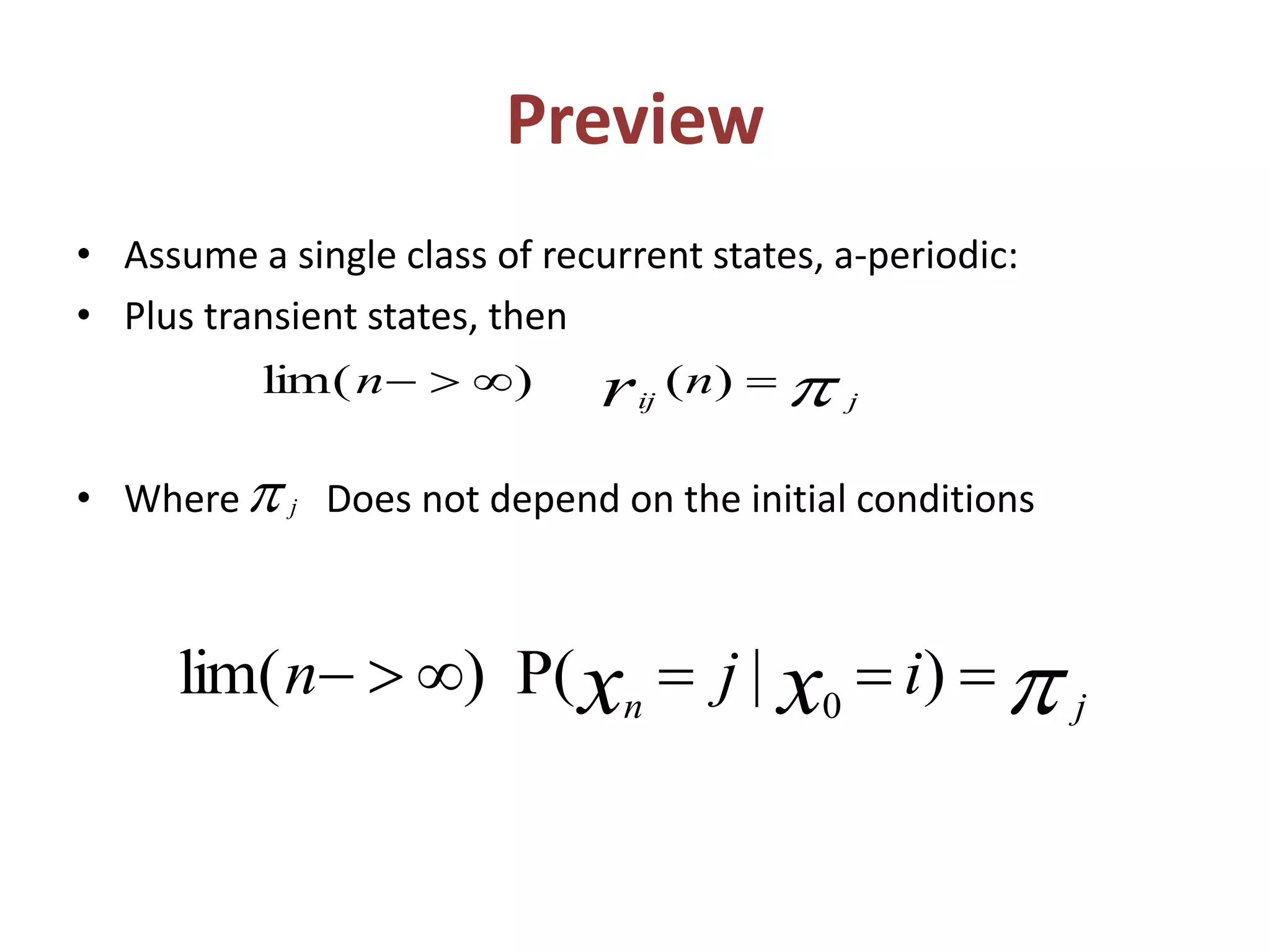
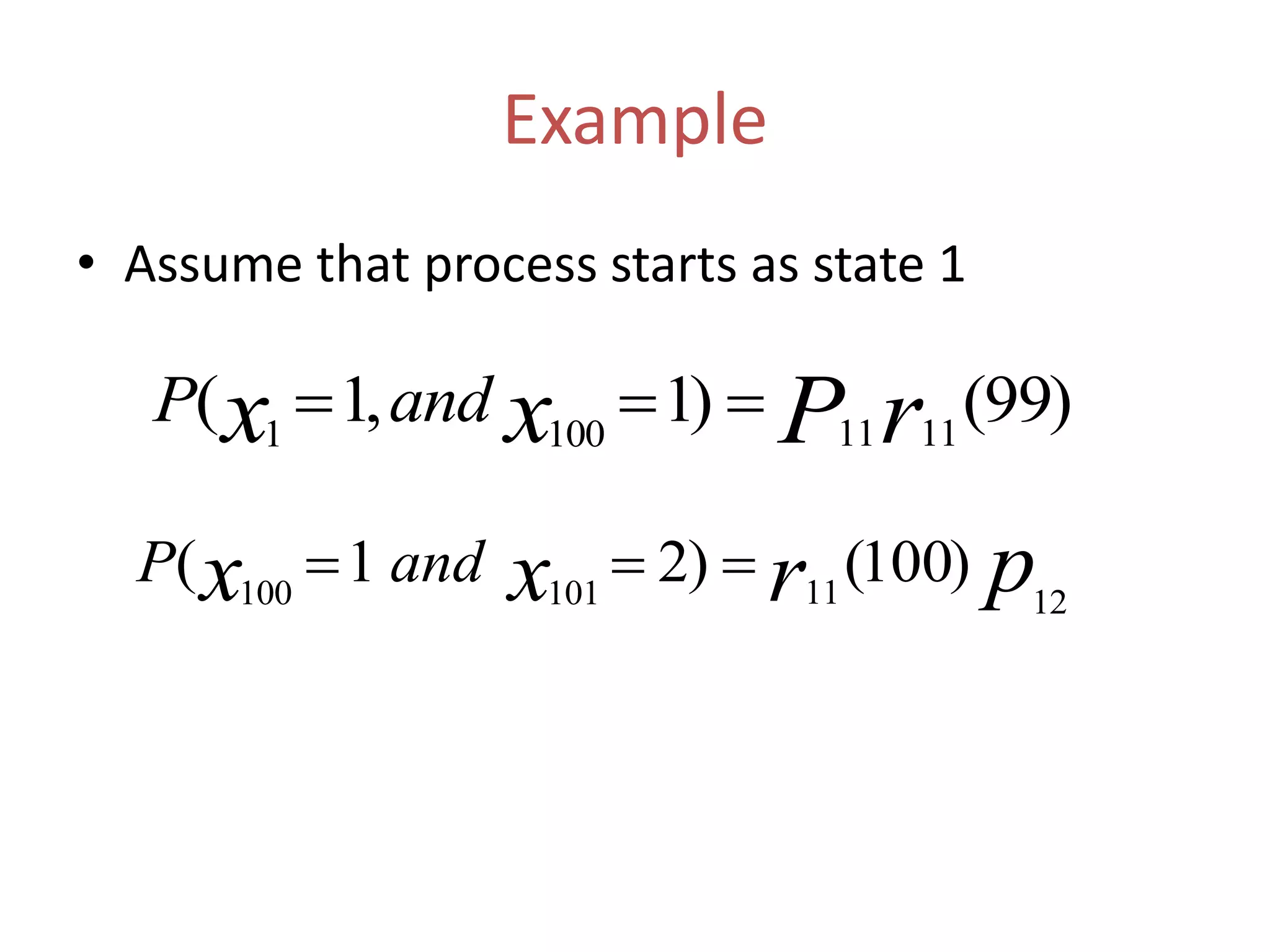
1. Markov processes can be used to model systems that transition between states based on probabilities. The document discusses several applications of Markov processes including calculating steady state probabilities, absorption probabilities, and expected times to absorption.
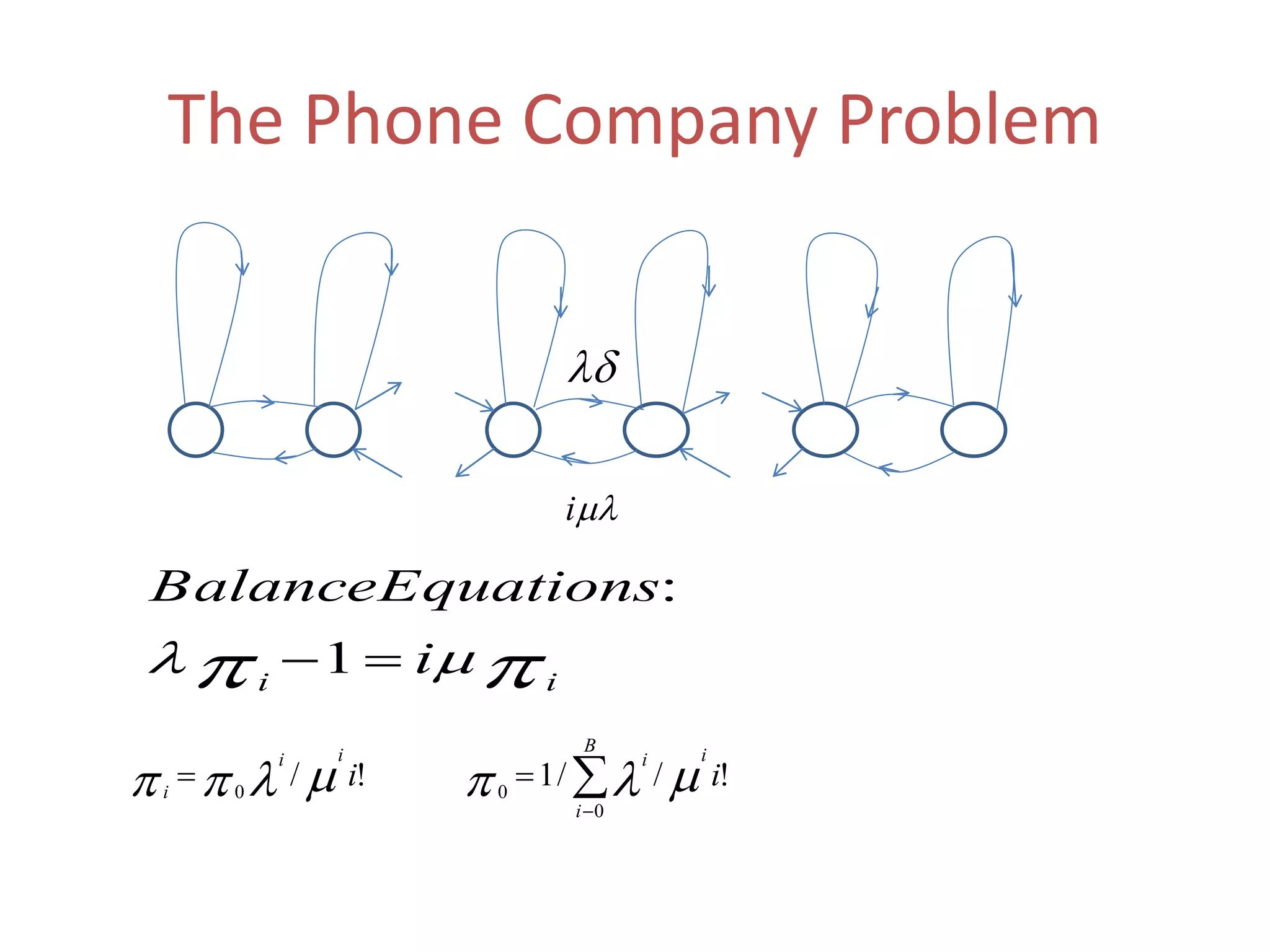
2. As an example, the document examines a phone company problem where calls arrive as a Poisson process and call durations are exponentially distributed. It shows how to set up and solve the balance equations to find steady state probabilities.
3. Other examples covered include finding the probability of an absent-minded professor getting wet during rain and calculating absorption probabilities and expected times for an example Markov chain. The document also discusses mean first passage and recurrence times.
















![Mean First Passage and Recurrence
Times
• Chain with one recurrent class;
• Fix s recurrent
• Mean first passage time from s to i
j
jiji
s
m
ni
siallfor
tosolutionuniquetheare
isthatsuchnE
tpt
t
ttt
XXt
1
0
,.
]|}0[min{
21
0
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/markovprocess-150603122924-lva1-app6892/75/Markov-process-21-2048.jpg)
![Mean First Passage and Recurrence
Times
• Mean recurrence time of s:
p
ssthatsuchnE
aj
j js
ns
tt
XXt
1
]|}1[min{ 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/markovprocess-150603122924-lva1-app6892/75/Markov-process-22-2048.jpg)