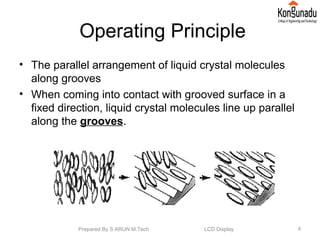
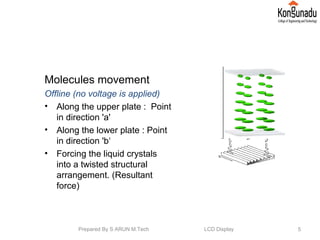
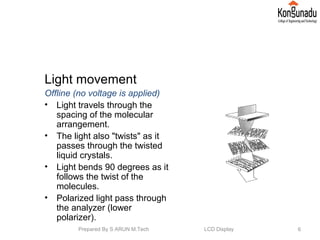
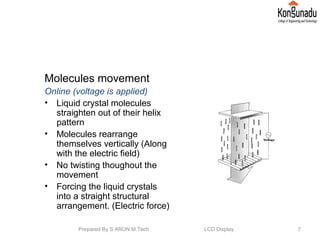
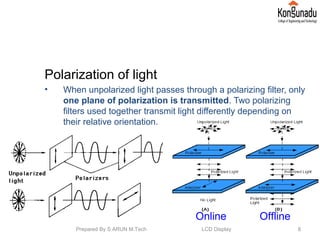
The document discusses liquid crystal displays (LCDs). It begins by introducing LCDs and how they use polarization of light to present information using pixels. It then describes different types of LCDs like passive matrix LCDs, active matrix LCDs, and thin film transistor LCDs. The document explains the operating principle of LCDs, including how liquid crystal molecules are arranged both with and without a voltage applied. It also discusses how polarized light interacts with and is filtered by the liquid crystal molecules. Finally, the document lists some key properties of LCD displays and provides references for further reading.