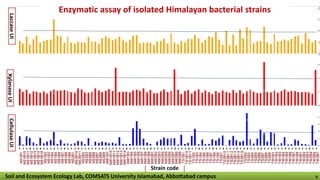
The document discusses the evaluation of novel lignocellulytic bacterial-fungal consortia from the Lower Himalaya region of Pakistan for their ability to excrete degrading enzymes. Samples of decaying wood and soil were collected from pine forests in the Galiyat region and microbial isolates were characterized biochemically and molecularly. The isolated bacterial strains were then tested for their enzymatic activity, including xylanase, laccase, and cellulase units, showing their potential for lignocellulosic degradation and use in enzyme-cocktail production.