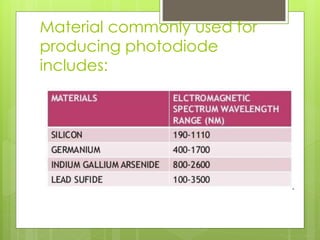
The document discusses photodiodes and LEDs. Photodiodes are a type of photo detector that can convert light into current or voltage. They have a PN or PIN junction and operate by generating a photocurrent when photons are absorbed in the depletion region. Photodiodes are used in applications like light sensors, smoke detectors, and for measuring light intensity. LEDs are semiconductors that emit light through electroluminescence when forward biased. They have advantages over incandescent bulbs like longer lifetime and higher efficiency. LEDs find applications in devices like phones and cameras.