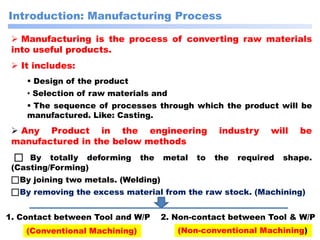
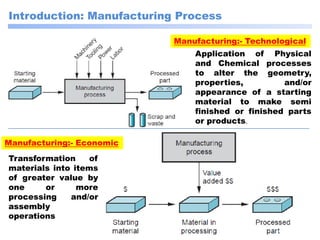
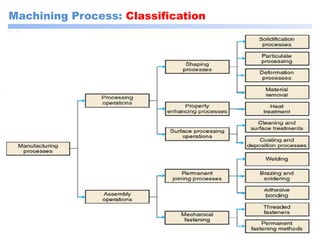
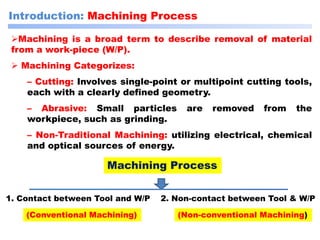
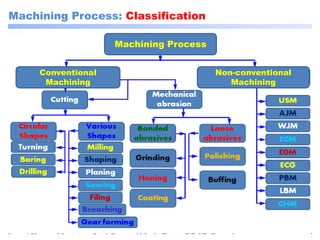
This document discusses manufacturing and machining processes. It defines manufacturing as the process of converting raw materials into useful products through processes like design, material selection, and specific manufacturing methods. Machining is described as a manufacturing process that removes excess material from a workpiece using tools to achieve the desired shape, size, and surface finish. The document classifies manufacturing processes and provides examples, and also classifies machining processes as conventional (using physical tools) or non-conventional (using non-physical methods like electrical or chemical processes). It compares conventional and non-conventional machining and discusses their purposes and differences.