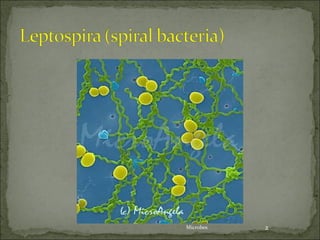
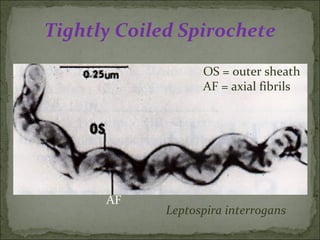
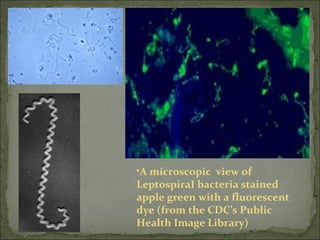
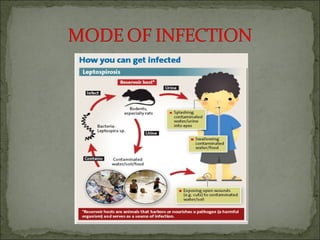
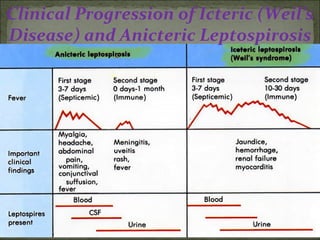
This document discusses Leptospira, a pathogenic spirochete bacteria that causes leptospirosis. It is a zoonotic disease transmitted through contact with infected animal urine. Leptospira has a thin, coiled morphology and grows slowly in culture. It can penetrate skin or mucous membranes, causing a mild flu-like illness or the potentially fatal Weil's disease characterized by jaundice and kidney damage. Diagnosis involves culture, serology, or ELISA testing of blood, urine or CSF. Treatment is with penicillin or doxycycline. Prevention involves controlling rodent populations, vaccinating livestock, and taking protective measures during high risk activities like farming.