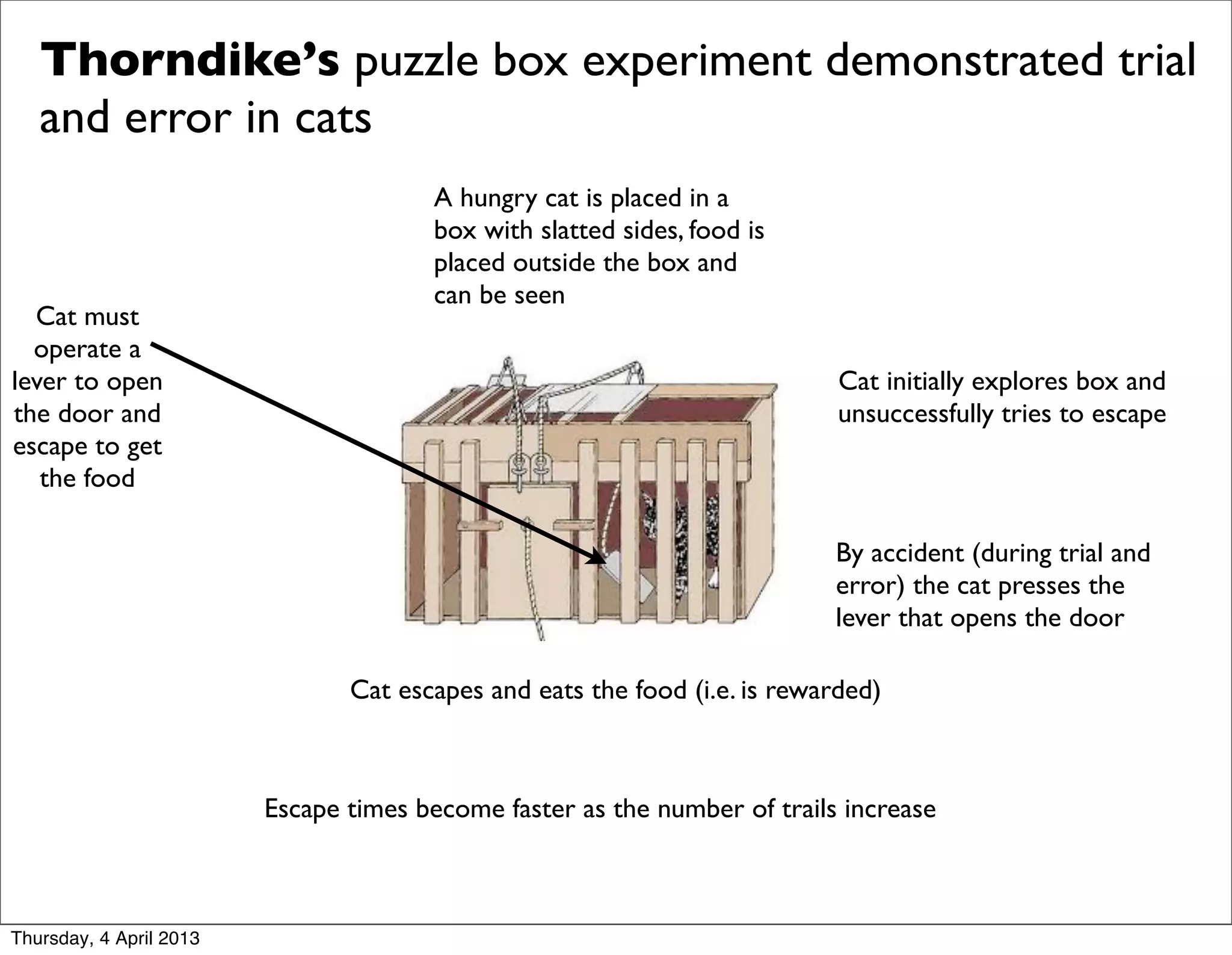
This document discusses trial and error learning. It explains that trial and error learning involves trying alternative possibilities until the desired outcome is achieved. It describes Thorndike's puzzle box experiment with cats that demonstrated trial and error. The cats initially explored the box unsuccessfully but eventually pressed the lever to open the door and escape to get food. Their escape times became faster with more trials as they learned. This led Thorndike to develop the law of effect, which states that behaviors followed by satisfying consequences are more likely to recur.