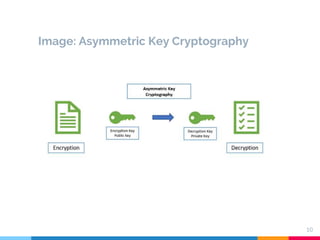
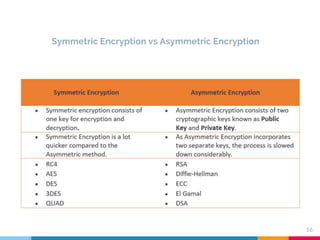
Asymmetric encryption, or public-key cryptography, uses a pair of mathematically connected keys—a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This method enhances security in data transmission, such as in SSL/TLS certificates, by allowing one-way communication and identity verification without sharing the private key. Despite its security benefits, asymmetric encryption is slower than symmetric encryption, which is why both methods are often used together.