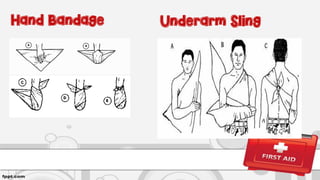
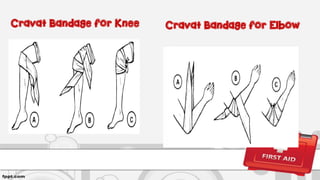
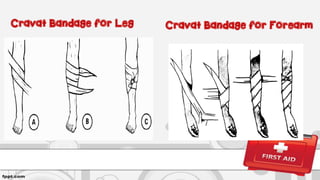
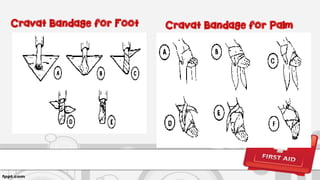
This document provides information on first aid, including definitions, principles, assessment of emergencies, wound treatment, transporting victims, and first aid for common injuries. It defines first aid, outlines the roles and objectives of first aid providers. It describes how to assess emergency situations, treat wounds through dressing and bandaging, safely transport victims using various carries, and provides steps for treating fractures, dislocations, heat exhaustion, choking, drowning, and other injuries.