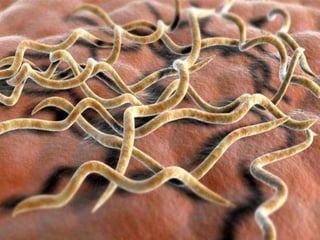
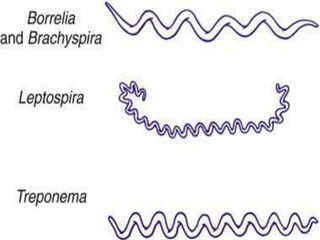
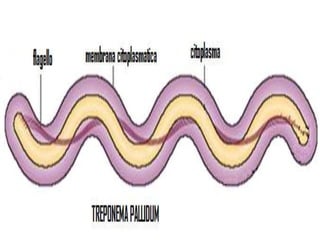
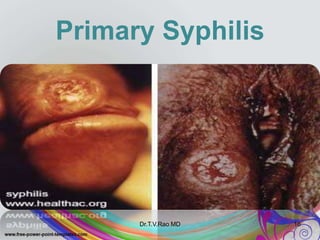
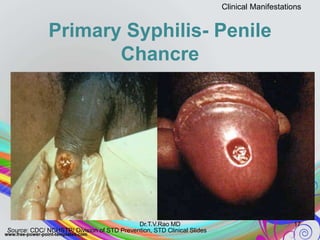
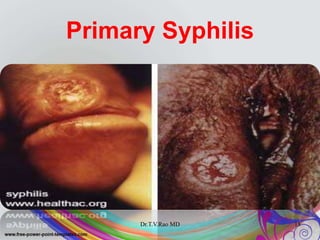
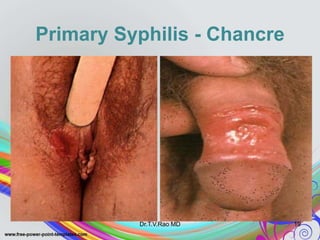
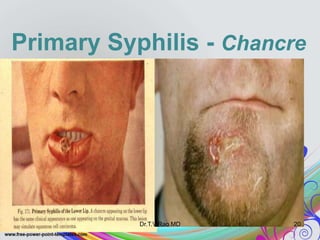
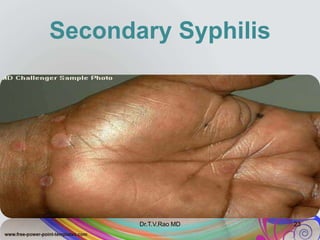
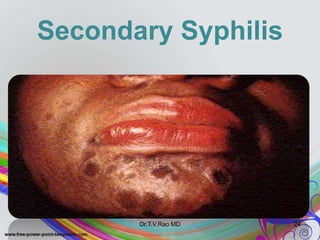
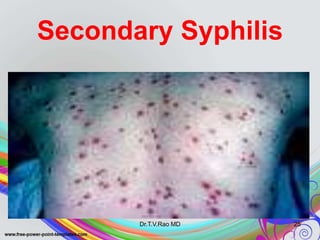
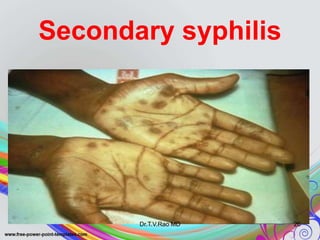
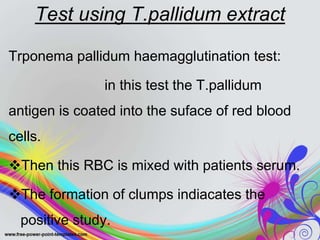
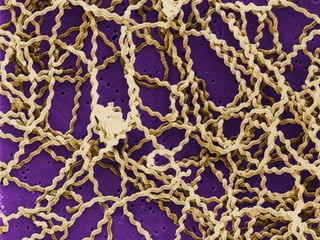
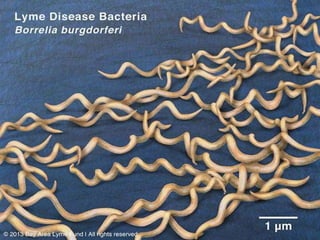
This document discusses spirochetes, a type of corkscrew-shaped bacteria. It focuses on Treponema pallidum, which causes syphilis. T. pallidum is thin and coiled, 6-14 micrometers in length. Syphilis has stages including primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. It is transmitted sexually or congenitally. Diagnosis involves tests to detect antibodies against T. pallidum antigens. Treatment depends on the syphilis stage, but may include benzathine penicillin. The document also briefly mentions Leptospira, another pathogenic spirochete that can cause leptospirosis.