The document discusses different types of learners:
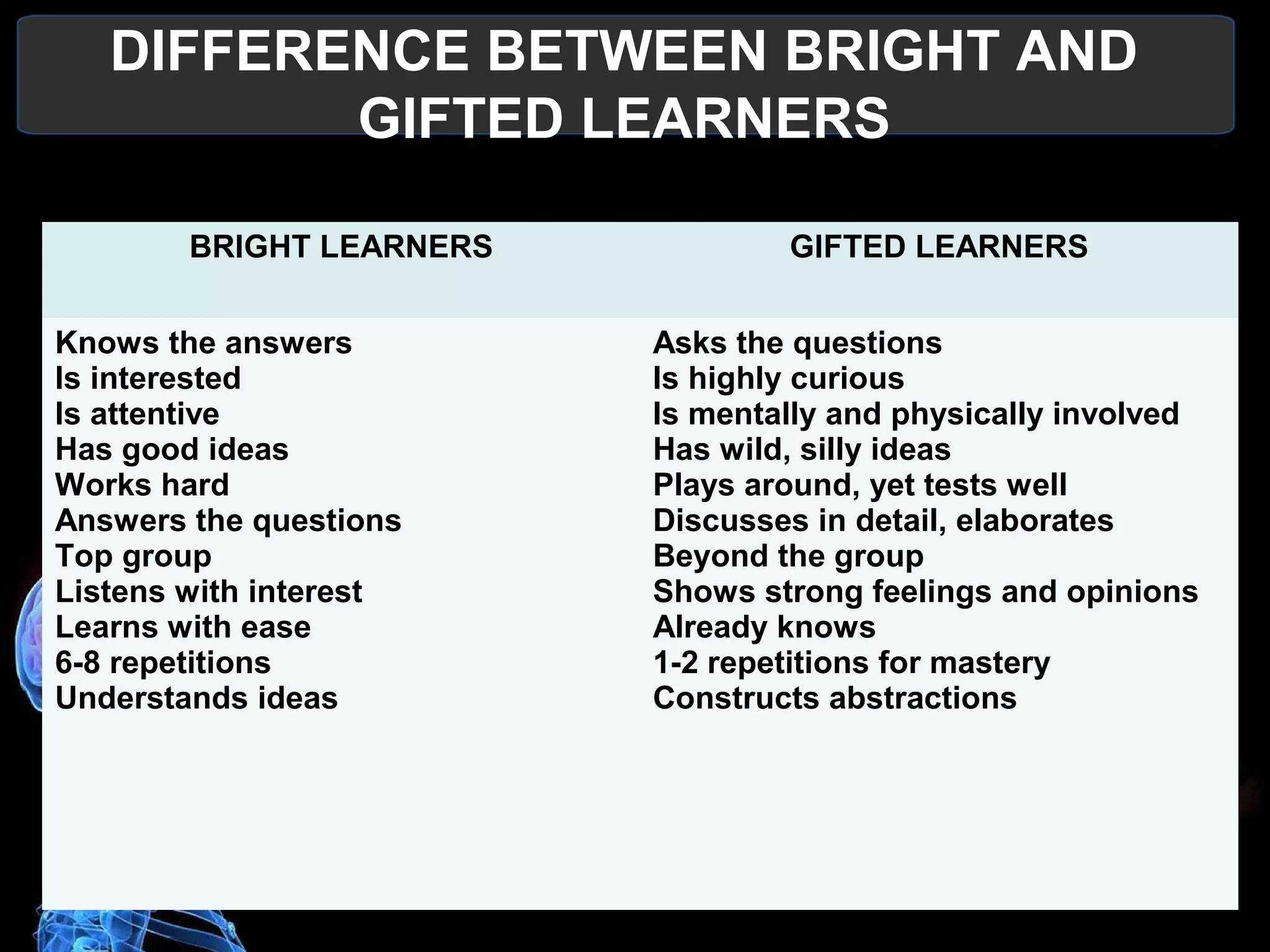
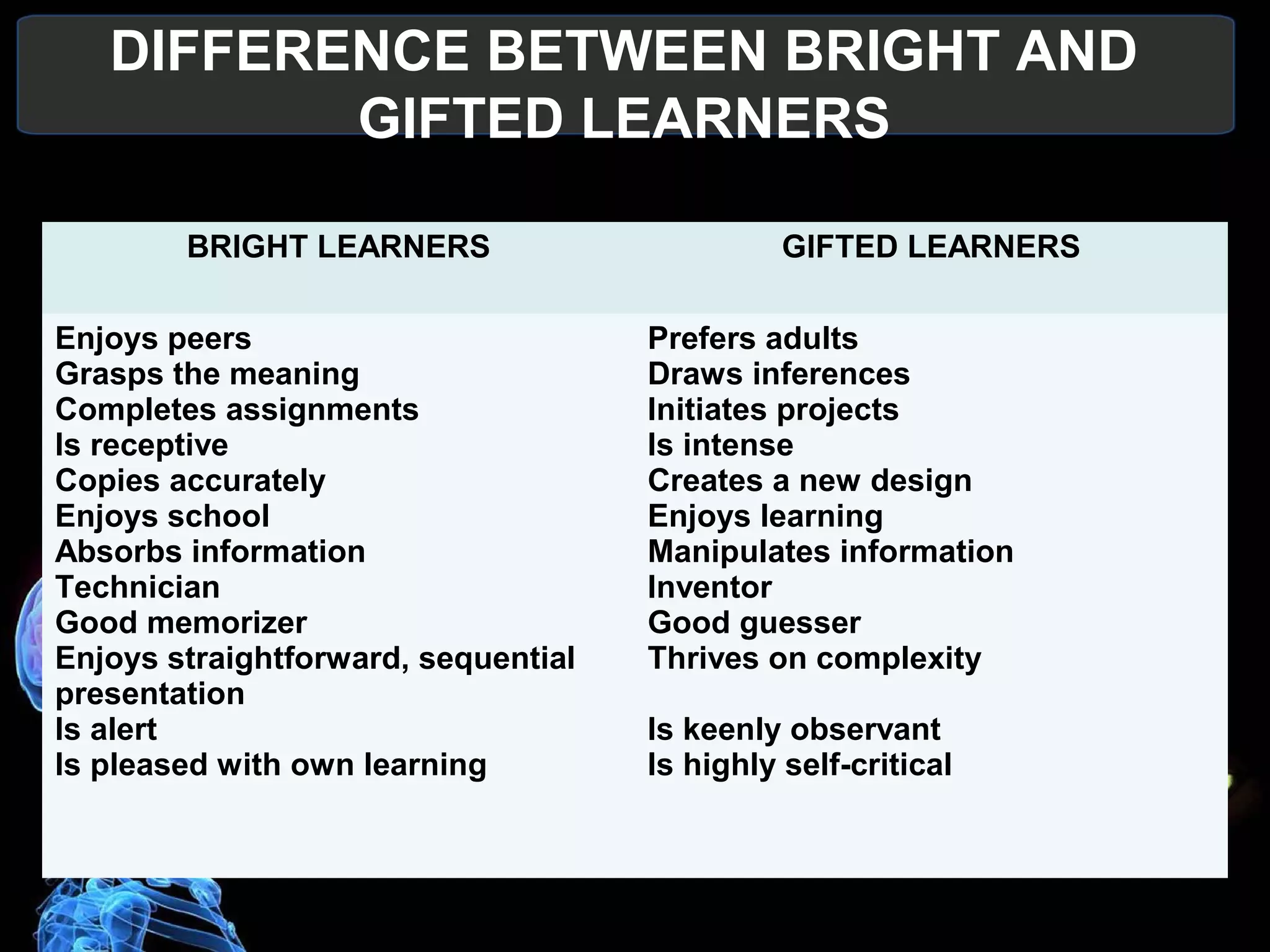
- Fast/gifted learners have exceptionally high IQs above 130, rank high academically, and learn quickly through creativity and leadership. Their education should challenge and develop their talents.
- Bright learners succeed in school through effort and enjoy learning. Their education can provide enrichment and individual projects.
- Average learners make up most students and do well with discovery of interests and complex questions.
- Slow learners have IQs below 90 and struggle with attention, memory, skills, and tests. Their education requires repetition, concrete lessons, motivation, and avoiding criticism.