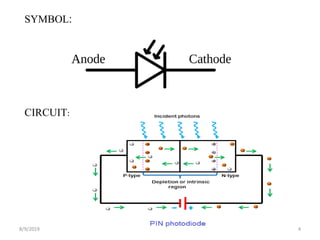
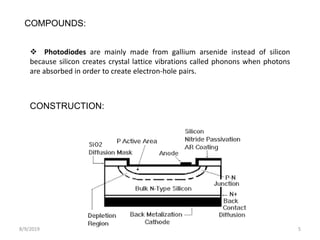
The document provides a comprehensive overview of photodiodes, semiconductor devices that convert light into electrical current. It covers their operation modes, types, characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Key highlights include the construction using gallium arsenide and the various modes of operation, such as photovoltaic and photoconductive modes.