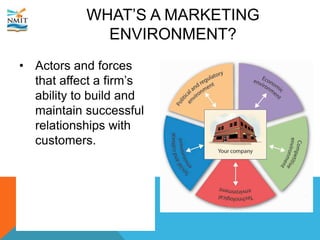
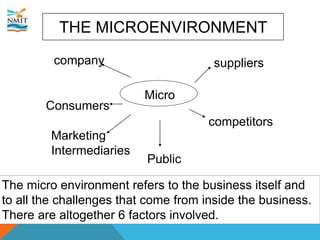
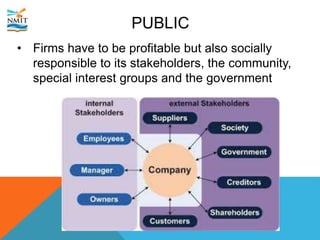
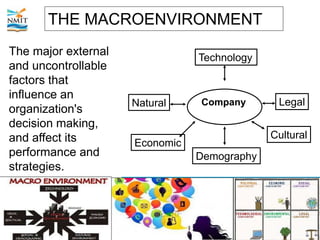
The document discusses the marketing environment that organizations operate within. It distinguishes between the internal environment, which is controllable by the organization, and the external uncontrollable environment. The internal environment includes factors like the company, suppliers, competitors, customers, and public. The external macroenvironment includes demographic, economic, natural, technological, legal, and cultural factors. Organizations must understand how these internal and external environmental factors will affect marketing efforts and strategize to either reactively adapt or proactively manage their marketing environment.