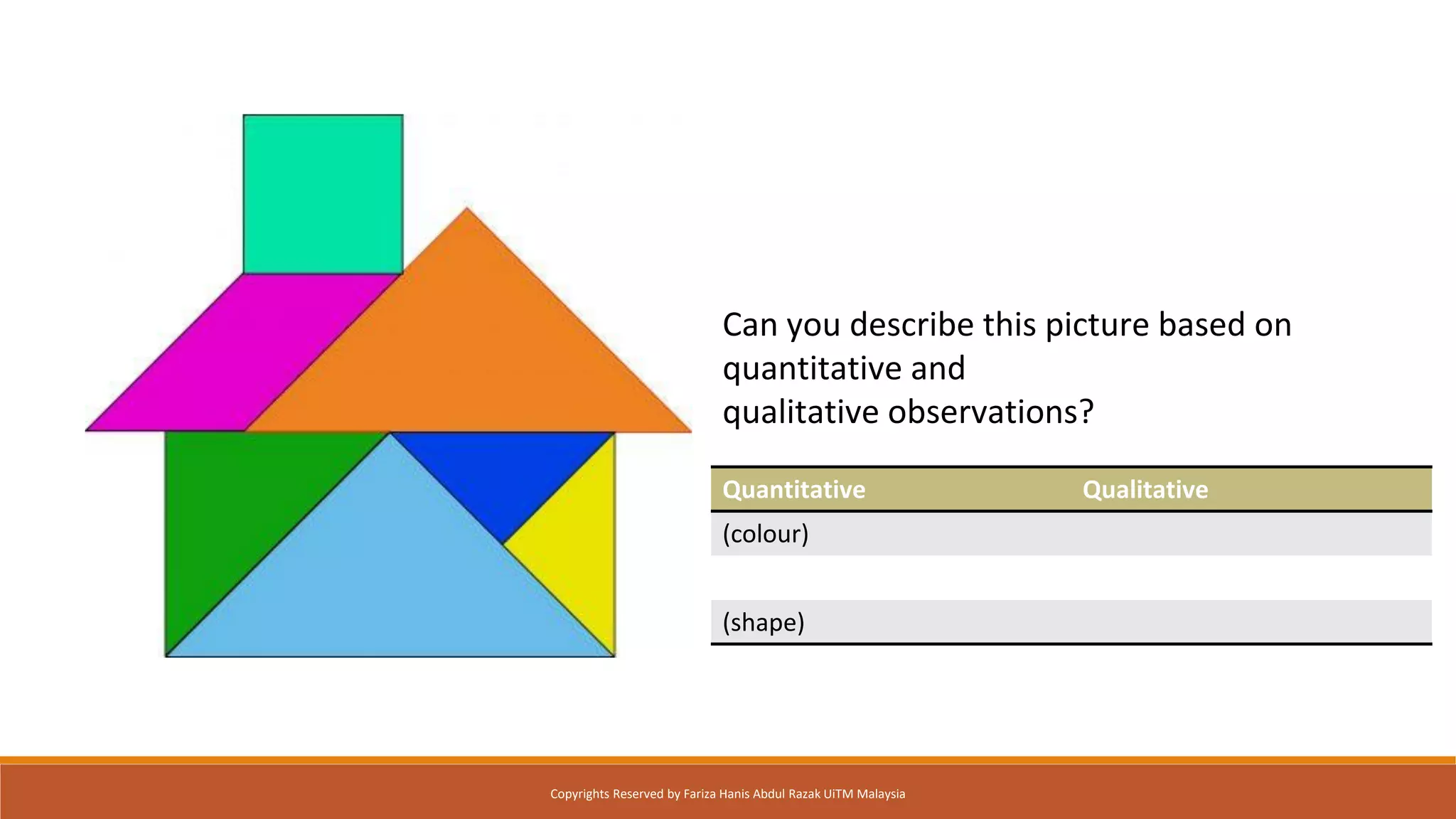
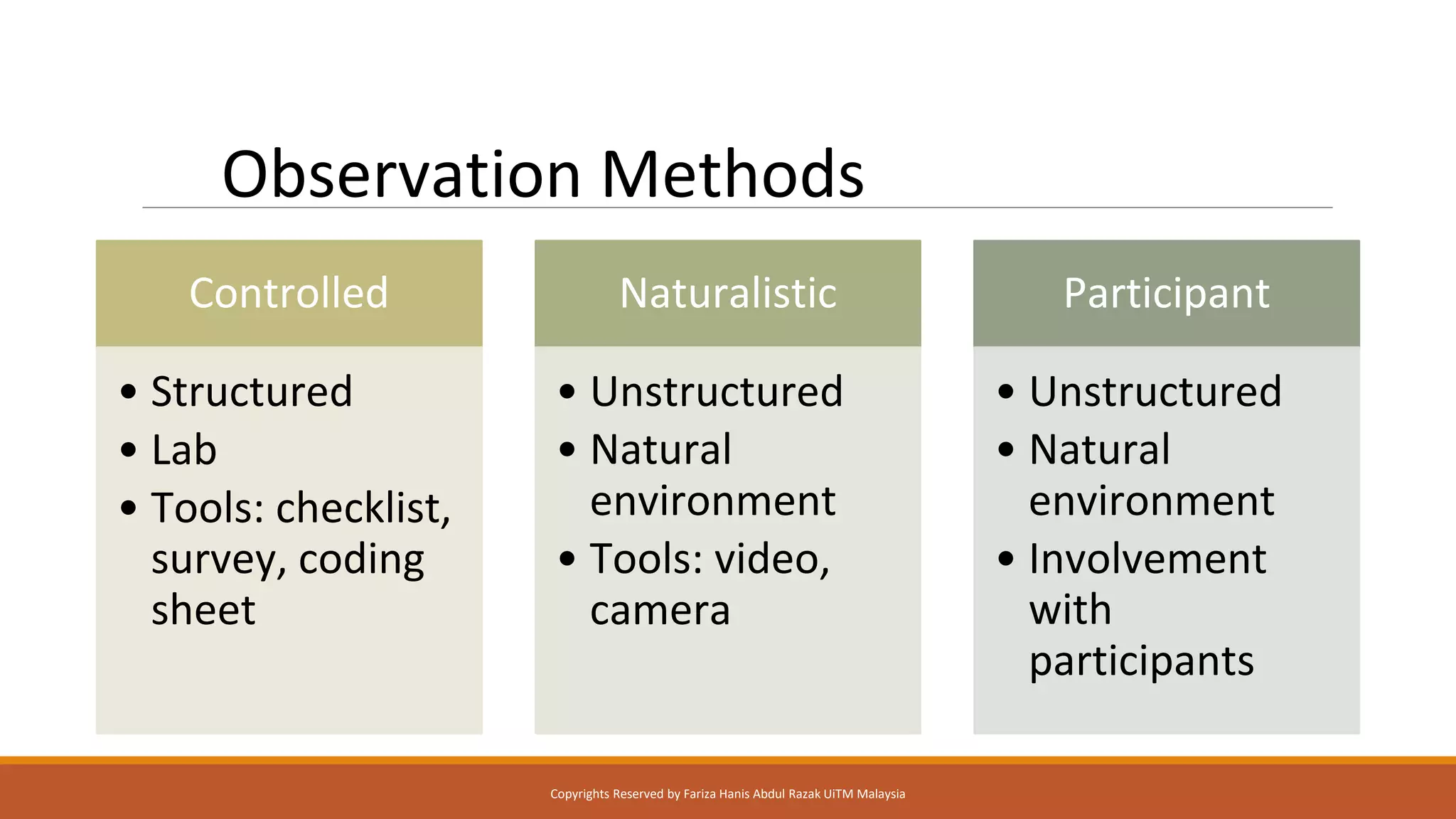
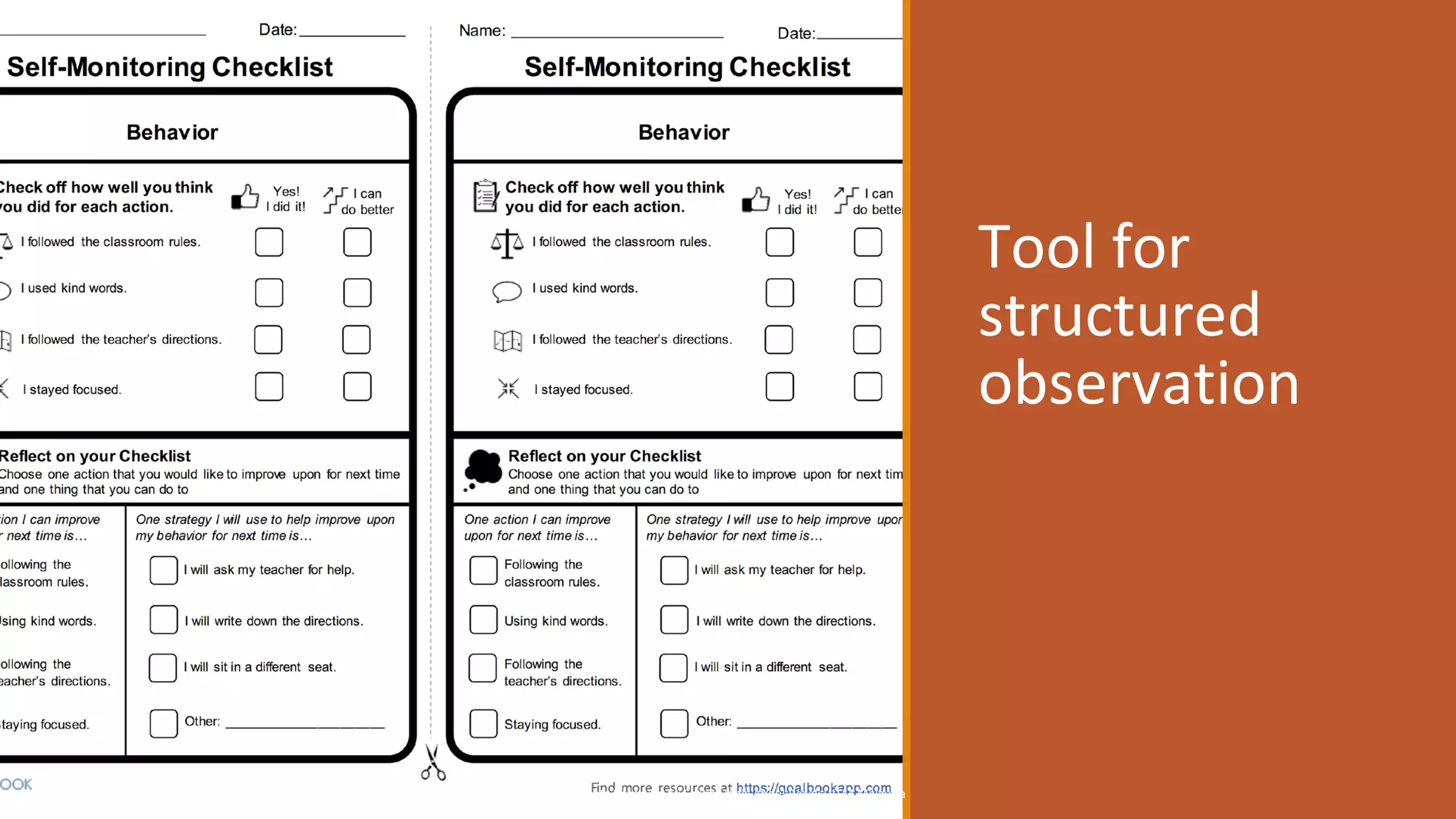
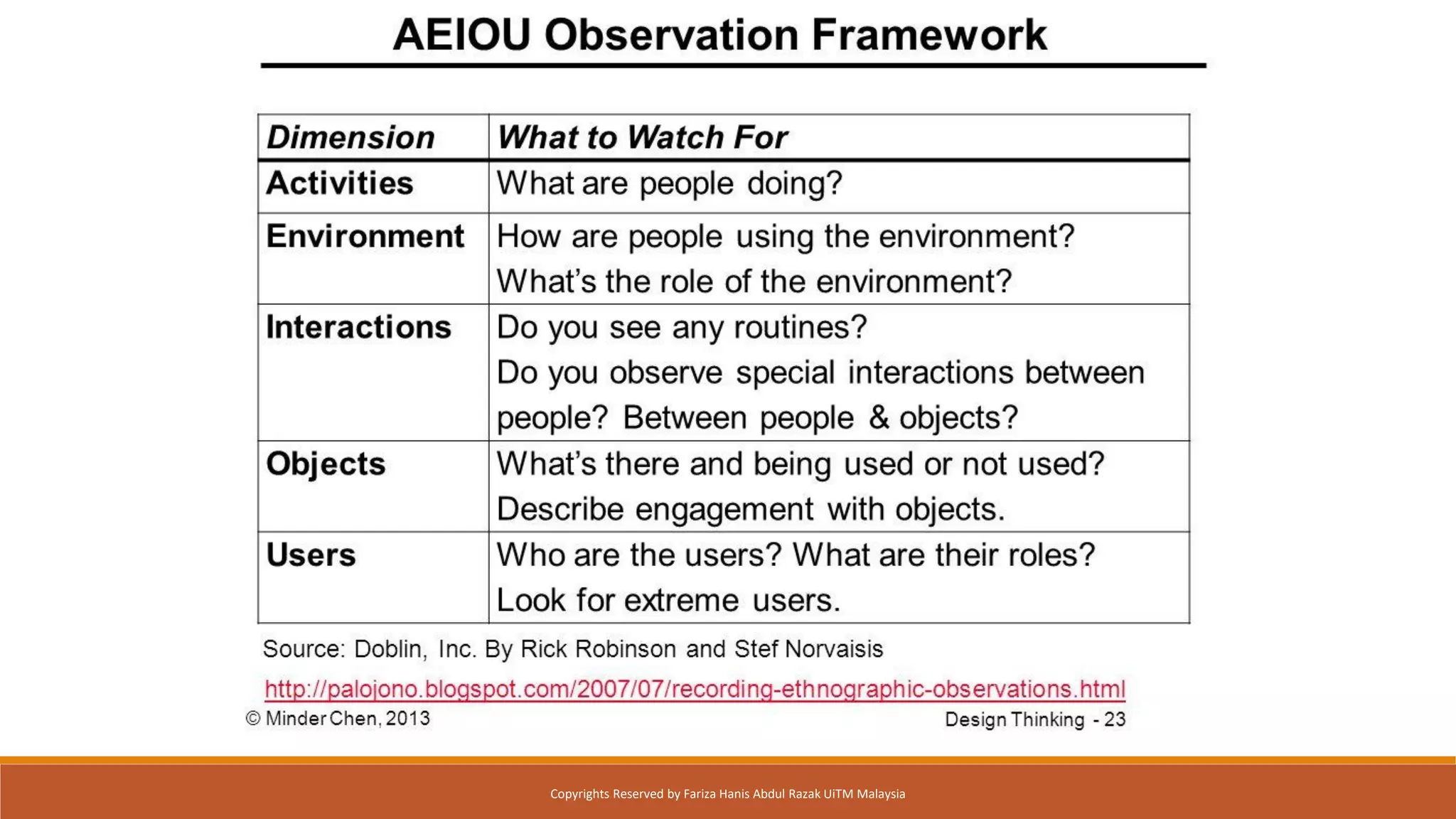
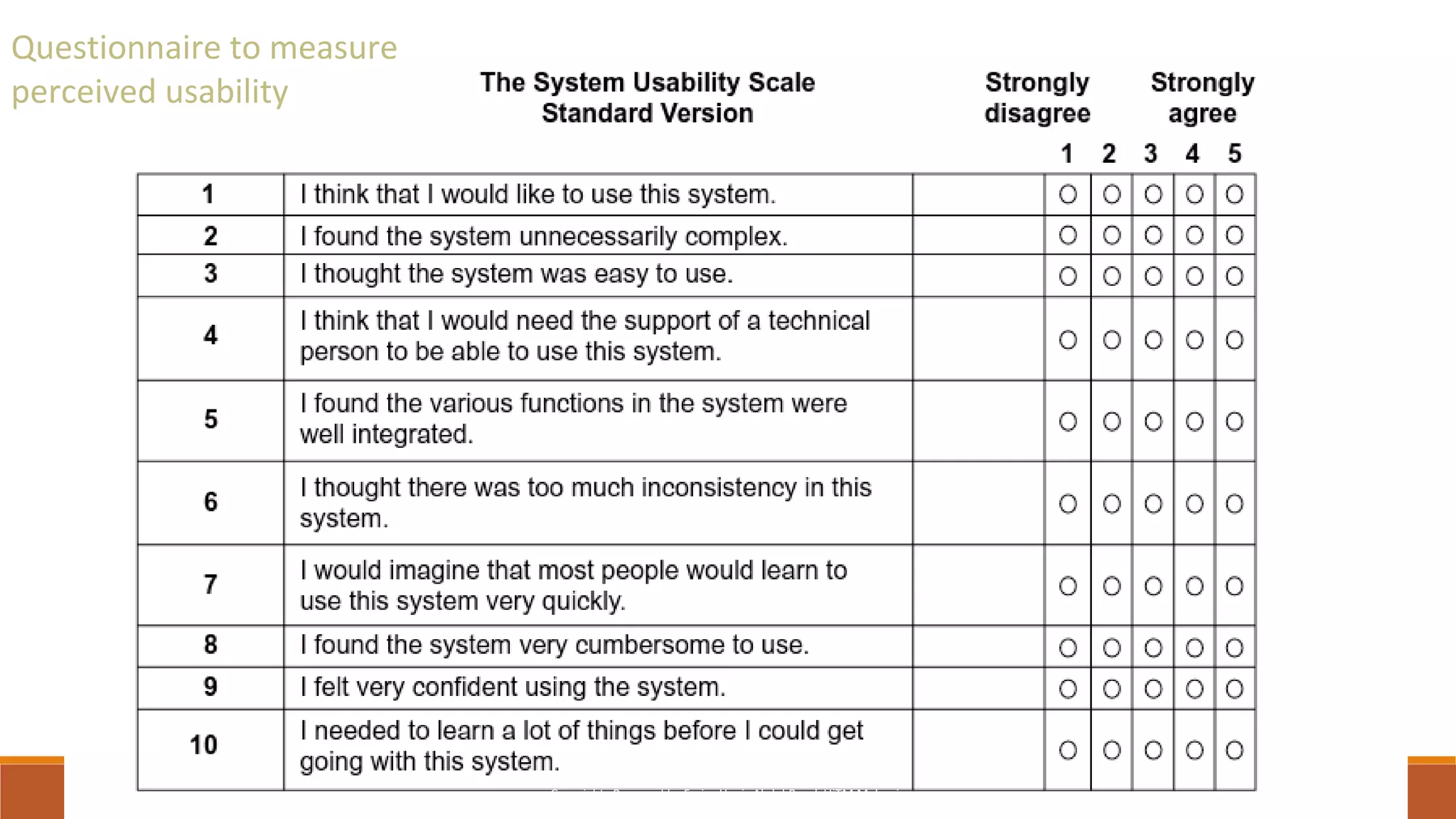
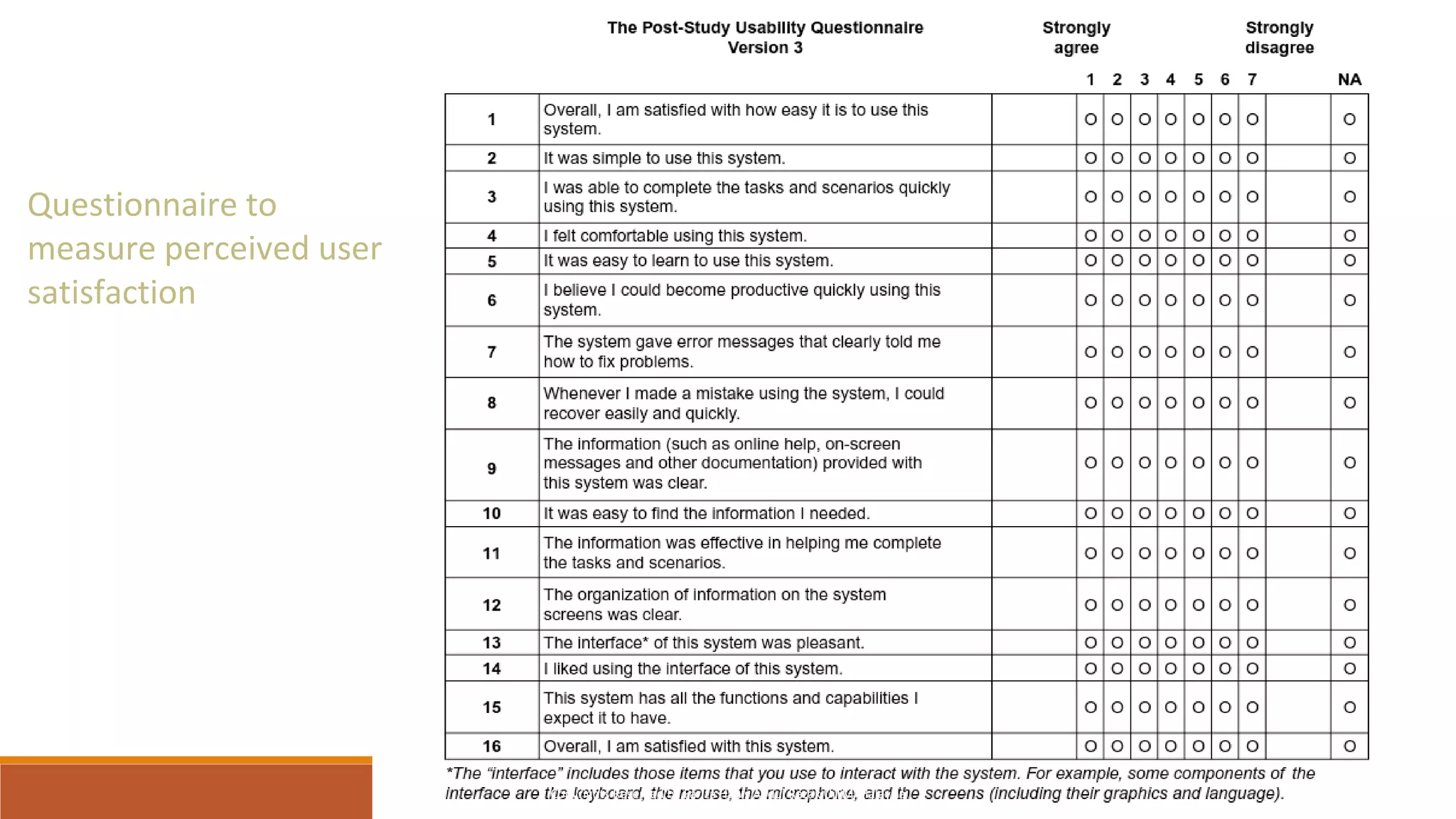
This document discusses different critical thinking tools and methods for observation and evaluation. It covers quantitative and qualitative observation, controlled, naturalistic, and participant observation methods. Examples of tools for structured observation like checklists are provided. Readers are given exercises to practice observation skills like tracking habits for a week and using the AEIOU framework to observe behaviors in different environments. Evaluation methods like usability testing and questionnaires to measure perceived usability and satisfaction are outlined. The document aims to describe critical thinking tools and have readers apply them to solve problems.