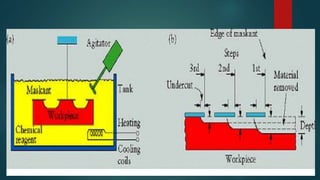
Chemical machining involves controlled chemical dissolution of a workpiece material using an acidic or alkaline etchant. The process includes preparing the workpiece, applying a maskant to protect areas, etching the exposed material using an etchant, removing the remaining mask, and finishing. It allows for producing pockets and contours and removing material from high strength parts. The main steps are preparing the workpiece through cleaning, applying a masking material, etching the exposed areas using an etchant, and removing the remaining mask. Chemical machining provides advantages like weight reduction and avoiding stresses but has disadvantages like difficulty achieving sharp corners and limited thickness machining.