The document discusses various optical phenomena related to diffraction and interference of light, including:
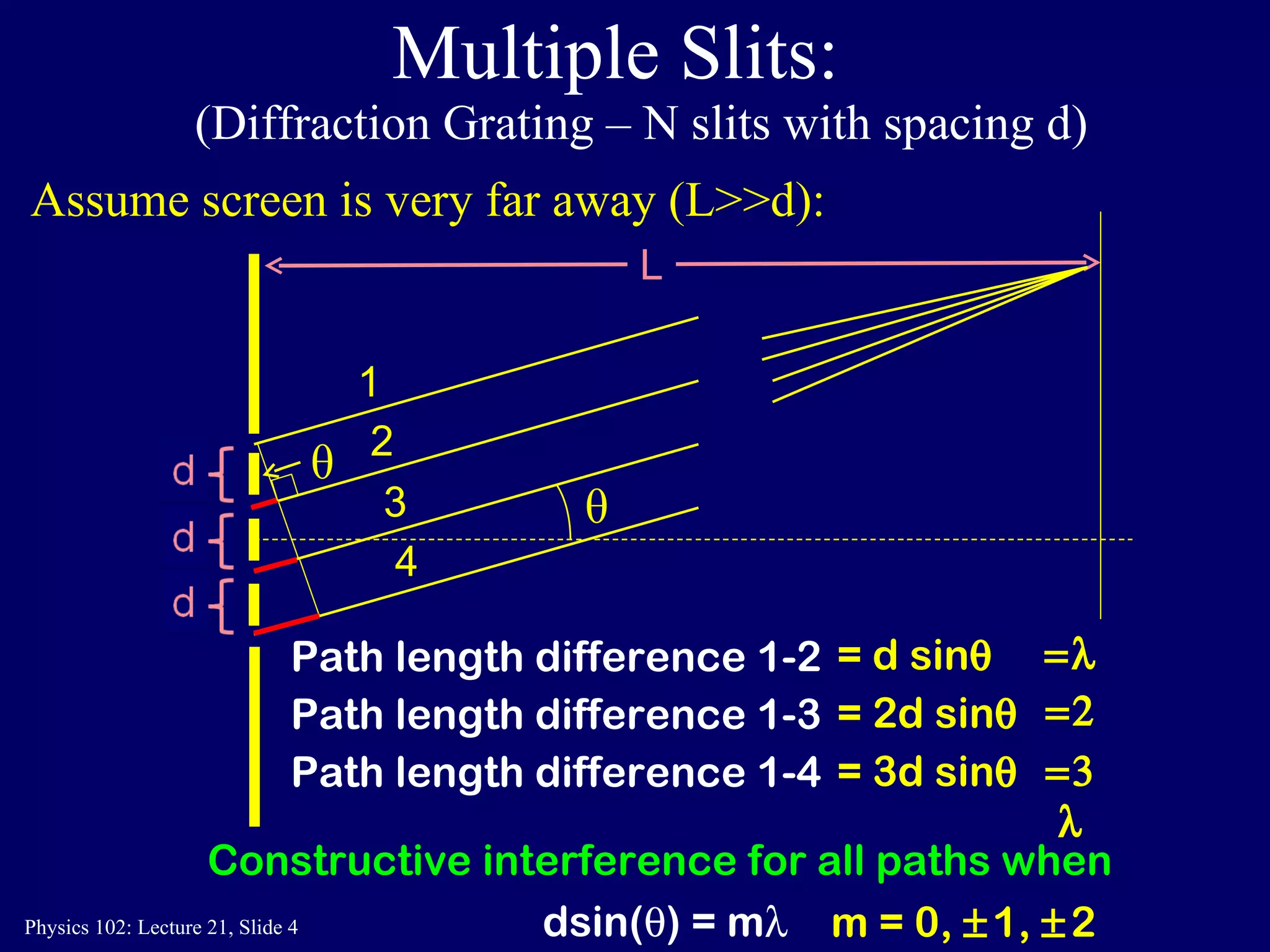
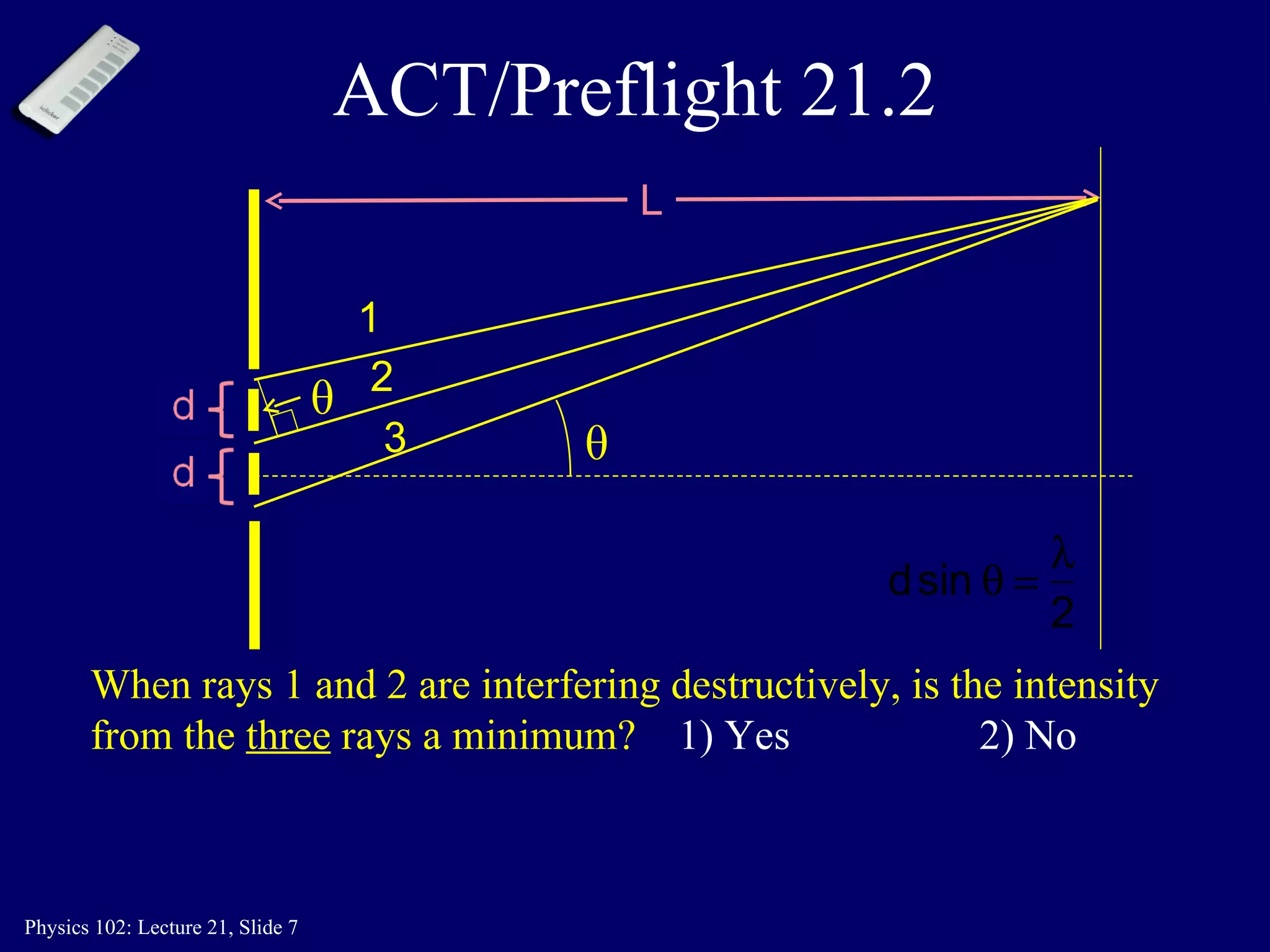
1) Light passing through multiple slits will produce constructive interference when the path length difference is an integer multiple of the wavelength.
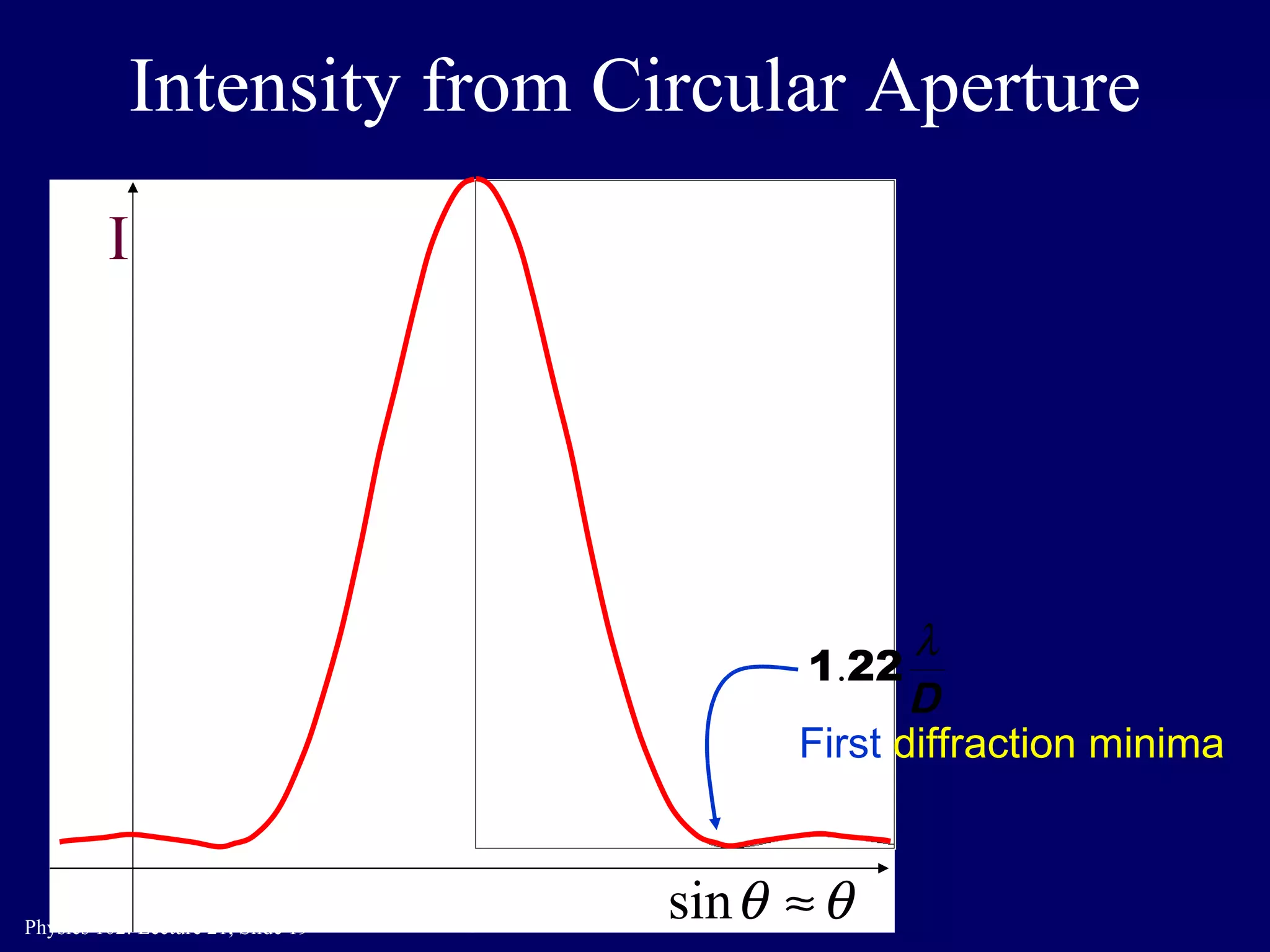
2) Single slit diffraction causes a diffraction pattern on a screen with alternating bright and dark bands. The location of the minima is determined by the slit width and wavelength.
3) Increasing the number of slits or decreasing the slit spacing results in narrower, brighter diffraction maxima.