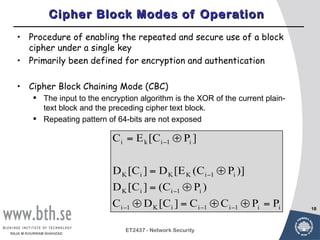
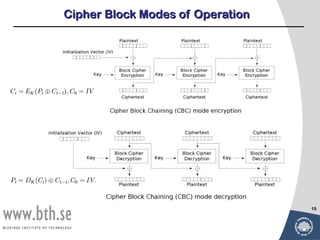
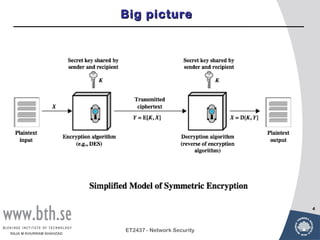
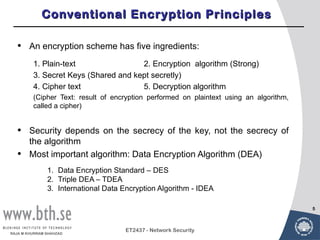
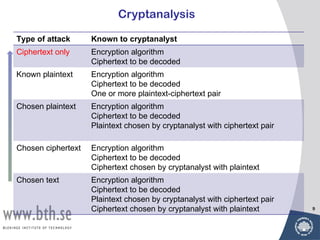
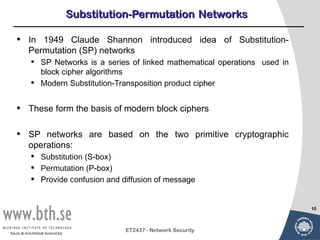
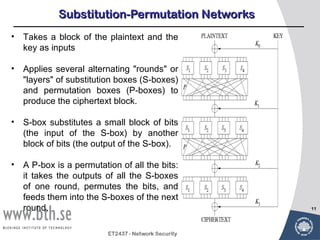
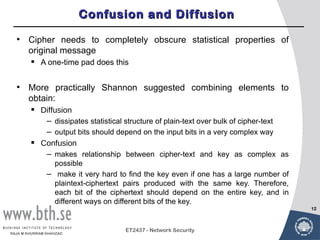
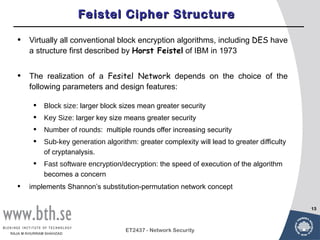
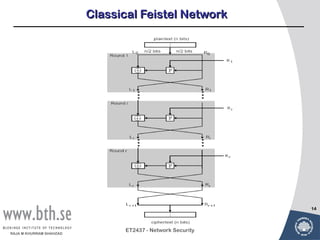
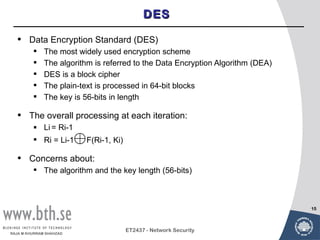
Symmetric encryption uses a single key to encrypt and decrypt messages. It provides confidentiality by ensuring encrypted information can only be understood by the intended parties who share the secret key. Symmetric encryption algorithms can be classified based on their operations, number of keys used, and how plaintext is processed. They use substitution and permutation operations along with multiple rounds to provide both confusion and diffusion of the plaintext. Popular symmetric algorithms include DES, Triple DES, and AES, which use the Feistel cipher structure and substitution-permutation networks. Keys must be distributed securely between communicating parties for encryption and decryption.




![Triple DEA
• Use three keys and three executions of the DES algorithm
(encrypt-decrypt-encrypt)
C = Cipher-text C = EK3[DK2[EK1[P]]]
P = Plain-text
EK[X] = encryption of X using key K
DK[Y] = decryption of Y using key K
• Effective key length
of 168 bits
16
ET2437 - Network Security
RAJA M KHURRAM SHAHZAD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture3a-symmetricencryption0-2-120612174147-phpapp02/85/Lecture3a-symmetric-encryption-16-320.jpg)