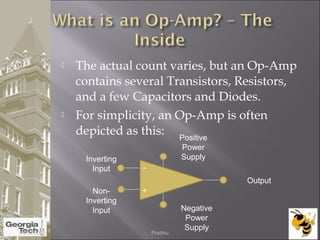
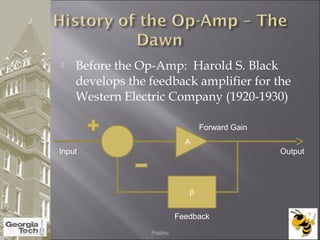
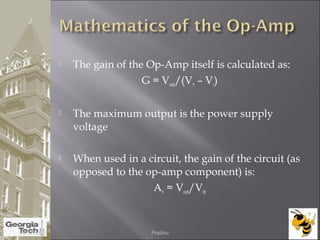
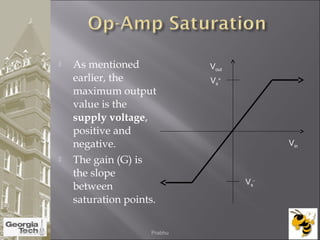
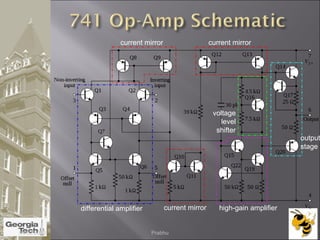
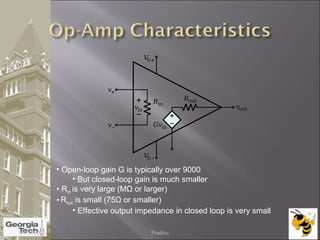
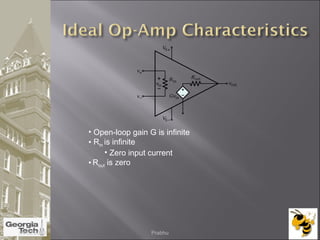
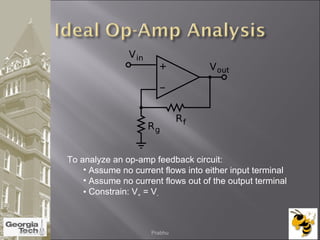
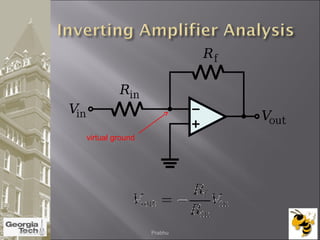
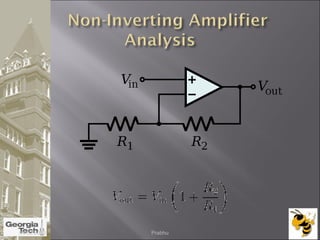
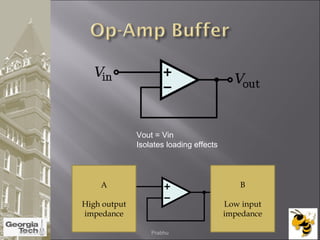
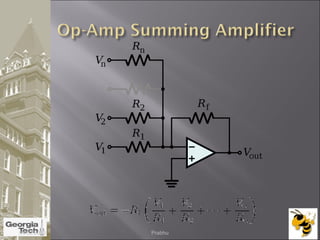
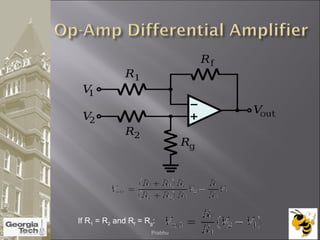
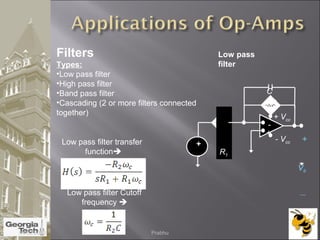
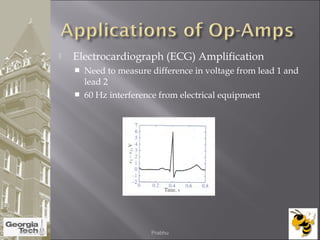
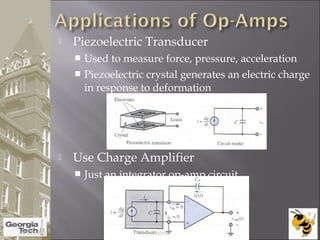
The document discusses the operational amplifier (op-amp), including its basic components and functionality. An op-amp is an integrated circuit that amplifies input voltage through high gain and is found in many electronic devices. It typically has 8 pins and contains transistors, resistors, and other components. Op-amps were developed in the 1920s-1960s and the advent of solid-state electronics allowed them to be widely used as circuit components. The document also covers op-amp characteristics, applications, and example circuits.