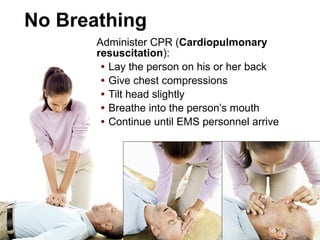
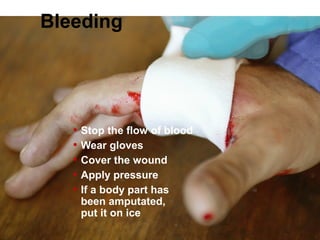
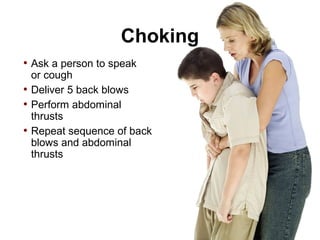
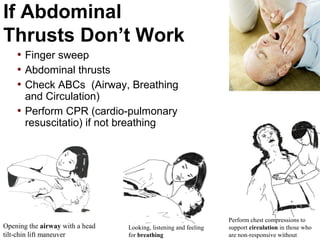
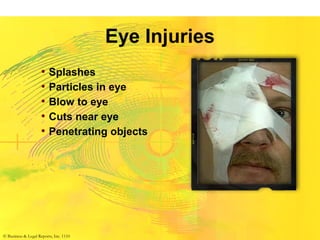
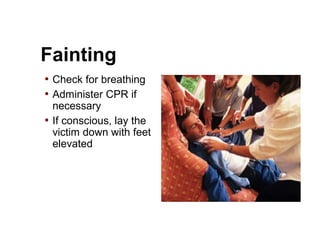
(1) First aid involves providing initial care to an injured or ill person until definitive medical treatment can be accessed. It generally consists of simple, life-saving techniques that one can be trained to perform with minimal equipment.
(2) First aid during disasters should provide both physical and mental aid. It is important to attend to physical injuries appropriately while also providing counseling and support to help victims cope with the mental trauma.
(3) The first aid given immediately after a disaster includes treating wounds, preventing infection, setting up communication, prioritizing patients, and ensuring hygiene and sanitation to reduce disease spread. It is crucial to respond properly and avoid causing further harm.