This document provides guidance on creating effective lesson plans. It discusses the importance of lesson planning for both novice and experienced teachers. Key points covered include:
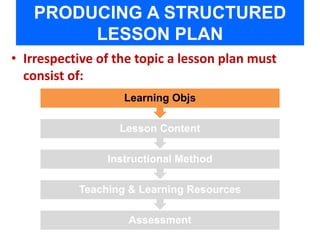
- The components of an effective lesson plan, including learning objectives, lesson content, instructional methods, teaching resources, and assessment.
- Distinguishing between macro planning, which involves planning for an entire course, and micro planning, which involves planning for a specific lesson.
- Guidance on writing measurable learning objectives and sequencing objectives from simple to complex.
- The three stages of instruction - presentation, practice, and production - and different instructional methods and seating arrangements.
- Common mistakes to avoid, such as not creating lesson plans, having