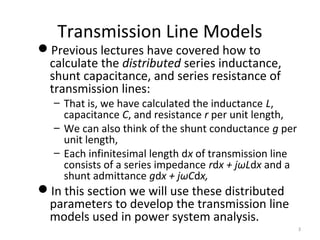
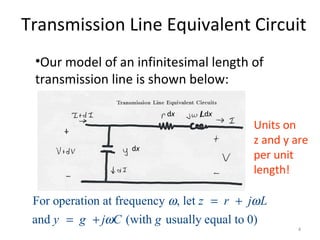
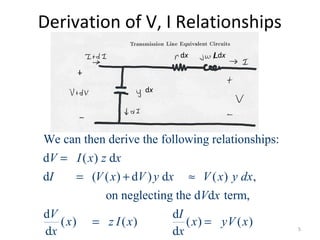
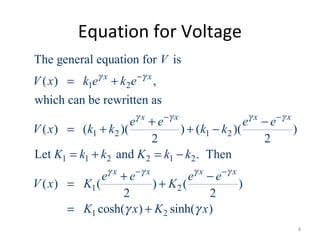
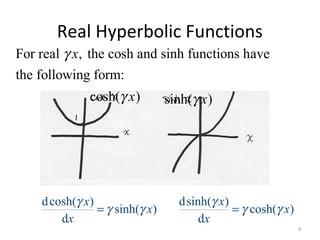
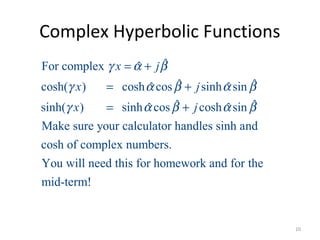
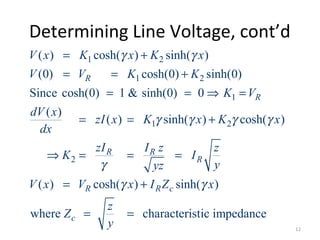
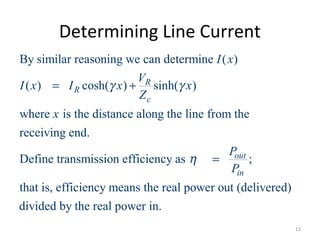
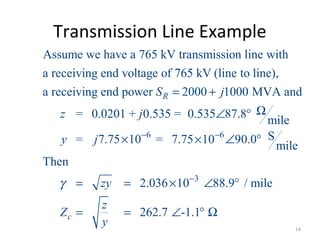
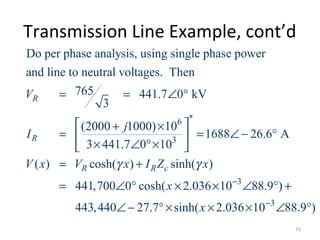
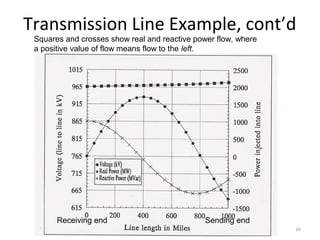
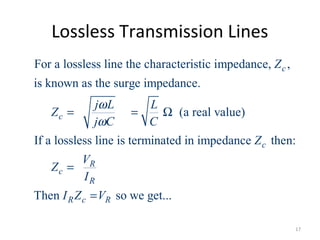
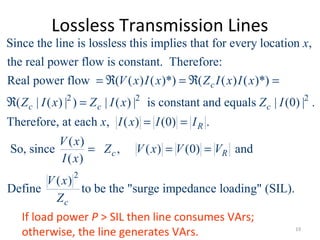
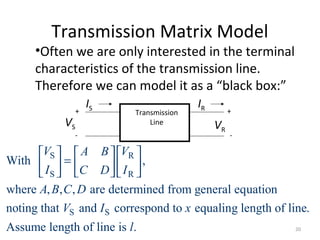
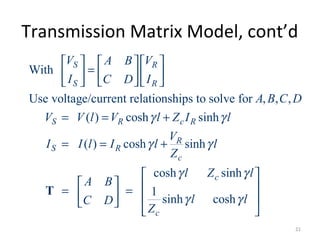
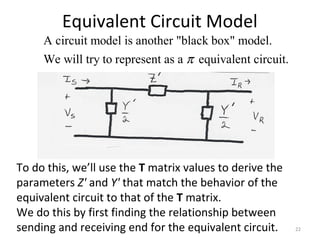
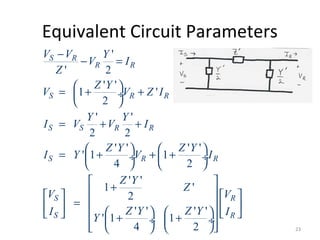
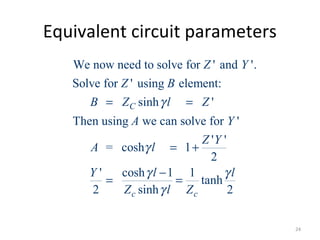
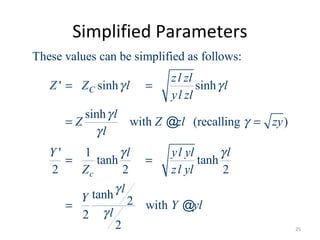
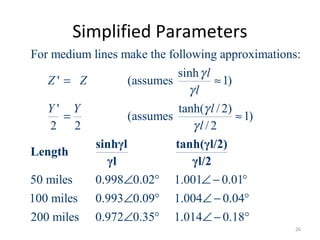
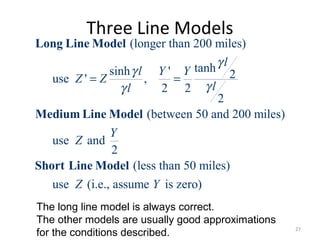
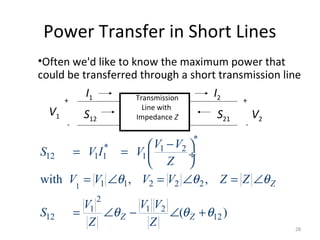
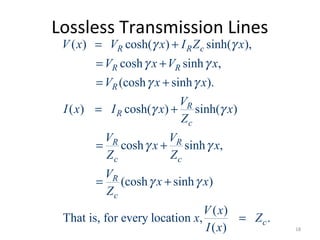This document discusses transmission line models used in power system analysis. It begins with an overview of the distributed parameter model that represents an infinitesimal length of transmission line using series impedance and shunt admittance. It then derives the telegrapher's equations and uses them to develop a single second-order differential equation for the voltage along the line. The document presents solutions for this equation that allow determining the voltage and current at any point on the line given conditions at one end. It introduces transmission line parameters including characteristic impedance and propagation constant and shows how they relate the sending and receiving end quantities. Equivalent lumped-parameter π models are also derived in terms of the transmission line parameters. Finally, it discusses short