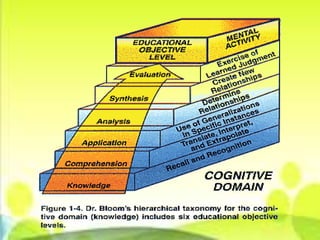
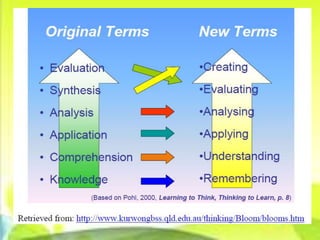
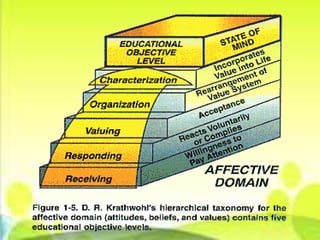
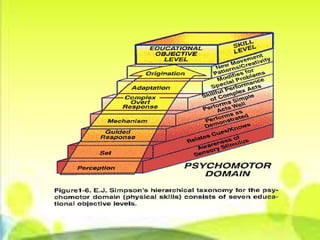
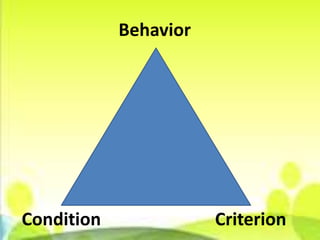
The document outlines the basic parts of a lesson plan including objectives, motivation, development, methods, materials, summaries, and assignments. It describes the components in detail, such as defining objectives using Bloom's taxonomy, examples of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation, and considerations for choosing instructional materials. Characteristics of effective assignments are provided like being interesting, incorporating previous lessons, and catering to individual differences.