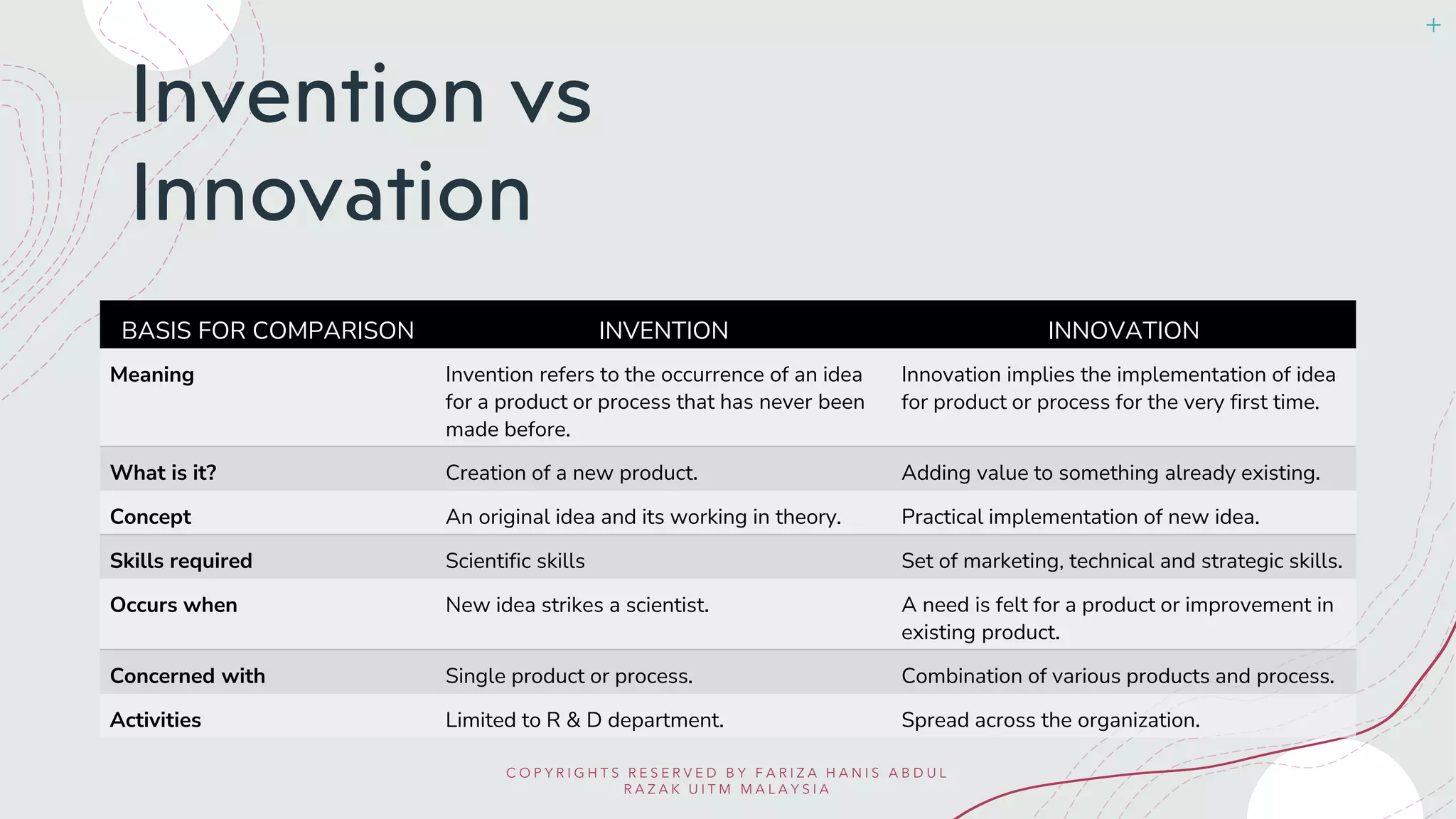
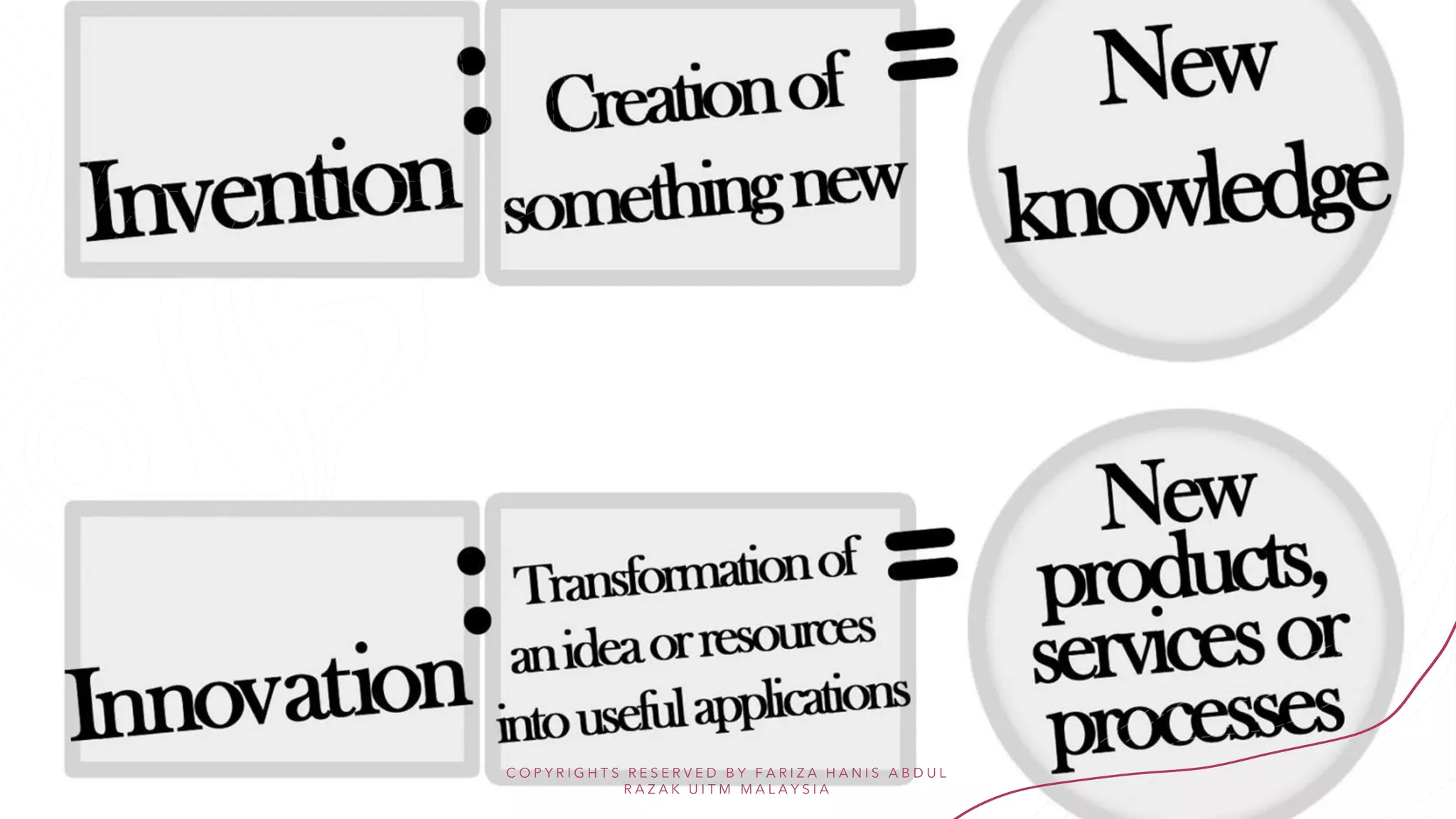
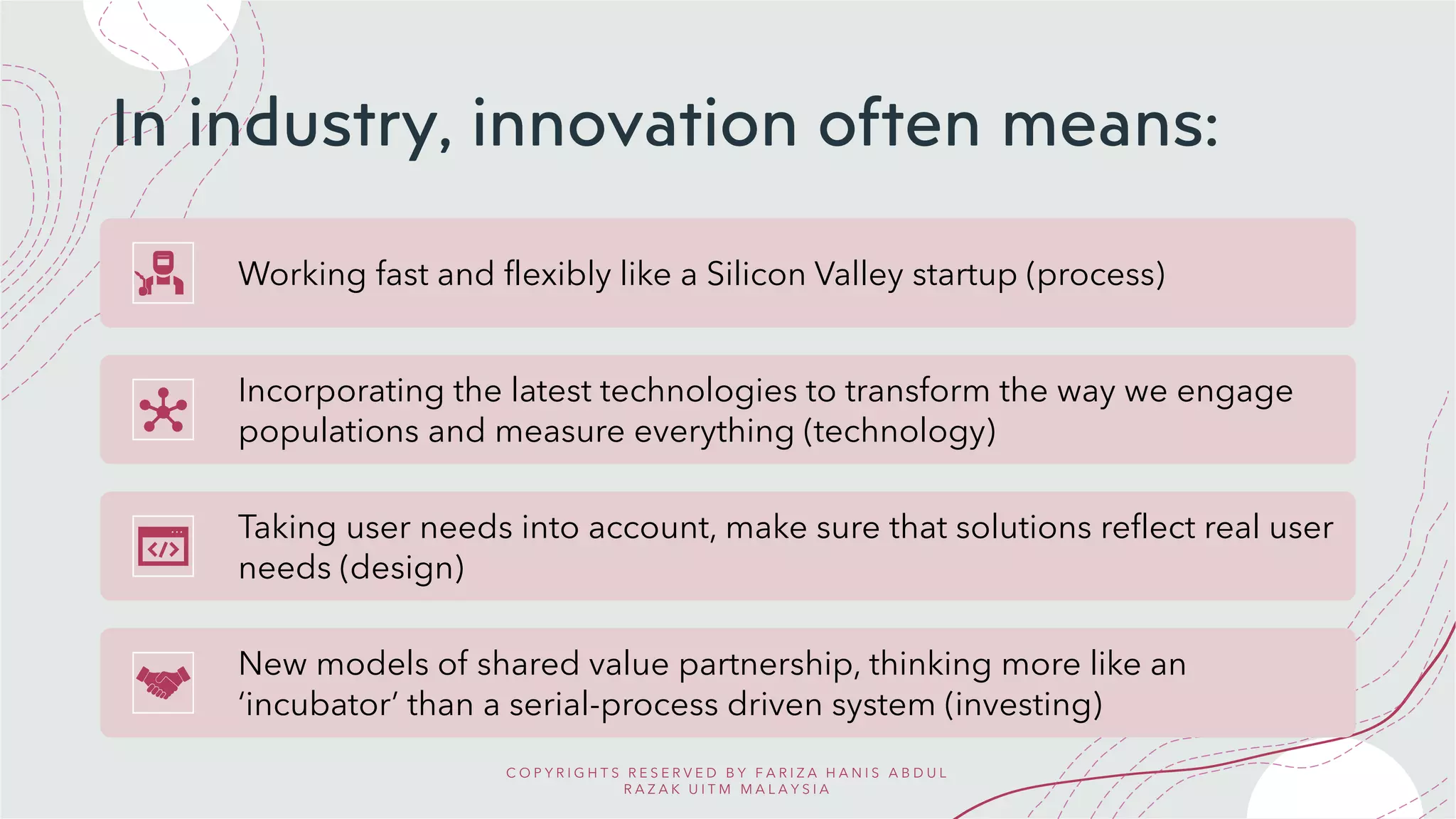
Invention is the creation of a new product or process, solving a problem through technology. Innovation takes invention further by transforming ideas into practical solutions that add value for customers. The key difference is that invention focuses on the original concept, while innovation implements and commercializes inventions. An ethical framework for innovation emphasizes designing with users, understanding contexts, and sharing knowledge openly to solve big problems through collaboration without harm.