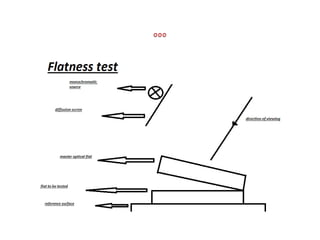
Optical flats are cylindrical transparent devices made of materials like fused quartz or borosilicate glass, with either one (Type A) or two flat surfaces (Type B) for testing flatness of measuring surfaces. The flatness is evaluated using interference patterns created by monochromatic light, while the parallelism of Type B surfaces can be assessed using the Fizeau interferometer method. Proper cleaning and careful placement are essential for accurate testing results.