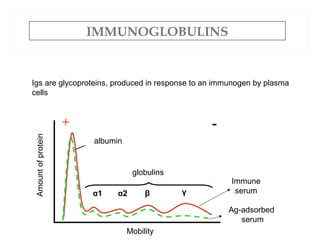
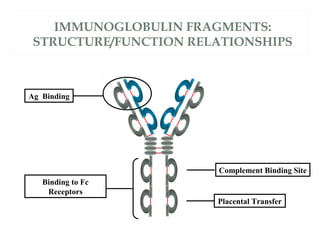
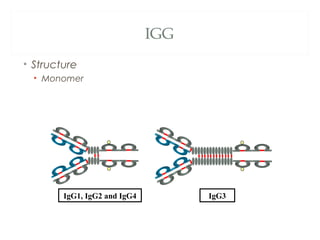
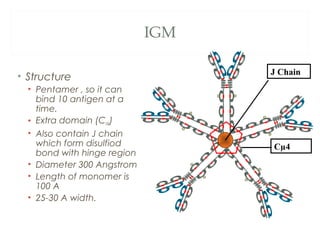
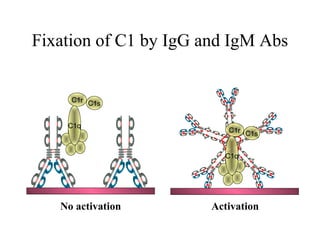
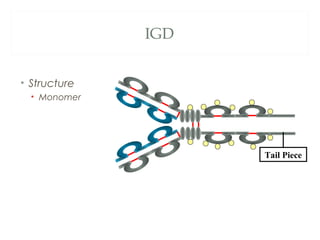
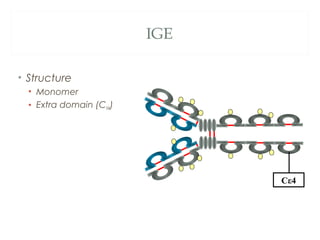
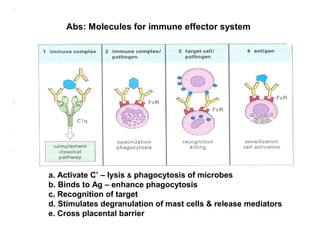
The document provides an overview of immunoglobulins, including their structure, types, and functions. It details the composition of antibodies, highlighting the differences between various immunoglobulin classes such as IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, and IgE. Additionally, it discusses the roles these antibodies play in the immune system, including antigen binding, complement activation, and their ability to cross the placenta.