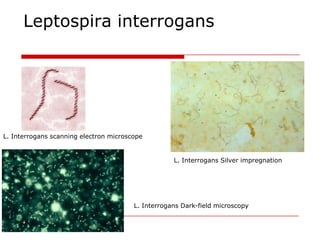
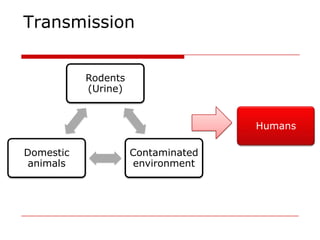
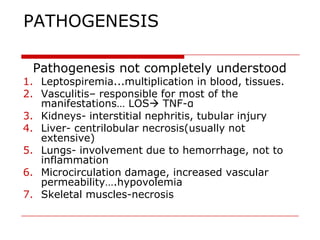
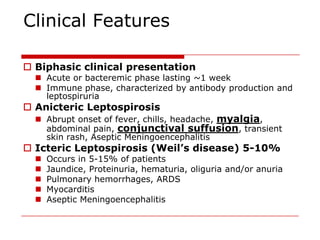
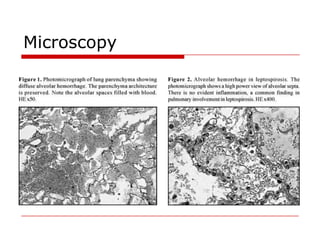
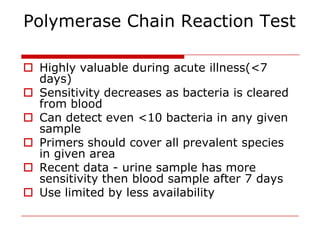
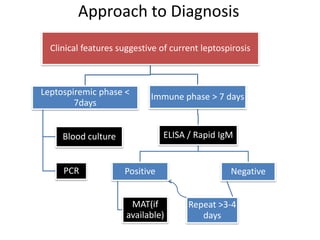
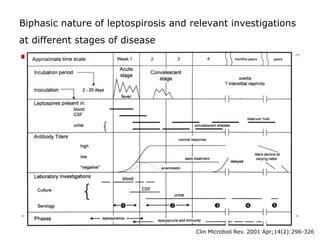
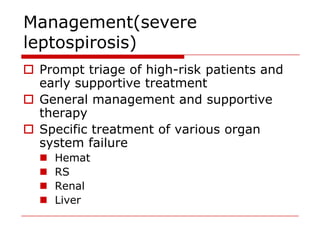
Leptospirosis is a zoonotic bacterial disease caused by Leptospira interrogans. It is transmitted to humans via contact with water or soil contaminated by the urine of infected animals. Clinical features range from a mild flu-like illness to a potentially fatal disease affecting multiple organ systems. Diagnosis involves serological tests, culture, PCR and microscopic examination of body fluids. Treatment of severe cases requires supportive care and antibiotics such as penicillin or doxycycline to shorten illness duration and reduce mortality. Prevention focuses on controlling animal reservoirs and interrupting transmission routes.