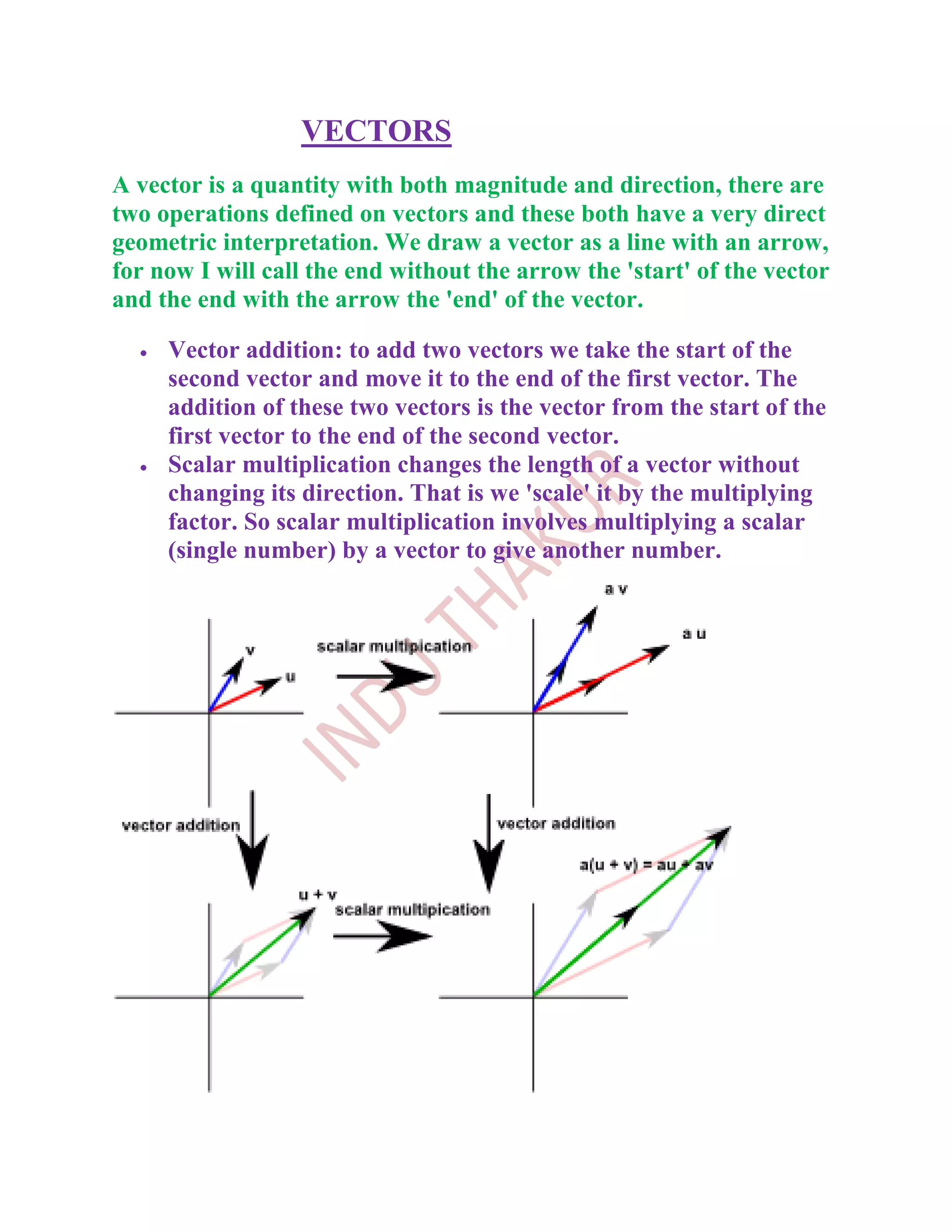
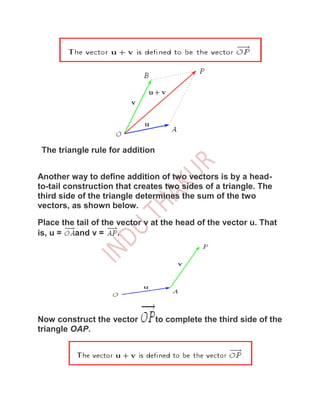
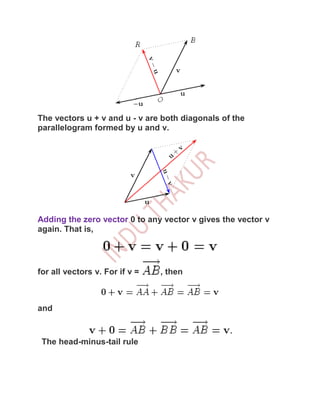
A vector is a quantity with both magnitude and direction. There are two main operations on vectors: vector addition and scalar multiplication. Vector addition involves placing the tail of one vector at the head of another and drawing the third side of the resulting triangle or parallelogram. Scalar multiplication scales the length of a vector without changing its direction. Vectors can be represented using Cartesian components, where the magnitude and direction of a vector are given by its x, y, and z values relative to a set of perpendicular axes.

























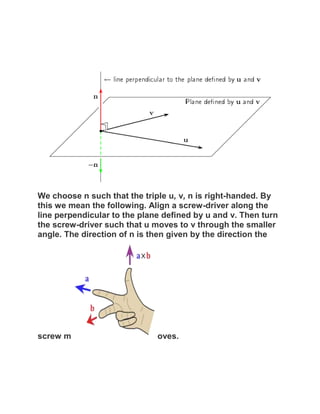
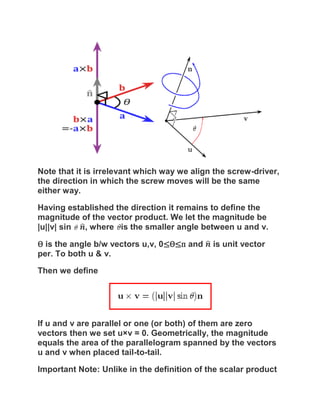

![Geometrically speaking, the vector that results from the cross
product of vectors and has a magnitude given by the product
of and times the sine of the angle from to ,
or .
The direction is given by the “right hand rule.” If you lay your right hand
palm-up along , then curl your fingers toward , the resulting vector is
in the direction of your thumb. Take a look:
Properties of the cross product:
[ lagrange’s identity]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vector1-120618011208-phpapp02/85/Vector-1-41-320.jpg)
![Proof: | sinѲ ∴ | |2 =( | |)2 (1-cos2Ѳ) [
=| cosѲ ] ∴ | 2
=
Scalar triple product identities
The triple product can be evaluated using the relation
The triple product of vectors a, b, and c is given by
=[ ]
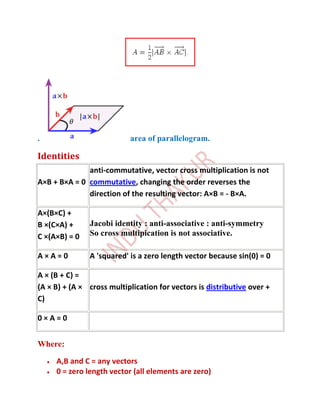
The value of the triple product is equal to the volume of the parallelepiped
constructed from the vectors. This can be seen from the figure since](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vector1-120618011208-phpapp02/85/Vector-1-42-320.jpg)
![Magnitude of this projection = [ repts. The vector area of
the base of the parallelopiped and the height of the parallelopiped is
the projection of along the normal to the plane containing vectors
. i.e., along ]
∴ volume of parallelepiped = [ ] {if repts. Three co-
terminus edges of a parallelogram }
[ ] = 0, if are coplanar vectors.
The scalar triple product has the following properties
⇨ 1. [ ]=[ =[
If these vectors are cyclically permuted. The value remains unaltered.
2. the position of dot and cross can be interchanged, provided the cyclic
order of vectors remains the same.
3. the value remains the same in mag. but changes the sign, if the cyclic
order of vectors is changed.(as shown above)
4. if any two vectors are same and parallel( or collinear),then scalar triple
product = 0 [ λ ]
5. if any three vectors and scalar λ , then [λ = λ[ ]
Triple vector product:
The triple vector product has the properties](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vector1-120618011208-phpapp02/85/Vector-1-43-320.jpg)




![EXAMPLE 29: Three vectors , , are satisfy the condition + +
=0. Evaluate the quantity μ = . + + . , if |=1, | =4
and| =2.
Solution: .( + + ) =0 ⇨ . + . = -| =-1………(i)
Similarily , we get . + = -| =-16…………(ii)
+ . = -4 ………(iii), by adding, 2μ=-21 ⇨ μ =-21/2
EXAMPLE 30: If with reference to the right handed system of
mutually per. Unit vectors I,j & k, = 3i-j, = 2i+j-3k, then express
In the form = , where are // & per. To resp.
Solution: let = λ , λ is scalar, i.e., = 3λi – λj , = - = (2-
3λ)I + (1+λ)j - 3k. since is to be per. To , we should have . =0
⇨ λ =1/2 ∴ = (1/2)i+(3/2)j-3k.
NCERT QUESTIONS WITH HINTS
EX.10.3 Question 4 Find the projection vector i+3j+7k on the vector 7i-
j+8k. [ Ans. Projection of = ⇨ ]
Question 8 Find the magnitude of two vectors , , having the same
mag. and such that the angle b/w them is 600 and their scalar product
is ½.
Ans. = cosѲ ⇨ ½ = cos600 = (1/2) (∵
)⇨ =1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vector1-120618011208-phpapp02/85/Vector-1-49-320.jpg)
![Question 12 If . = 0 & . = 0, then what can be concluded
about the vector . [Ans. These eqns. For =0 ⇨ is any vector.]
Question13 If , , are unit vectors such that + + =0, find the
value of . + + .
Ans. + =- ……..(i) take dot product with ⇨ ( + )= . (-
⇨1+ . + = 0 ……(ii), similarily with & , we get 1 + . +
= 0 …..(iii) & 1 + . + = 0 …..(iv) [∵ |= |= 1], by adding
(ii),(iii)&(iv) , we get . + + = -3/2
Question 14 If either =0 or =0, then . = 0. But the converse
need not be true. Justify your answer with an example.
Ans. Let = i-3j+4k, = 2i-2j+k are non- zero vectors but their dot
product is zero.
Question 16 Show that the points A(1,2,7), B(2,6,3),C(3,10,-1)are
collinear.
ANS. The position vectors of A,B,C are i-2j+7k, 2i+6j+3k, 3i+10j-k
= = i+4j-4k, | | = √33, | |=√33 & | |= 2√33
| |+| |= | |= 2√33 ⇨ A,B, C are collinear.
Question 17 show that the vectors 2i-j+k, i-3j-5k & 3i-4j-4k form the
vertices of a right angled triangle.
Ans. = = -i-2j-6k ,| |= √41, | |=√6 & | |= √35
| |² = | |²+ | |² ⇨ ABC IS a right angled triangle.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vector1-120618011208-phpapp02/85/Vector-1-50-320.jpg)
![EX. 10.4 Question 3 If a unit vector makes angles п/3 with I, п/4
with j & an acute angle Ѳ with k, then find Ѳ and hence, the
component of .
Ans. Let = a1i+a2j+a3k, | =1 , according to ques.
(a1i+a2j+a3k).i= п/3 ⇨ a1= ½, similarily a2=1/√2 & a3 = ½
[∵a1²+a2²+a3²=1+ , (1/2i+1/√2j+1/2k).k=|1/4+1/2+1/4|cosѲ⇨Ѳ=п/3
Question 6 given that . = 0 and = 0. What can you conclude
about the vectors and ?
Ans. given that . = 0 and =0⇨ =0 or =0 or per. To
And =0 or =0 or // ⇨ =0 =0 [∵ per. To & // can
Never hold at a time]
Question 8 if either =0 or =0, then = 0. is converse true?
Justify your answer with an example.
Ans.| |=| |sinѲ = 0 [∵ =0 ] similarily for =0
Converse: let ≠0=i+j+k ≠0=2i+2j+2k, = 0 i.e., // so
Ѳ=0 but | |=| |sinѲ = 0
Question 9 find the area of △ with vertices A(1,1,2), B(2,3,5), C(1,5,5).
Ans. Area of △ABC = ½| |=½ = ½ √61 * position
vectors of and are i+j+2k & 4j+3k]
Question 10 find the area of //gm. Whose adjacent sides are
determined by the vectors i-j+3k and 2i-7j-k.Find unit vector // to its](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vector1-120618011208-phpapp02/85/Vector-1-51-320.jpg)
![diagonal [Ans. Area of //gm whose adjacent sides are given |
|= 15 √2, where = ,unit vector=( + )/ + |
MISC. Question 3 A girl walks 4 km. towards west, then she walks 3
km in a direction 300 east of north and stops. Determine the girl’s
displacement from her initial point of departure.
Ans. N A
300 3 km
displacement
W B (4 km) O
Let the girl starts from O and the girl walks 4 km towards W. again she
walks 3 km along WA.(let repts. and repts. j) = +
=-4i+(3cos600i+3sin600j) ⇨ = -4i+3j/2+3√3j/2 = -5i/2+3√3j/2
[ = + = 3cos600i+3sin600j ] , so displacement from O to A =
)² = √13 km along .
Question 4 If = + , then is it true = +| ? justify your
answer.
Ans. ²= + = + + ) = =| |²+ | |²+2| || |cosѲ
When Ѳ=00 ² =( + , if Ѳ≠00 , ≠ +|
Question 9 Find the position vector of a point R which divides the line
joining two points P and Q whose position vectors are (2 + ) & ( -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vector1-120618011208-phpapp02/85/Vector-1-52-320.jpg)
![3 ) externally in the ratio 1:2. Also, show that P is the mid point of
the line segment RQ.
Ans. R divides PQ externally in the ratio 1:2 ∴ position vector of a
point R is =(3 + ) mid point of RQ is (2 + )=
position vector of P ⇨ P is mid point of RQ and the point R is (3 + )
Question 12 let = i+4j+2k, = 3i-2j+7k and = 2i-j+4k. find a vector
which is per. To both & , and . = 15.
Ans. Let =d1i+d2j+d3k, since is per. To = i+4j+2k, = 3i-2j+7k,
then d1+4d2+2d3=0 & d1-2d2+7d3=0 , by solving d1=32λ, d2=-λ, d3=-
14λ (by cross multi.) , put in . = 15 ⇨ (2i-j+4k).(32λi -λj -
14λk)⇨λ=5/3, then = 160i/3-5j/3-70k/3
Question 13 the scalar product of the vectors i+j+k with a unit vector
Along the sum of vectors 2i+4j-5k and λi+2j+3k is equal to one. Find
the value of λ.
Ans. + = = (2+λ)i+6j-2k , unit vector of = [(2+λ)i+6j-2k]/ |
(i+j+k). *(2+λ)i+6j-2k]/ |= 1 ⇨ (λ+6)/ |= 1, where |=
⇨λ =1
Question 14 If are mutually per. Vectors of equal mag., show
that the vectors is equally inclined to .
Ans. )=λ |cosѲ [ ∵ |= λ,
=0 . ] ⇨ cosѲ= , similarily dot product with](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vector1-120618011208-phpapp02/85/Vector-1-53-320.jpg)
![Give same angle Ѳ = cos-1 )
EXTRA QUESTIONS:
Q. 1 If are unit vectors and Ѳ is the angle b/w them, then
show that sin(Ѳ/2)= ½ | |.
Ans. | |²= ( ). ( )= | |²= 2-2cosѲ
[| |=1, A•B = |A| |B| cos(θ)] ⇨ | |²= 4sin2(Ѳ/2)
Q.2 If = , = , show that - is // to -
Ans. By subtracting above results , we get - )= -
⇨ - )= - ⇨( - ) - )=0 ⇨ - is // to
-
Q.3 If the sum of two unit vectors is a unit vector, show that the mag.
of their diff. is √3. [ Hint :use | + |² ⇨ 2 . = -1, put in | - |²]
Q.4 If are three unit vectors such that = =0 and
angle b/w is п/6, prove that = ∓ 2( ).
Ans. = =0 ⇨ , ⇨
& ⇨ ⇨
) …….(i) , λ is scalar ⇨| )|=
|sinп/6 ⇨ |λ| = 2 ∴ |λ| = ∓2 , put in (i)
Q. 5 If are resp. the position vectors of the vertices A,B,C of
△ABC, Prove that area of the △ ABC is given by =1/2 |
)+ )|](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vector1-120618011208-phpapp02/85/Vector-1-54-320.jpg)
![Ans. Area of △ABC = ½ | )| = ½ |( ) ( )|
∵ = - , =
Q. 6 If | |=12 | |=10 & | | = 2, find | |.
Ans. We know that | |² +| |² = | |² ⇨ 16 [ by
lagrange’s identity, | |²sin²Ѳ=| |²(1-cos²Ѳ) ]
Q.7 if = 0 , show that = = .
Ans. )= ⇨ = , simily take cross
product with vector b , we get = , by above results ]
Q.8 ABCD is quad. Such that = , = , =m +p
.Show that the area of the quad. ABCD is ½ |m+p|| |
Ans. + = ⇨ = = ∴ area of
quad. ABCD = ½ | | = ½ |( m +p ) ( )| = ½ | m
)- p( )| = ½ |m+p|| |∵ )= - ( )]
Q. 9 Let A,B,C &D be any four points in space. Prove that
| + + | = 4 ( area of △ABC)
Ans. Taking A as orgin , let the position vectors of B,C &D be
resp. then are resp. & = , =
, = ∴| + + |=
| )+ ) +( ) ( )|= 2| |
Q.10 Three vectors are coplanar vectors ⇨ ). =0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vector1-120618011208-phpapp02/85/Vector-1-55-320.jpg)
![Questions on scalar triple product:
1.If = 2i-3j+4k, =i+2j-k, =3i+4j-k then find .( )=
. ? [ ans. 36=36 ]
2. find the volume of parallelepiped whose edges are =2i-3j+4k,
=i+2j-k and = 2i-j+2k [ ans. Use scalar triple product 2 cubic units]
3. Show that three vectors -4i-6j-2k, -i+4j+3k and -8i-j+3k are co-
planar. [ find scalar triple product is zero]
4. Show that three vectors i-2j+3k, -2i+3j-4k and i-3j+λk are co-planar.
If λ = 5 [ take scalar triple product is zero , put λ=5]
5. Show that four points with position vectors 6i-7j, 16i-19j-4k, 3j-6k
and 2i+5j+10k are not co-planar.
[hint: = =10i-12j-4k , = =-6i+10j-6k, = =-4i+12j+10k
And show scalar triple product =840≠ 0]
6. For any three vectors prove that
[ + ]= 2 [ ]
[hint: [ + X( )] =[ X + X )]
7. If the vectors =ai+j+k , = i+bj+k, =i+j+ck are co-planar, then
+ + =1, where a,b,c ≠ 1.
8. Show that if vectors are co-planar, then are also
co-planar.
9.Find the value of λ if the points A(-1,4,-3) , B(3,λ,-5) , C(-3,8,-5), D(-3,2,1) are
co-planar. [ ans. Is 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vector1-120618011208-phpapp02/85/Vector-1-56-320.jpg)
![10. Let = 5i-j+7k & = i-j+mk . find m, such that + & - are
orthogonal. * ans. Is √(73) +
*11. Let , be two given non-cillinear vectors. Then any vector
coplanar with vector & can be uniquely expressed as = x + y
,where x , y are scalars.
Find the value of p which makes the vectors co-planar , where
= 2i-j+k, = i+2j-3k, = 3i-pj+5k.
[hint: by using above result , we get x+3y=2, 2x-py=-1 & 5y-3x =1⇨
x=1/2, y=1/2 , p= 4]
12. if & are unit vectors and Ѳ is the angle b/w them, then show
that sin = ½ | - |
[hint: - |2 = ( - ). - )= 2
+ | |2 -2 || |cosѲ =2(1-cosѲ)
As | |= | |=1]
13. If two vectors =i+j+k , = j-k , find a vector such that X =
& . =3. [ ans. Is 5/3i+2/3j+2/3k ]
14 . Find angle b/w two vectors with mag. 1 & 2 resp. and when
X |= √3. [ hint: use sinѲ= , Ѳ=п/3]
15. If X = X , X = X , show that – is // to - .
[ hint: by subtracting above given results X( - )=( - )X ⇨( -
)X( - )=0 ⇨ sinѲ=0, where Ѳ is angle b/w two vectors, ≠ ; ≠ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vector1-120618011208-phpapp02/85/Vector-1-57-320.jpg)