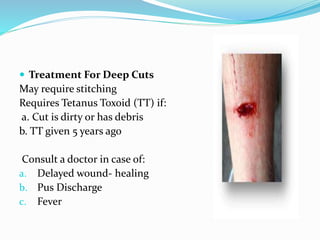
This document provides information on various first aid procedures. It begins by defining first aid as the initial care given to an injured or ill person. It then lists the contents of a typical first aid kit and outlines steps to take before providing first aid such as introducing yourself and getting consent. The document provides detailed procedures for treating cuts, bleeding, nosebleeds, head injuries, burns, fractures, sprains, bites, stings, snake bites, choking, fainting, dog bites, and heat-related issues.