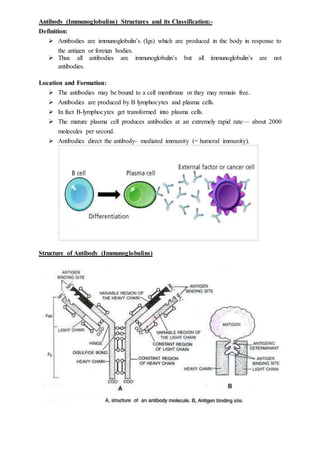
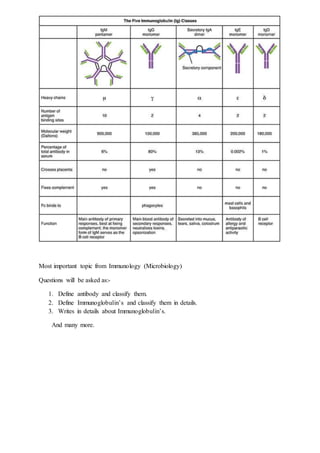
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped globular plasma proteins produced by B cells and plasma cells in response to antigens. They have two types of polypeptide chains called heavy chains and light chains which give them a basic structure. There are five types of heavy chains that determine the five classes of immunoglobulins - IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, and IgE. Immunoglobulins are classified based on their heavy chain constant region and distributed differently throughout the body to serve various functions in antibody-mediated immunity. The variable region of the antibody binds to antigens and the constant region remains the same.