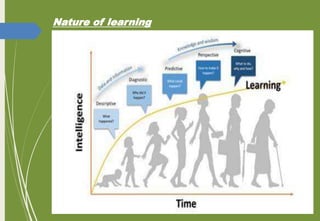
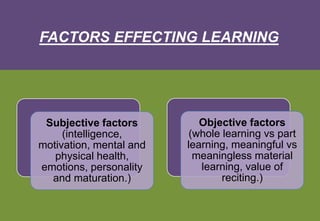
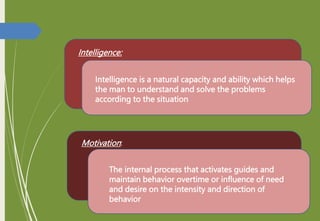
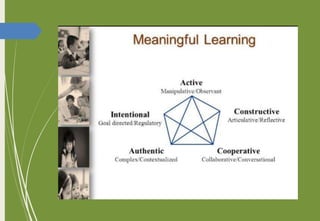
The document introduces key concepts in psychology related to learning, defining it as a process that leads to change through experiences. It discusses various factors influencing learning such as intelligence, motivation, and maturation, and outlines Thorndike's trial and error learning theory, which emphasizes problem-solving through experimentation. Additionally, it presents Thorndike's three laws of learning: readiness, effect, and exercise.