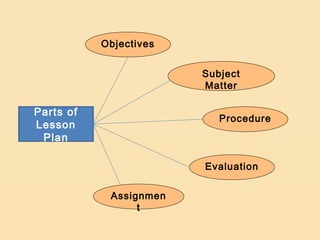
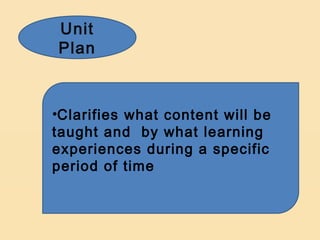
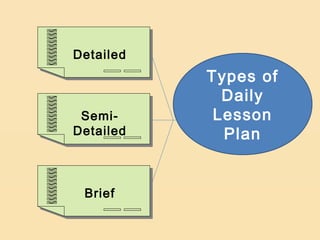
Lesson planning is an important aspect of instructional planning that serves as a blueprint for what the teacher and students intend to accomplish. It includes objectives, activities, methods, strategies and materials. Lesson planning is important because it helps ensure pupils' educational growth and stimulates teacher creativity. It also prevents wasted time and helps substitute teachers. Lesson plans have parts including objectives, subject matter, procedures, evaluation, and assignment. There are different types of lesson plans including course plans, unit plans, and daily lesson plans which can be detailed, semi-detailed, or brief.