular to U .
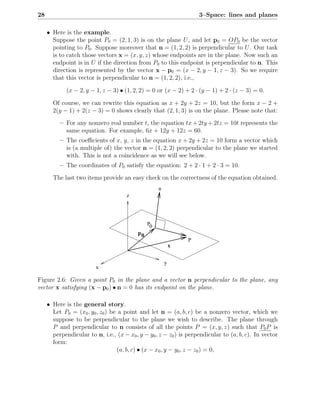
2.9 Tesselations of planes
2.9.1 Sometimes the outside of a flat wall is given a special pattern. For instance, the plane is
covered with rectangles, triangles or other shapes with a certain degree of regularity or
symmetry. Over the years quite a bit of attention has gone into understanding the kinds
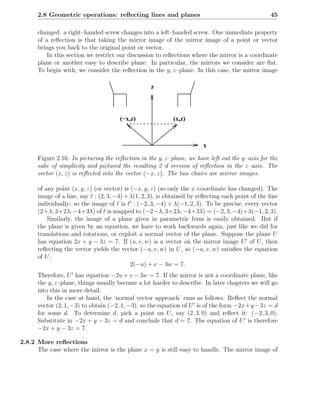
Figure 2.17: Two examples of regular subdivisions of a plane: a rectangular pattern on
the left and a triangular pattern on the right. In the case of a full plane, the patterns are
supposed to extend infinitely.
of symmetry that can occur in such subdivisions of a plane or in producing decorations of
a plane. This section only touches upon the subject. Deeper investigations require more
advanced mathematical tools. See also [2] for more extensive discussions.
The patterns shown in Figs (2.17), (2.18), (2.19) and (2.20) admit various kinds of
symmetry. Here is a brief overview of the kinds of symmetry that are usually distinguished.
a) Translational symmetry Translating the pattern over the vectors a, b or an inte-
gral combination m · a + n · b (with m and n integers) transforms the pattern into
itself. For instance, if you translate over 2a, the whole pattern is moved two steps to
b
a
Figure 2.18: Translational symmetry.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linesandplanesinspace-121127133616-phpapp01/85/Lines-and-planes-in-space-27-320.jpg)



![52 3–Space: lines and planes
c) Geometrically, it is clear that the answer to b) should be a plane. Use your geometric
intuition to find directly, without using a) or b), a vector perpendicular to the plane
and a point in the plane. Construct the equation from these data.
9 Pitfalls when rewriting equations
The equation 2x1 − 3x2 + 5x3 = 10 can be rewritten as, e.g., 3x2 = 2x1 + 5x3 − 10.
a) What is wrong with rewriting the equation as
(3x2 )2 = (2x1 + 5x3 − 10)2 ?
b) Explain why this new equation actually represents two planes. [Hint: bring both
terms to the left–hand side, don’t expand, and use a2 − b2 = (a + b)(a − b) in a
suitable way.]
10 Describing a plane through three given points
It is quite obvious that through three distinct points which are not on a line precisely
one plane passes. This exercise is about finding the plane’s parametric description and its
equation. Here are the three points: P = (1, 2, −1), Q = (2, 0, 3) and R = (2, 1, 0).
a) Set up the parametric equation for the line ℓ through P and Q and show that R is
not on ℓ.
b) Use P Q and P R as direction vectors and set up a parametric description of the plane
U through P , Q and R.
c) Starting from the result in b) find an equation for U .
11 Describing planes
a) Find an equation of the plane U which is perpendicular to the vector (1, −1, 1) and
passes through the point (2, −1, 1).
b) Find a parametric equation of the plane U .
c) Find an equation of the plane V which is parallel to U but passes through the origin
(0, 0, 0). Also provide a parametric equation of this plane.
d) Find an equation of the plane V which is parallel to U but passes through the point
(3, 3, 3). Parametric equation?
12 Transforming a parametric description of a plane into an equation
The plane U has parametric description (1, 1, −1) + λ(1, 2, 0) + µ(0, 2, 3).
a) Determine a vector perpendicular to the plane.
b) Set up an equation for the plane.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linesandplanesinspace-121127133616-phpapp01/85/Lines-and-planes-in-space-32-320.jpg)



