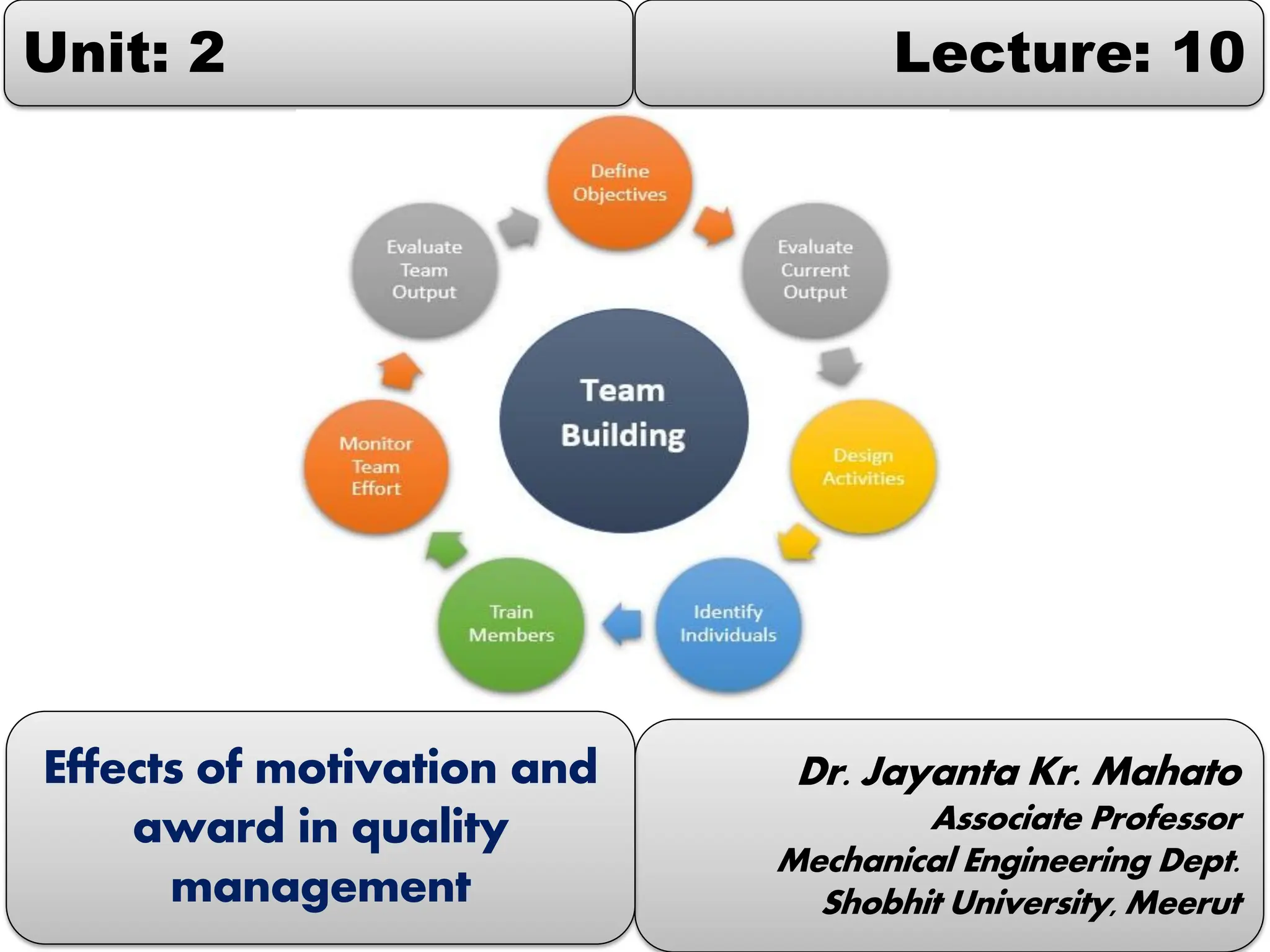
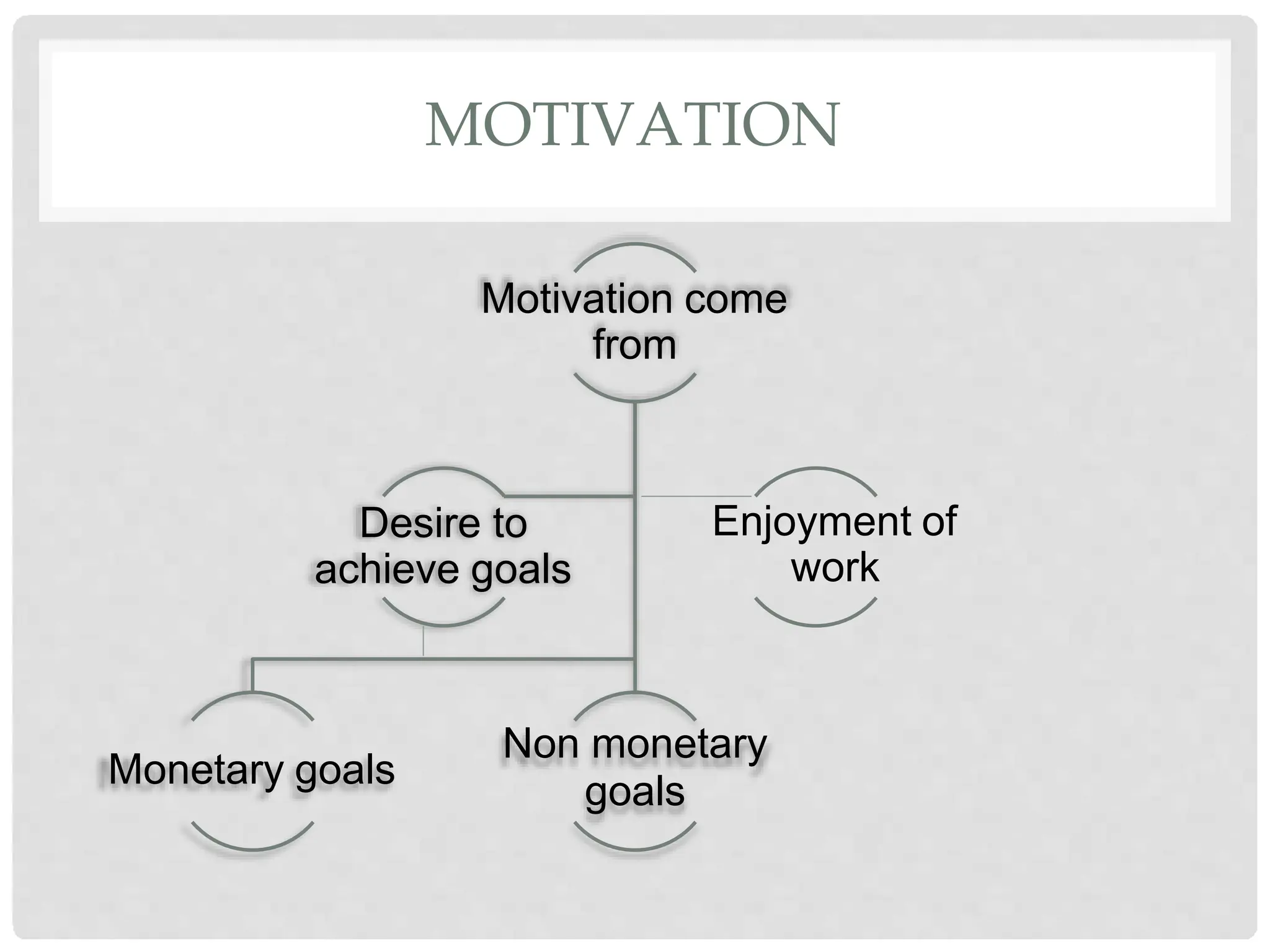
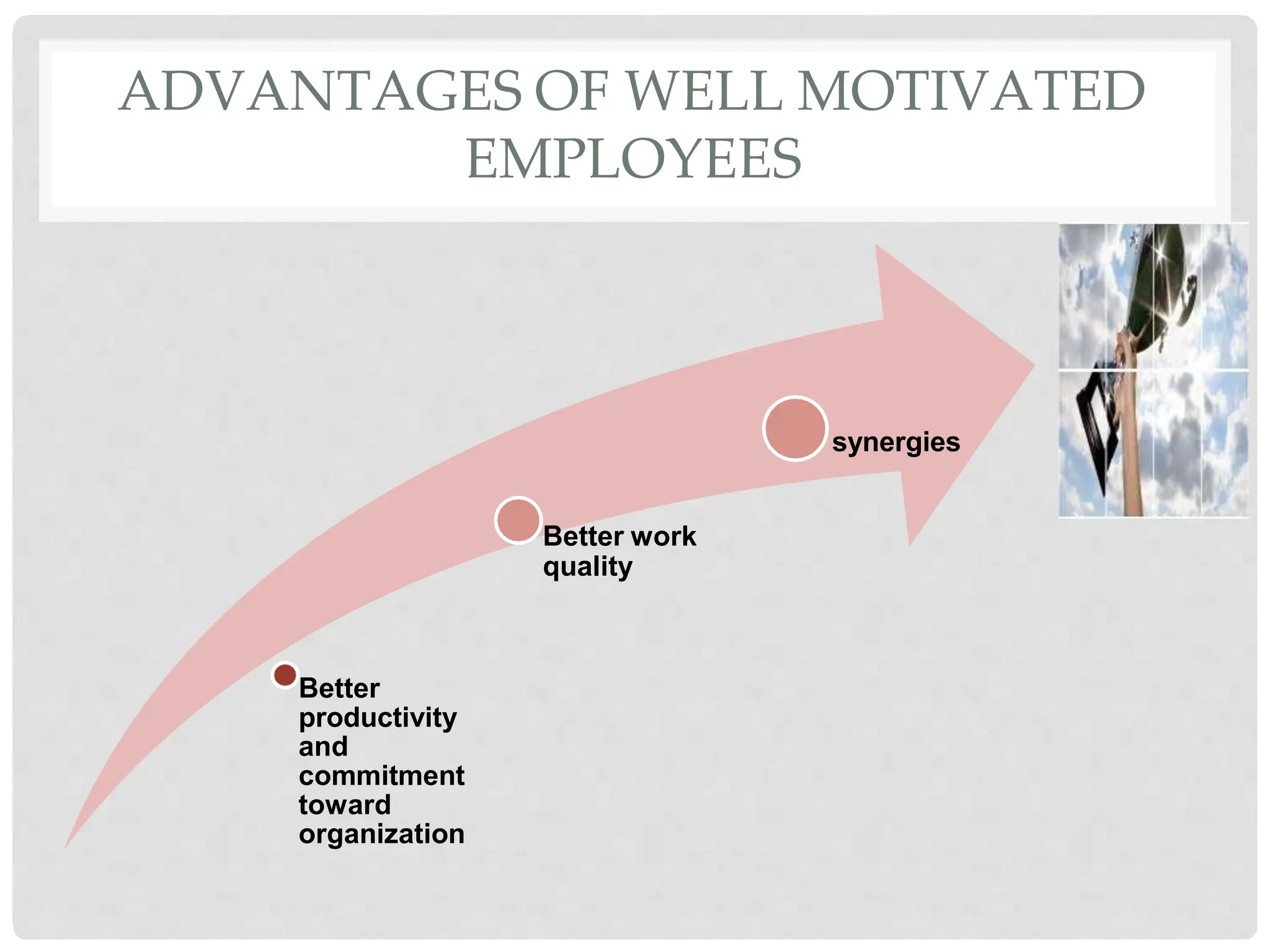
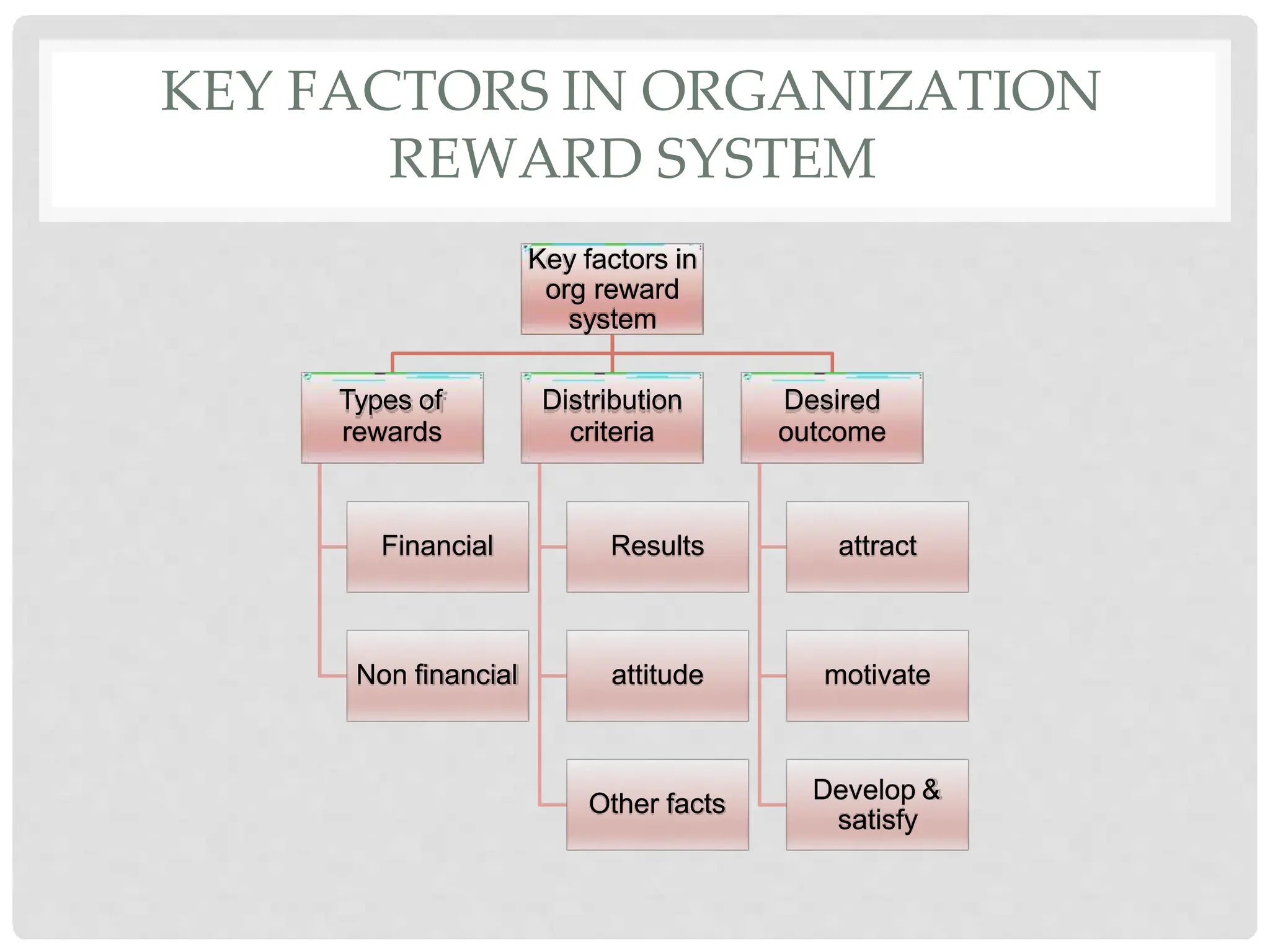
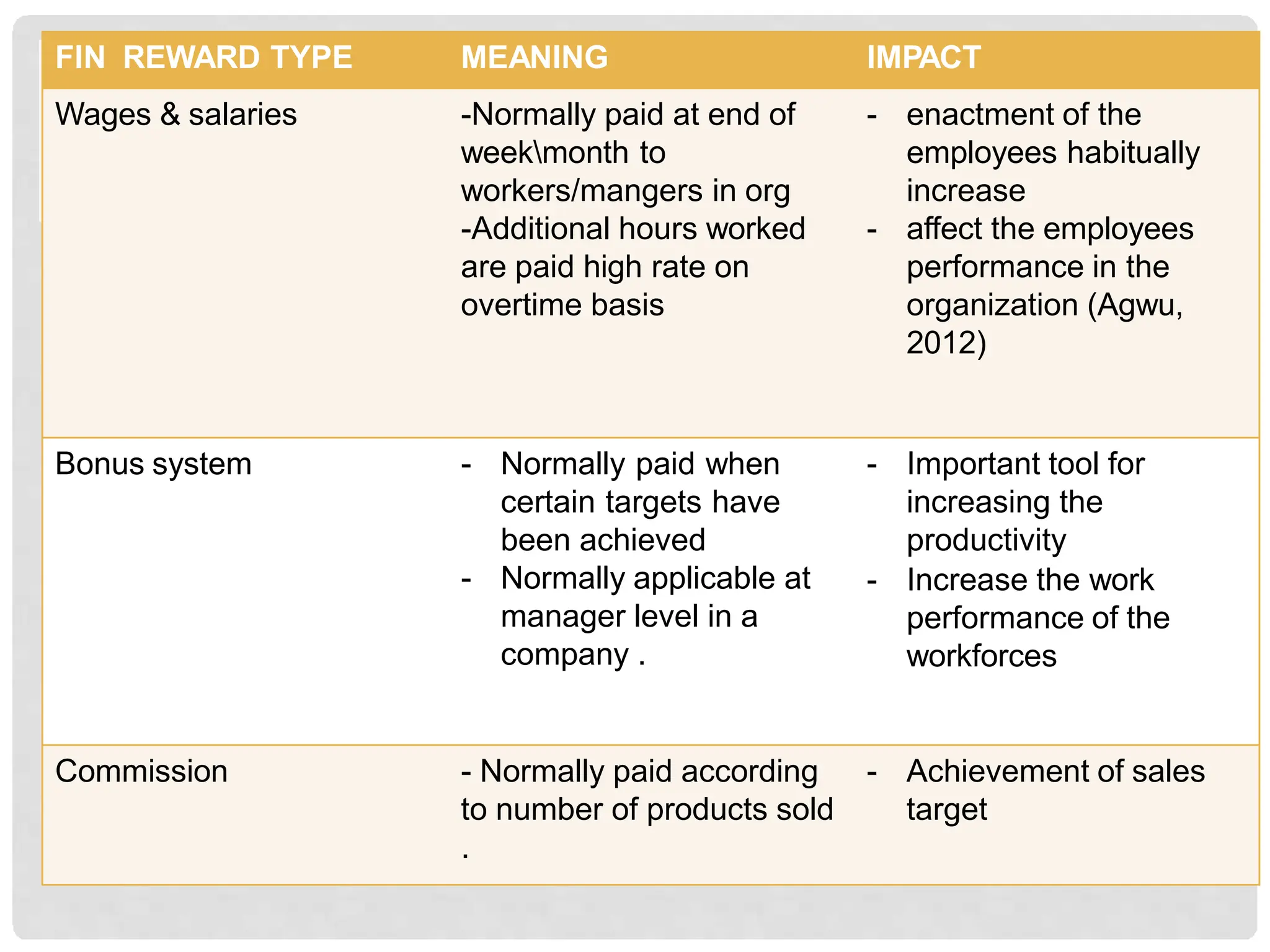
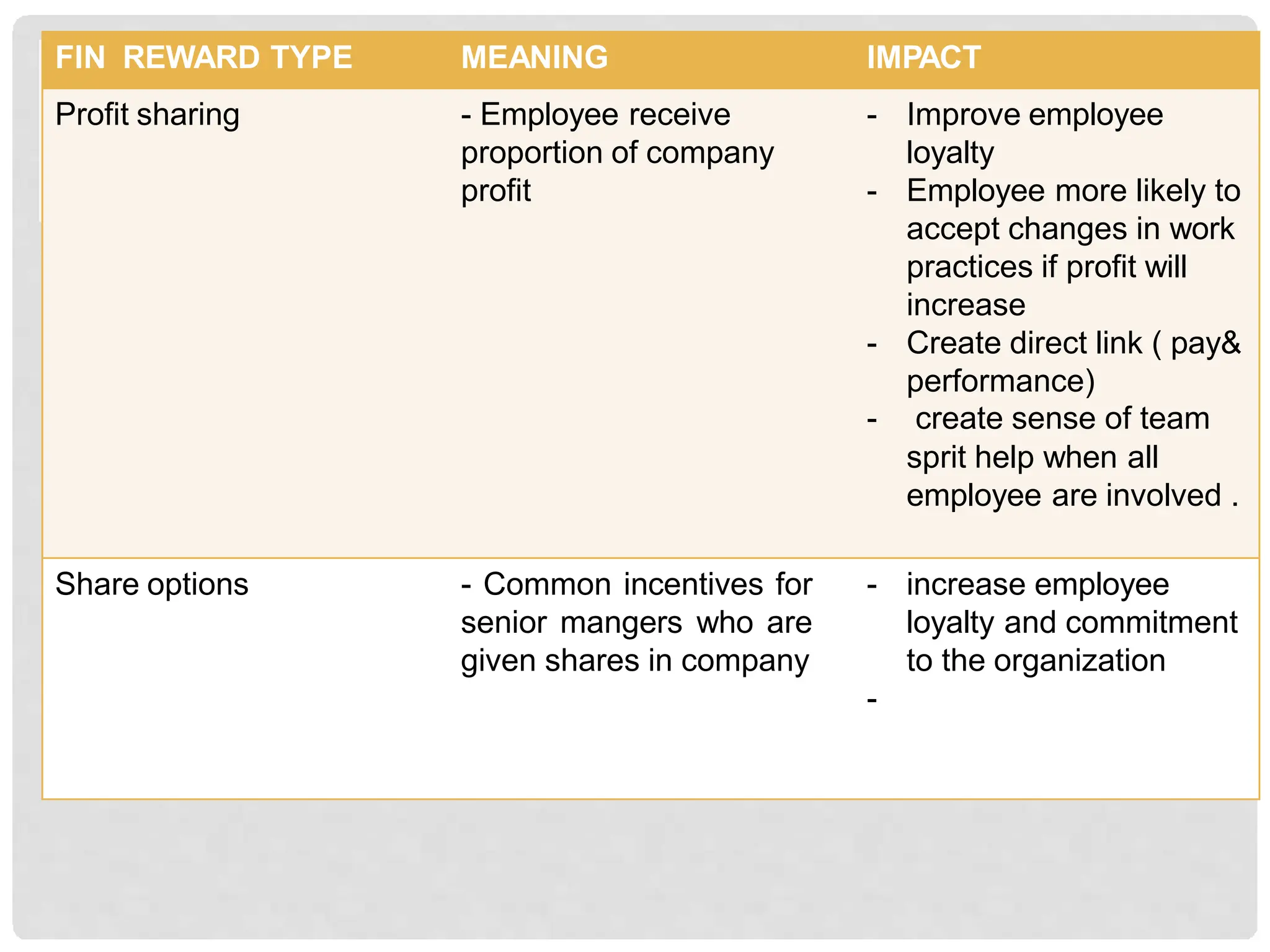
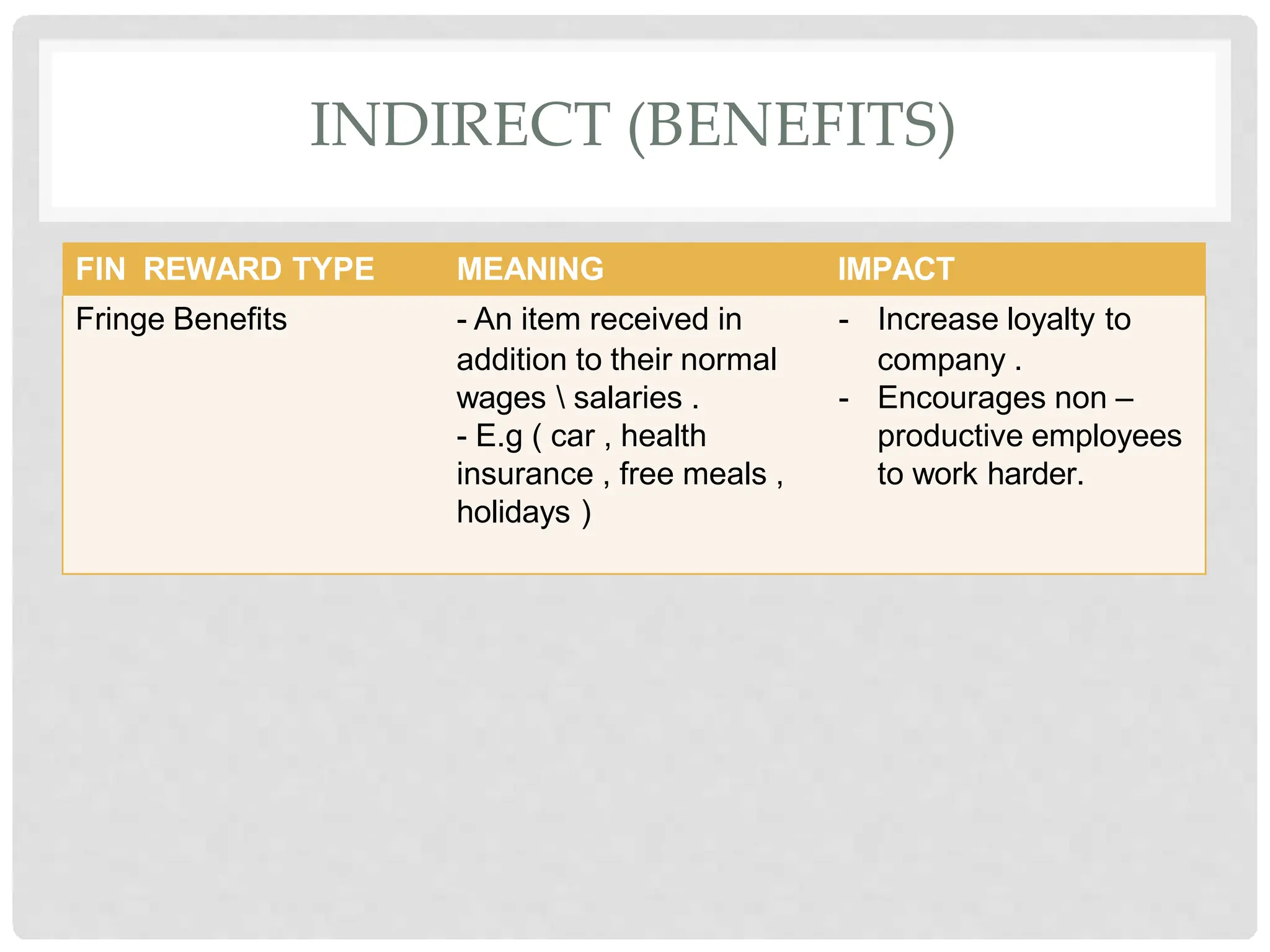
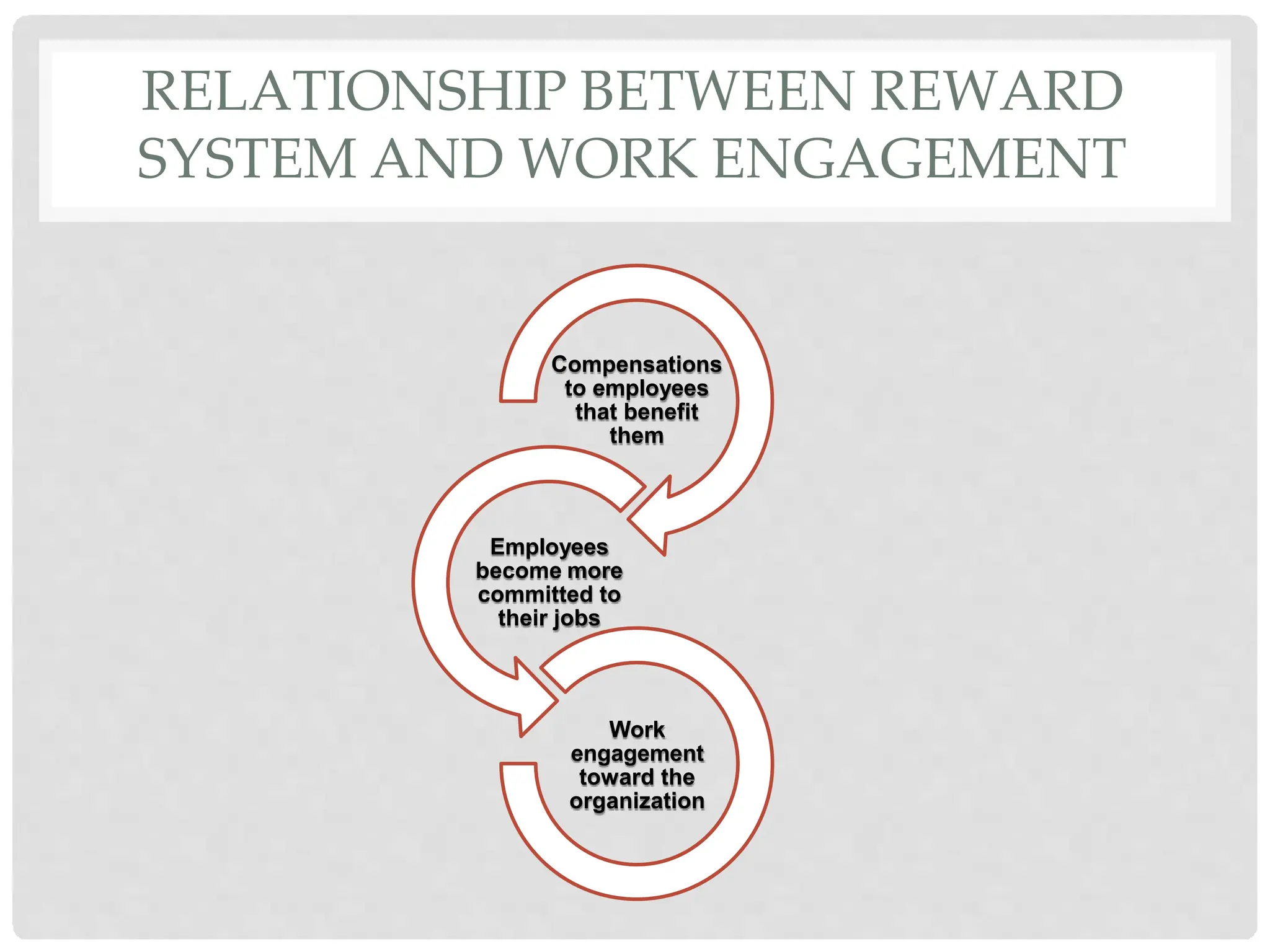
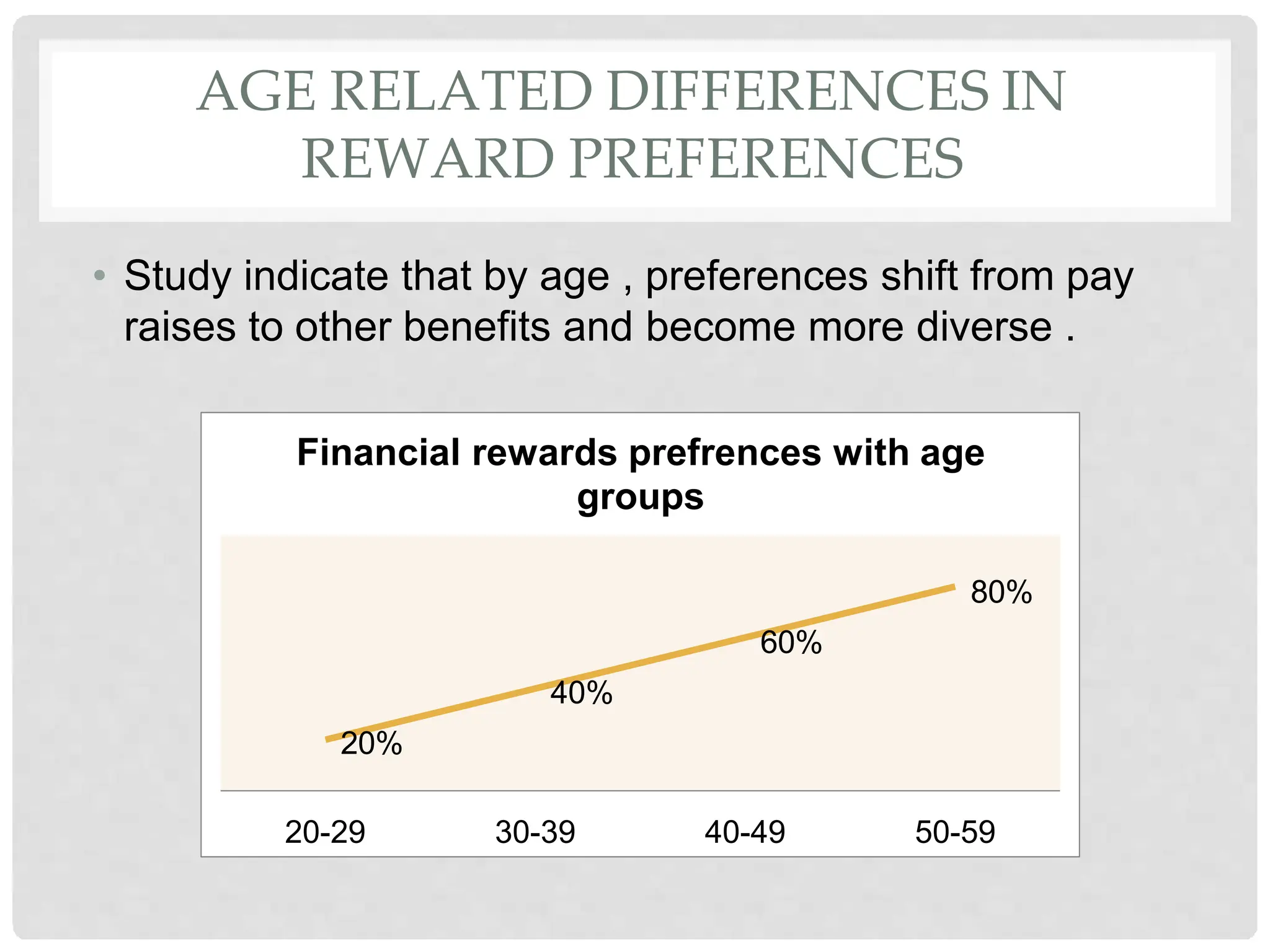
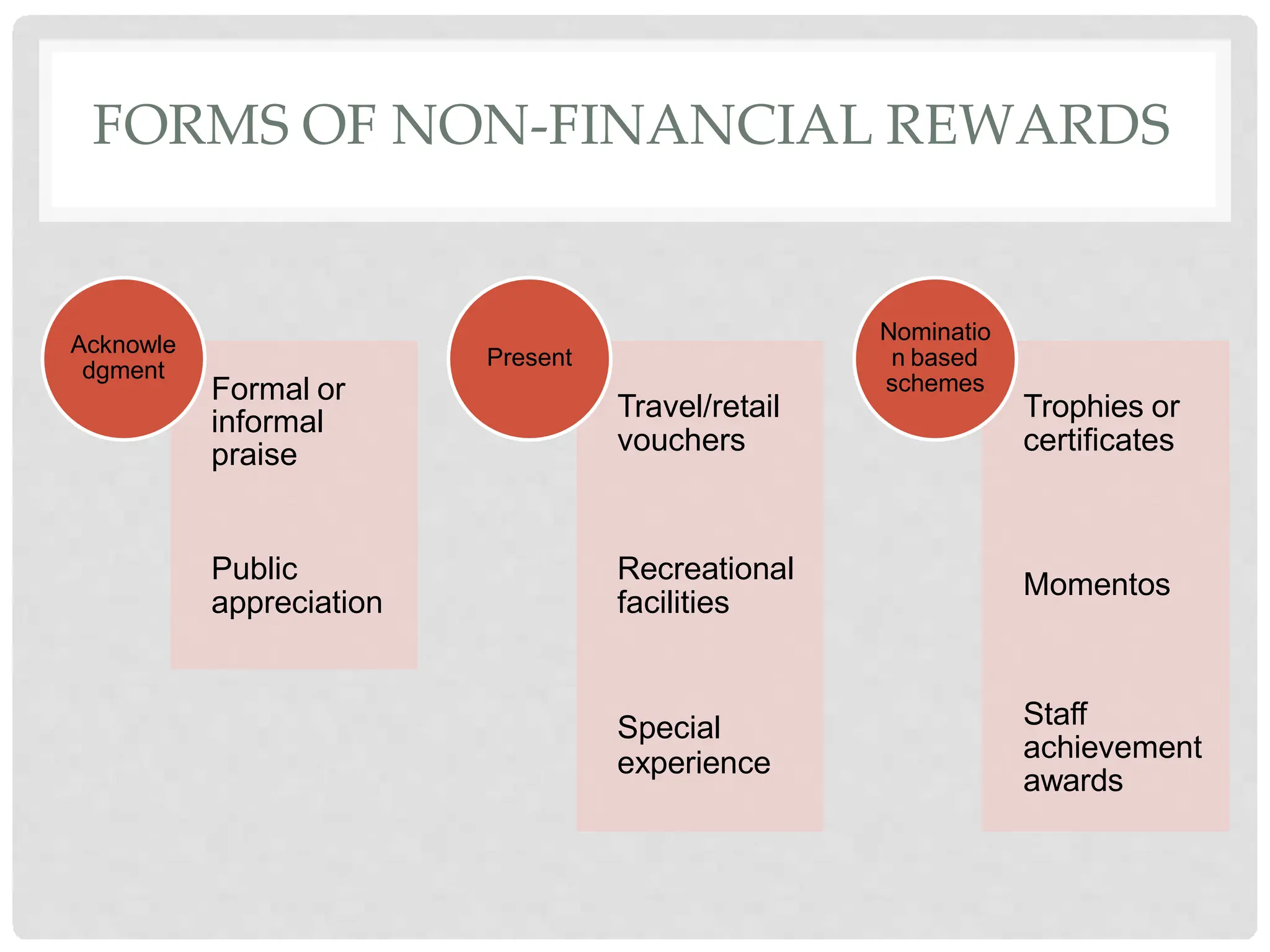
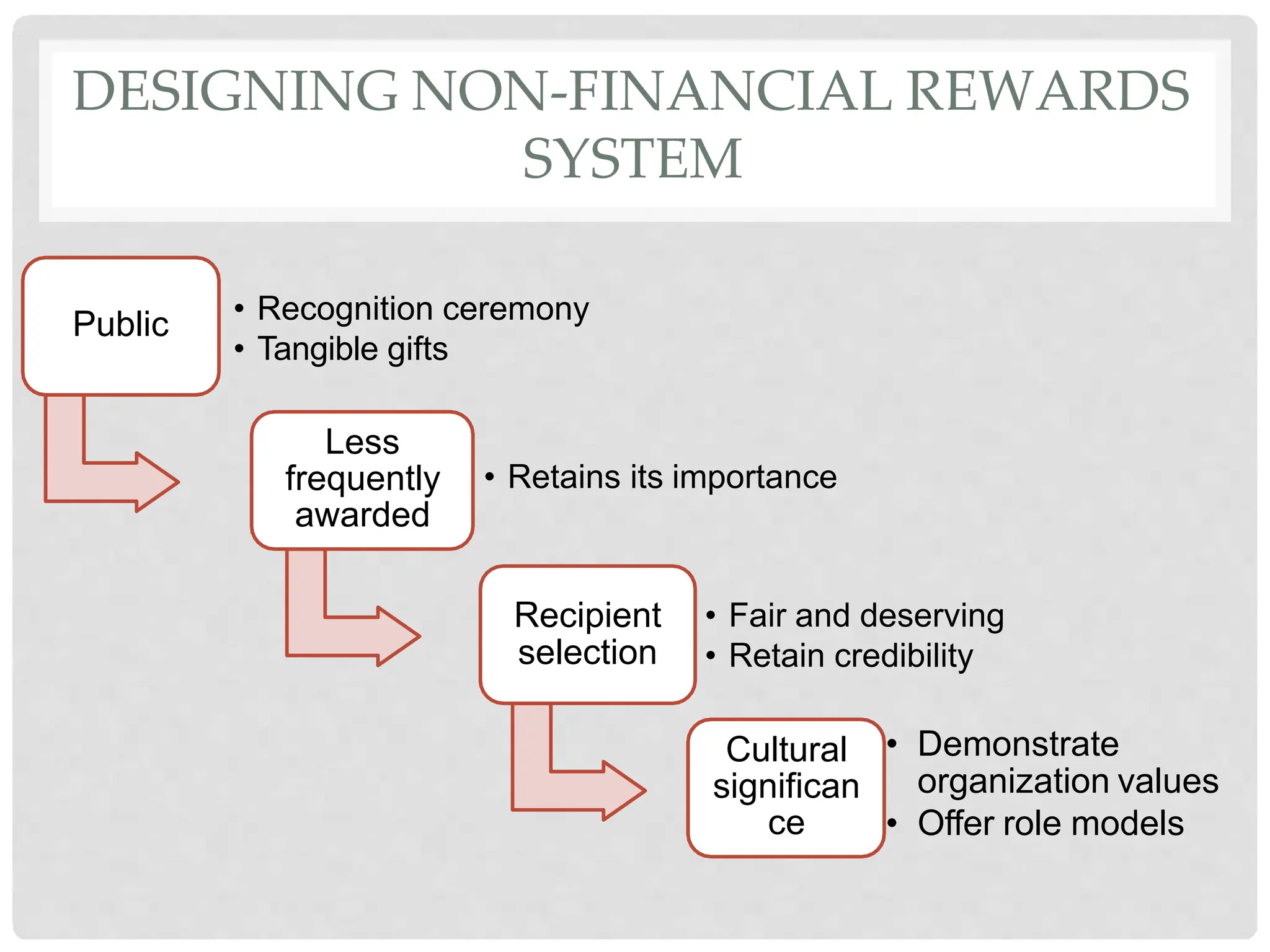
This document discusses the effects of motivation and rewards in quality management. It covers both financial and non-financial rewards. For financial rewards, it describes different types like wages, bonuses, profit sharing, and benefits and their impact on employee performance and engagement. For non-financial rewards, it discusses how they can direct employee behavior towards productivity and satisfaction through praise, recognition, and developmental opportunities. It also outlines factors for an effective rewards system like fairness, behaviors to recognize, designing the system, and potential benefits and failures.