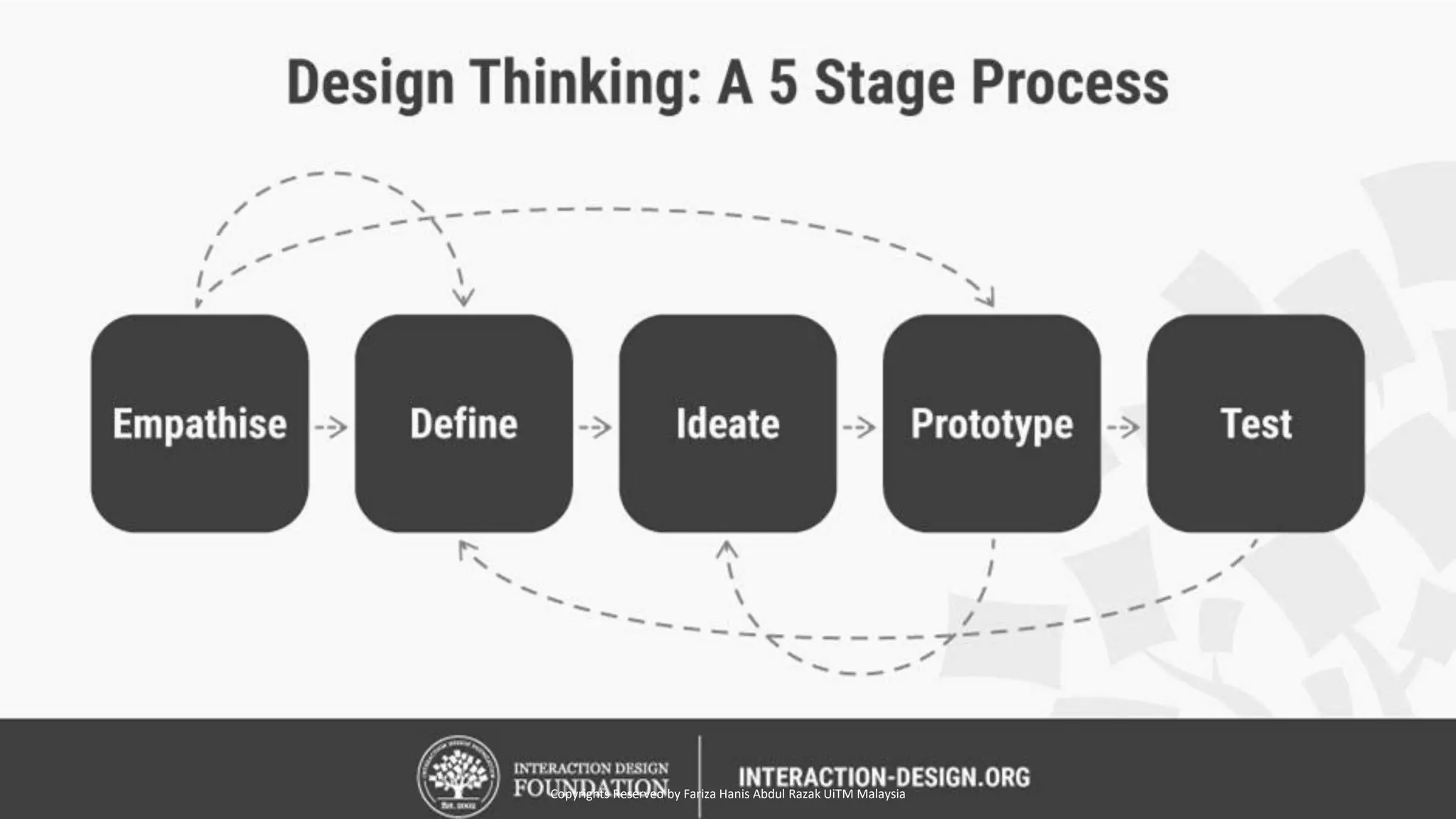
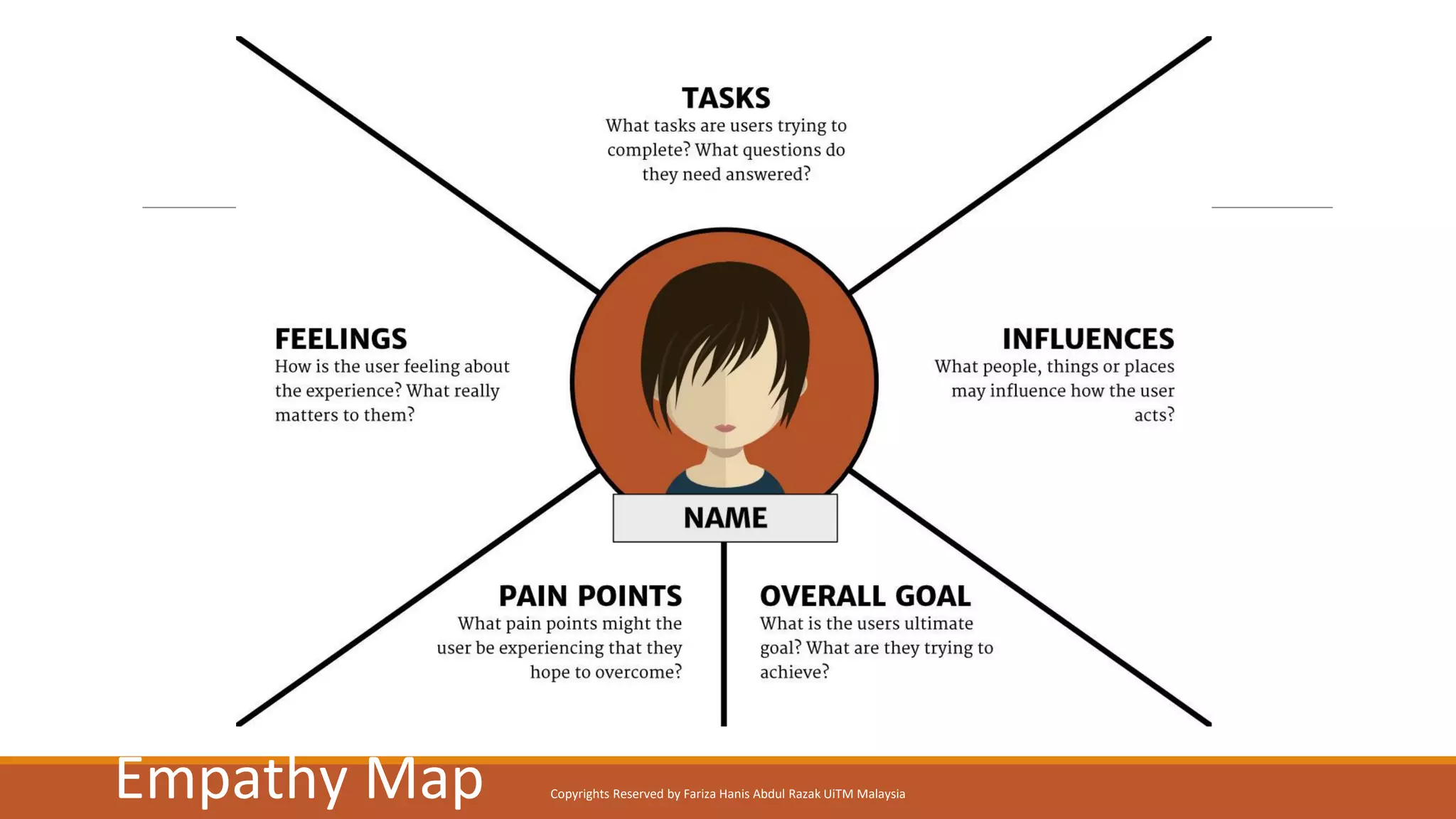
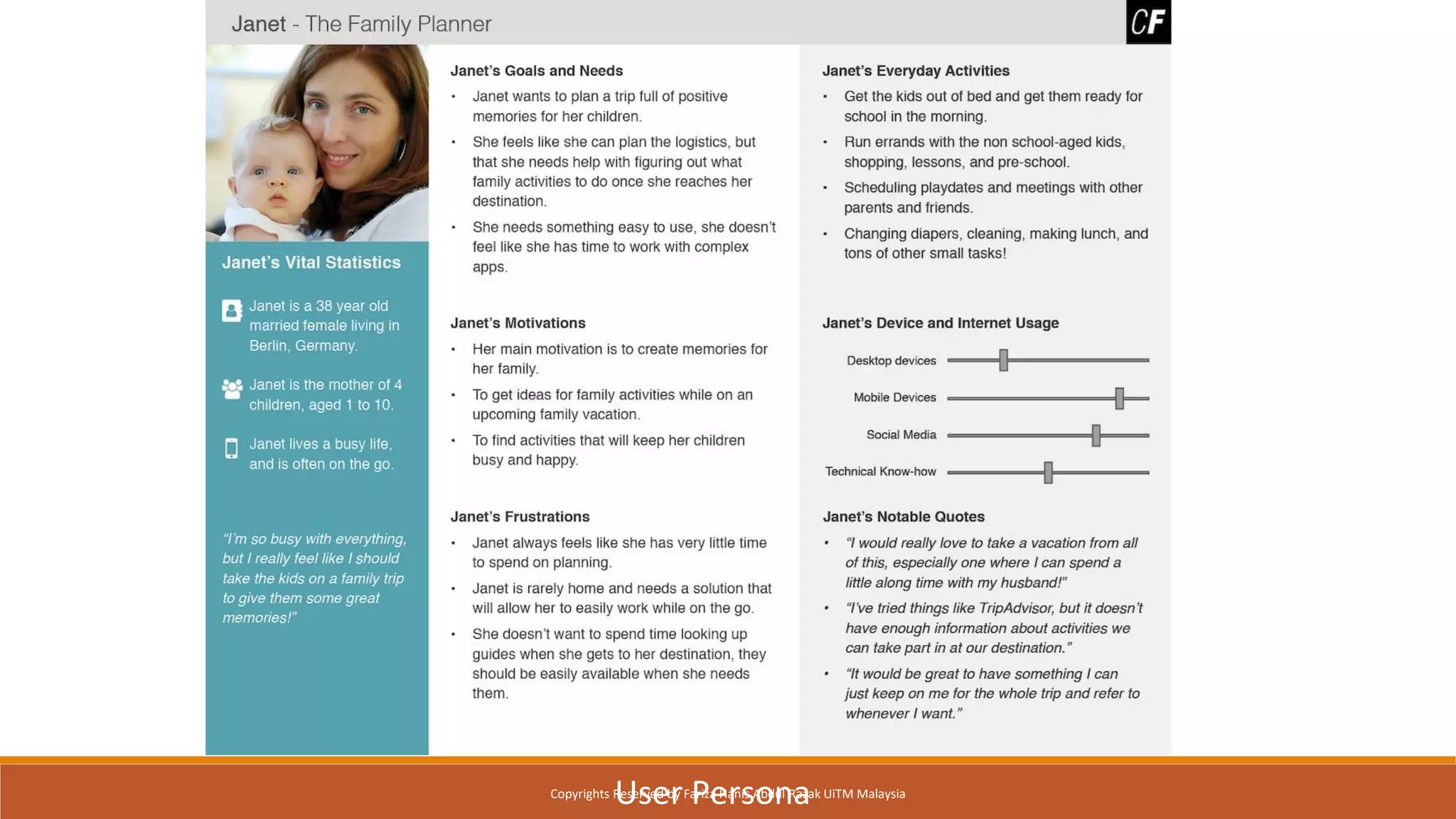
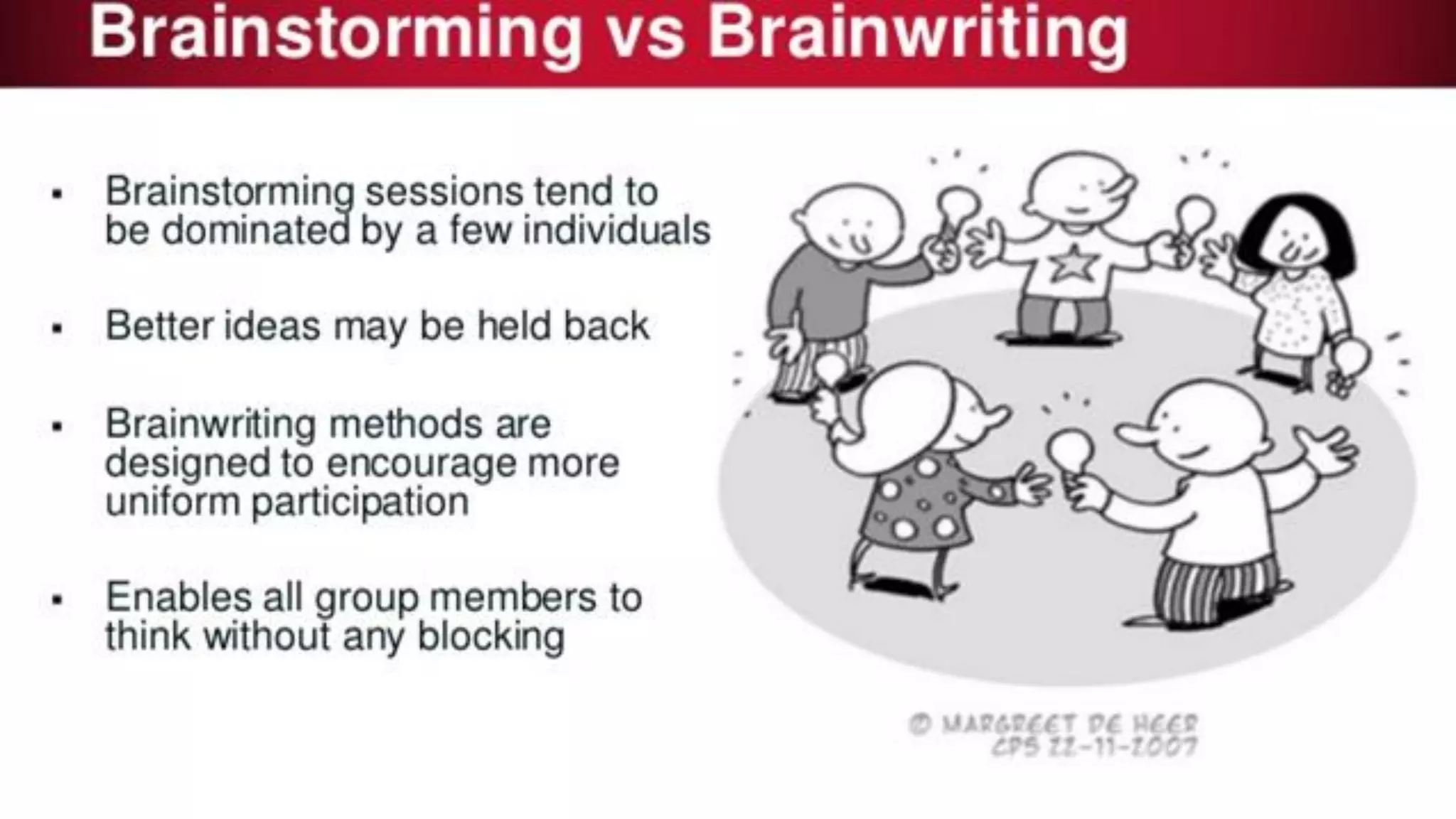
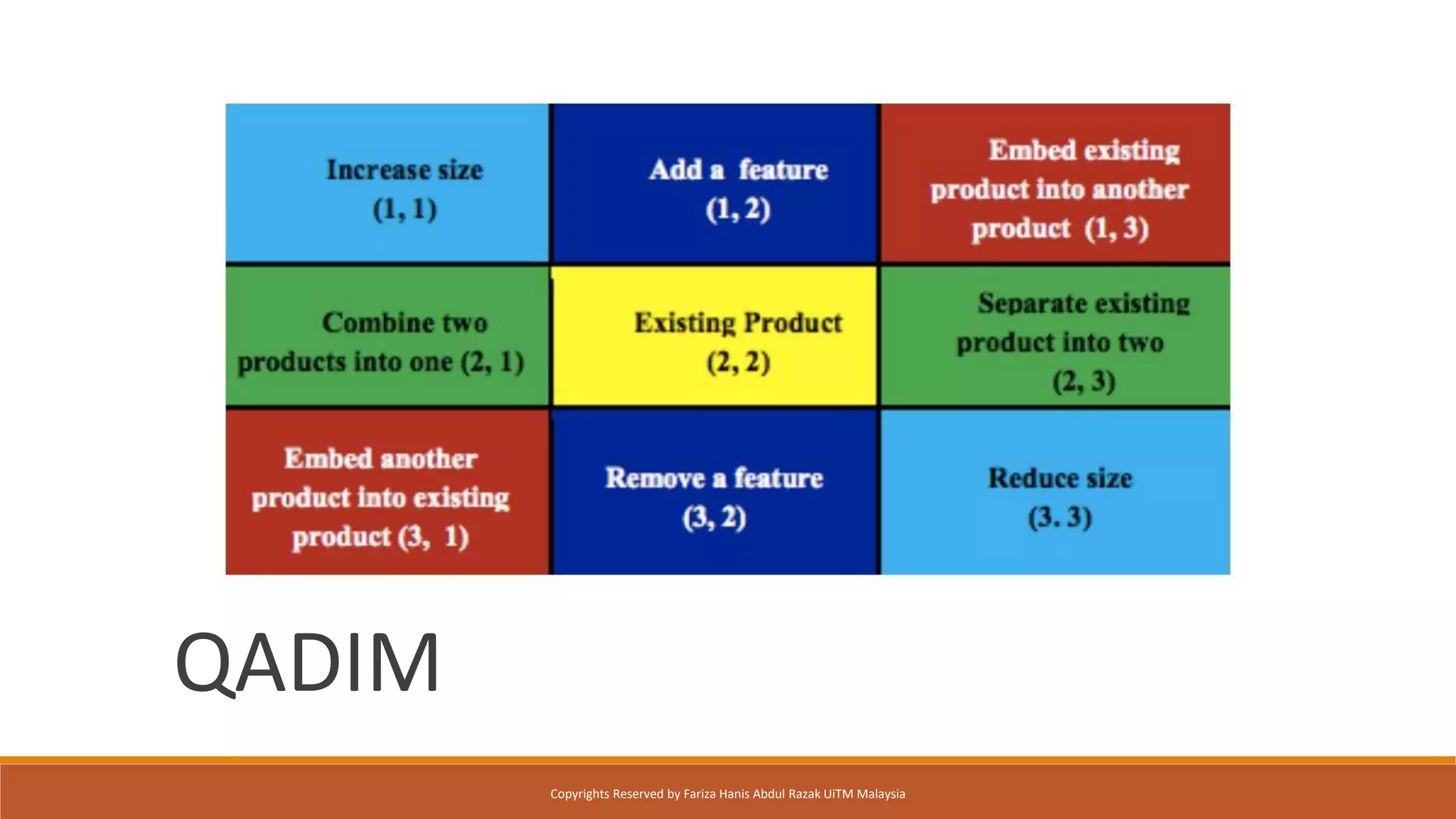
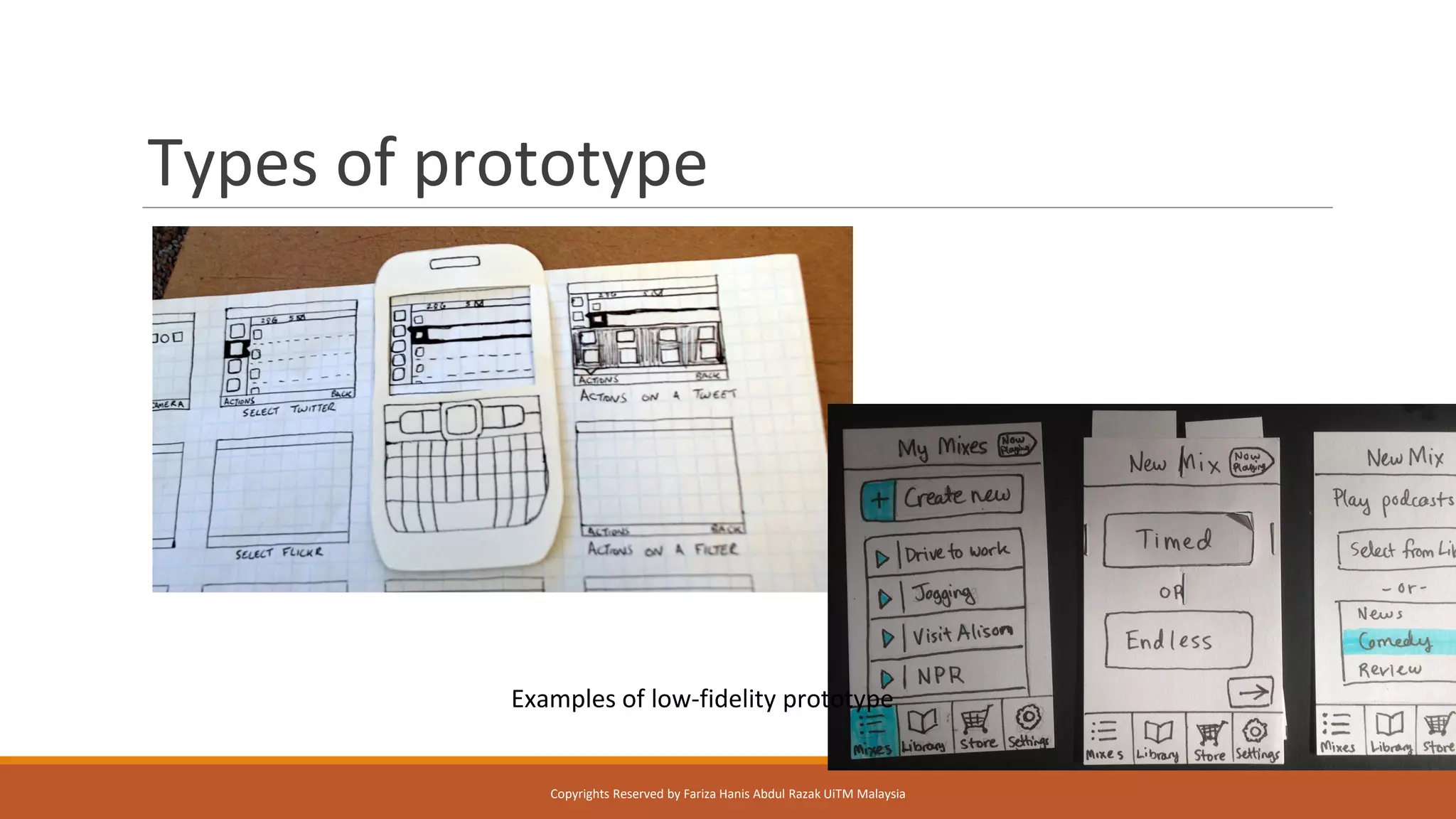
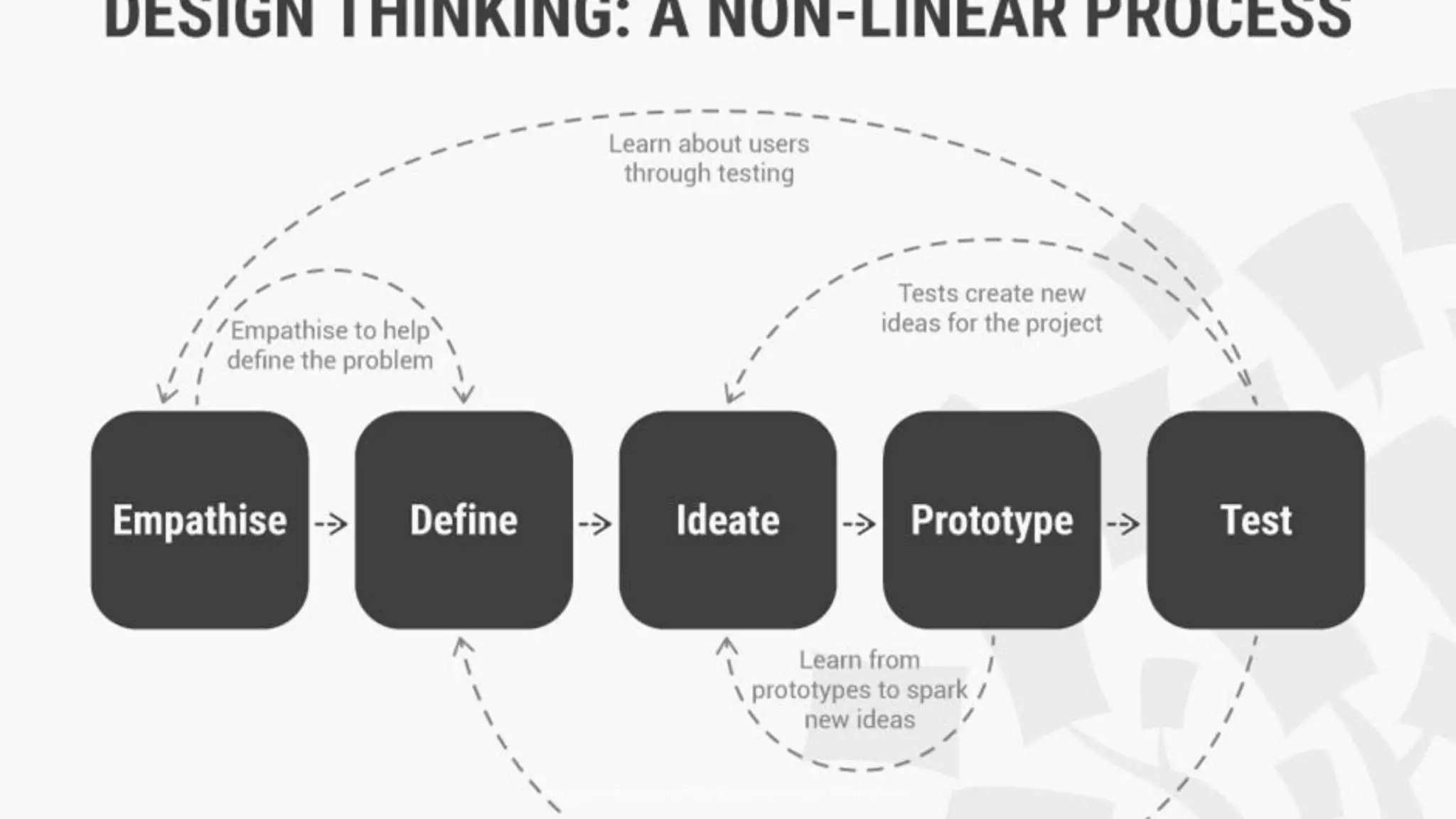
Design Thinking is a human-centered design methodology that uses a five-stage process: 1) empathizing to understand people's needs, 2) defining the core problem, 3) ideating potential solutions, 4) prototyping solutions, and 5) testing them with users. The five stages are meant to be iterative, with insights from testing used to redefine problems or solutions. The process aims to solve complex, ill-defined problems by reframing them in human terms and applying hands-on prototyping and testing of ideas.