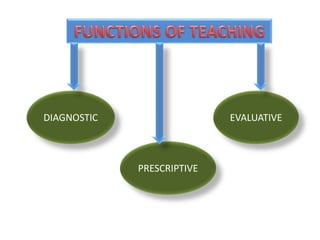
Teaching is a complex, interactive process involving a teacher, students, and a curriculum, aimed at imparting knowledge and skills while fostering understanding and behavior changes. It incorporates various methods and techniques, is characterized by communication, and requires planning and assessment to achieve educational objectives. Teaching encompasses both formal and informal dimensions and is considered an art, craft, and science, vital for developing students' capabilities and motivation.