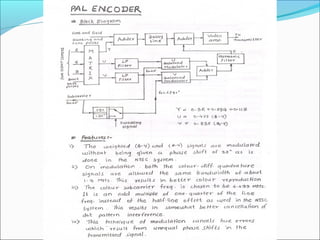
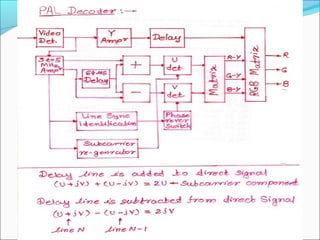
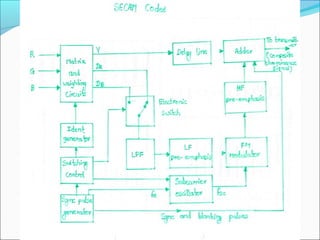
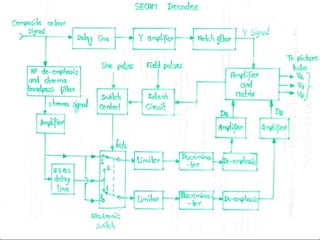
The document discusses analog television transmission and reception. It covers topics such as:
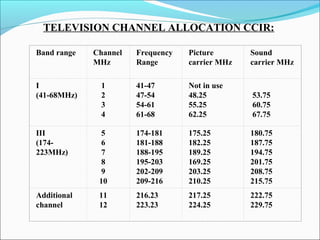
- TV broadcast channel allocation standards and frequencies
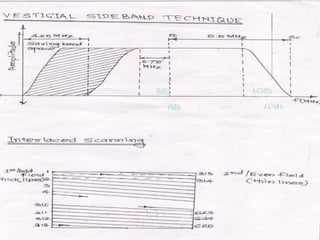
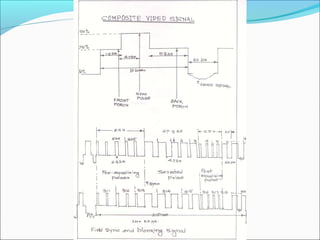
- Analog TV signal parameters including video scanning, signal bandwidths, and modulation techniques
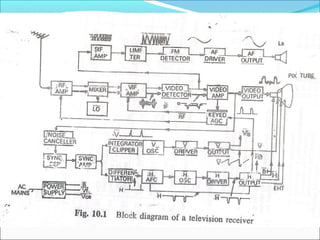
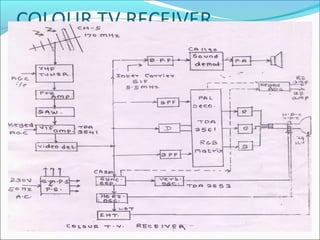
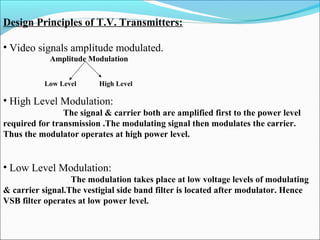
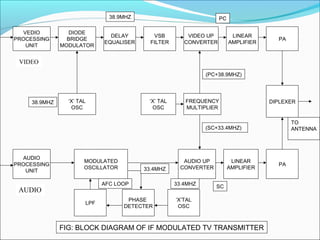
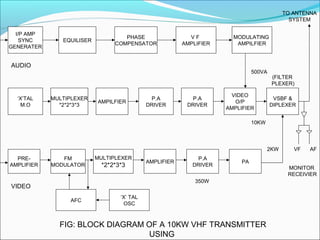
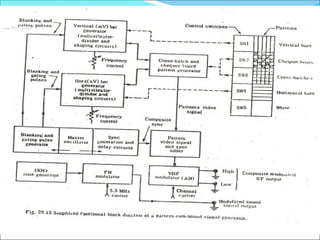
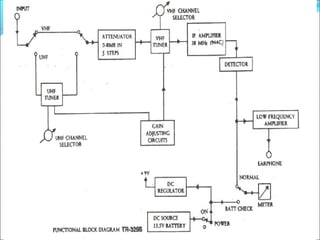
- Components of analog TV transmitters and receivers such as tuners, amplifiers, detectors and more
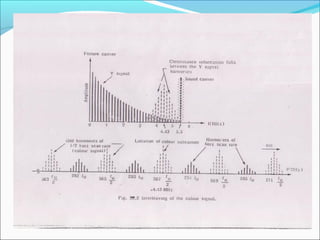
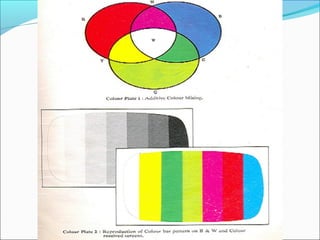
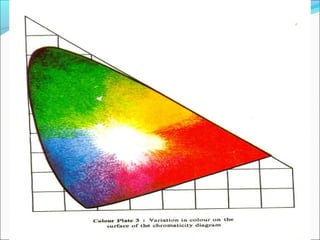
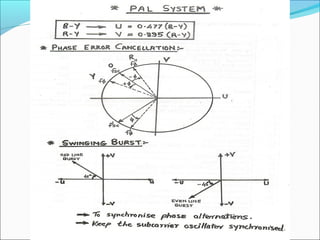
- Color TV fundamentals including color encoding and transmission systems like PAL, NTSC, and SECAM
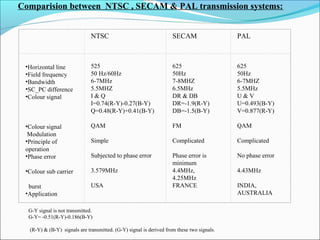
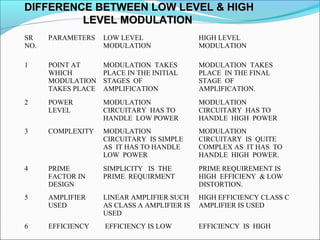
- A comparison of the features of different analog color TV transmission standards



![ CCIR-B Standard
1) Video characteristics:
Number of lines/picture-625
Interlace ratio-2:1
Scanning sequence for lines-left to right
Scanning sequence for field-Top to bottom
Field freq-50 fields/sec
Line freq-15625 Hz
Aspect ratio-4:3
Video bandwidth-5 MHz
Vertical resolution-0.7 x (625-40)=409lines.
Horizontal resolution =[410 x (4/3)]=546
alternate Black & white lines.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ave1ppt-161116095320/85/Audio-Video-Engineering-5-320.jpg)