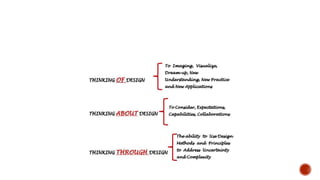
The document discusses design thinking, which is a structured, human-centered approach to problem solving. It involves empathizing with users to understand their needs, defining the core problems, ideating potential solutions, prototyping ideas, and testing them. Design thinking aims to facilitate innovative solutions and reduce risk. It has benefits like improving standards of living, enabling innovation, and enhancing processes. While research has shown success, challenges include disagreements in diverse teams and delays from over-testing ideas. Overall, design thinking can lead to more innovative, user-focused solutions and better collaboration.