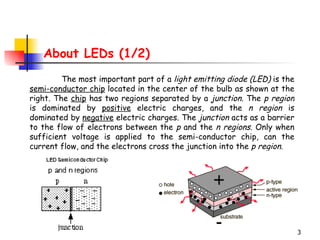
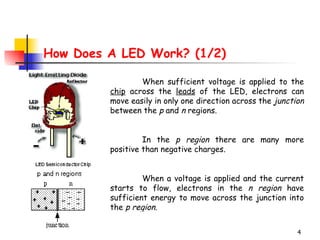
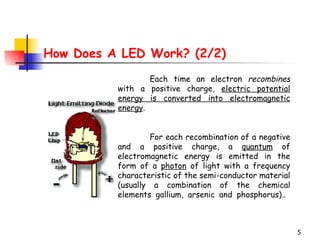
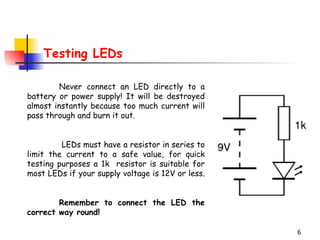
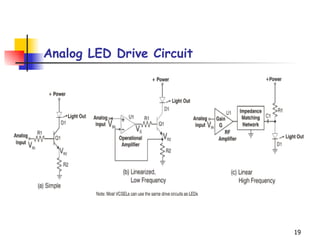
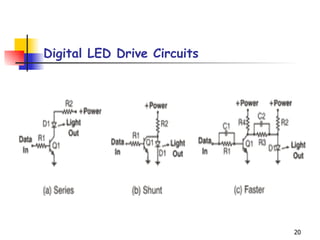
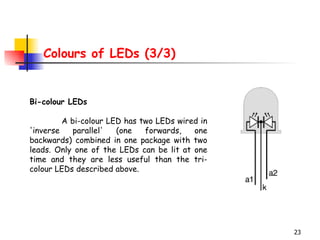
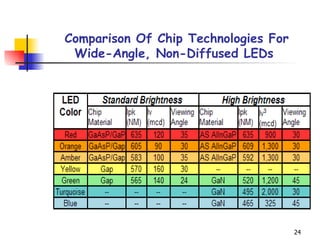
LEDs emit light when operated in a forward biased direction through a semiconductor chip. They convert electrical energy into light energy and are used as indicator lights. The chip has a PN junction that allows current to flow when voltage is applied, causing electrons to recombine with positive charges and emit photons of light. LEDs come in different colors depending on the semiconductor material and require a resistor and correct polarity to operate safely without burning out.