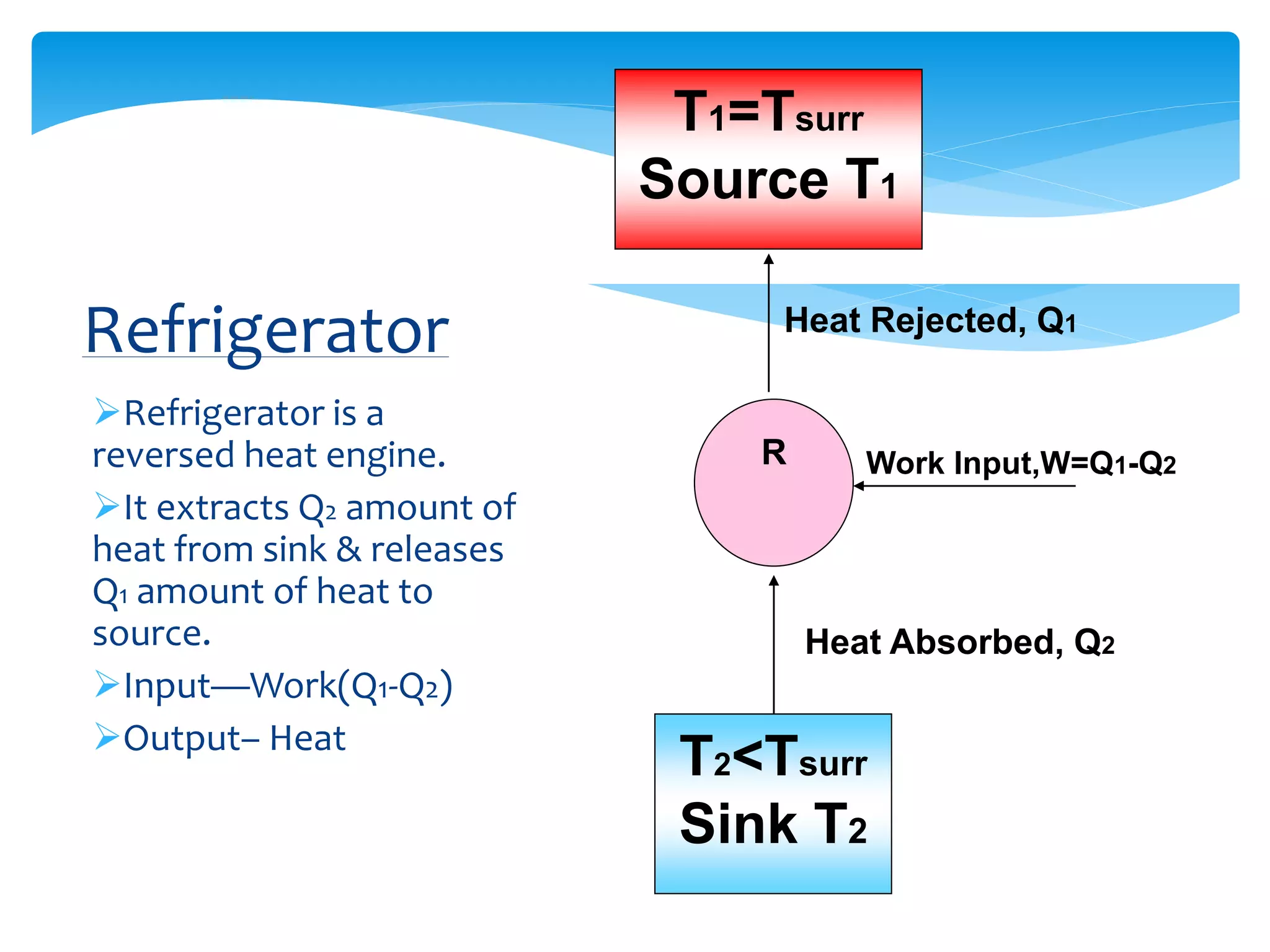
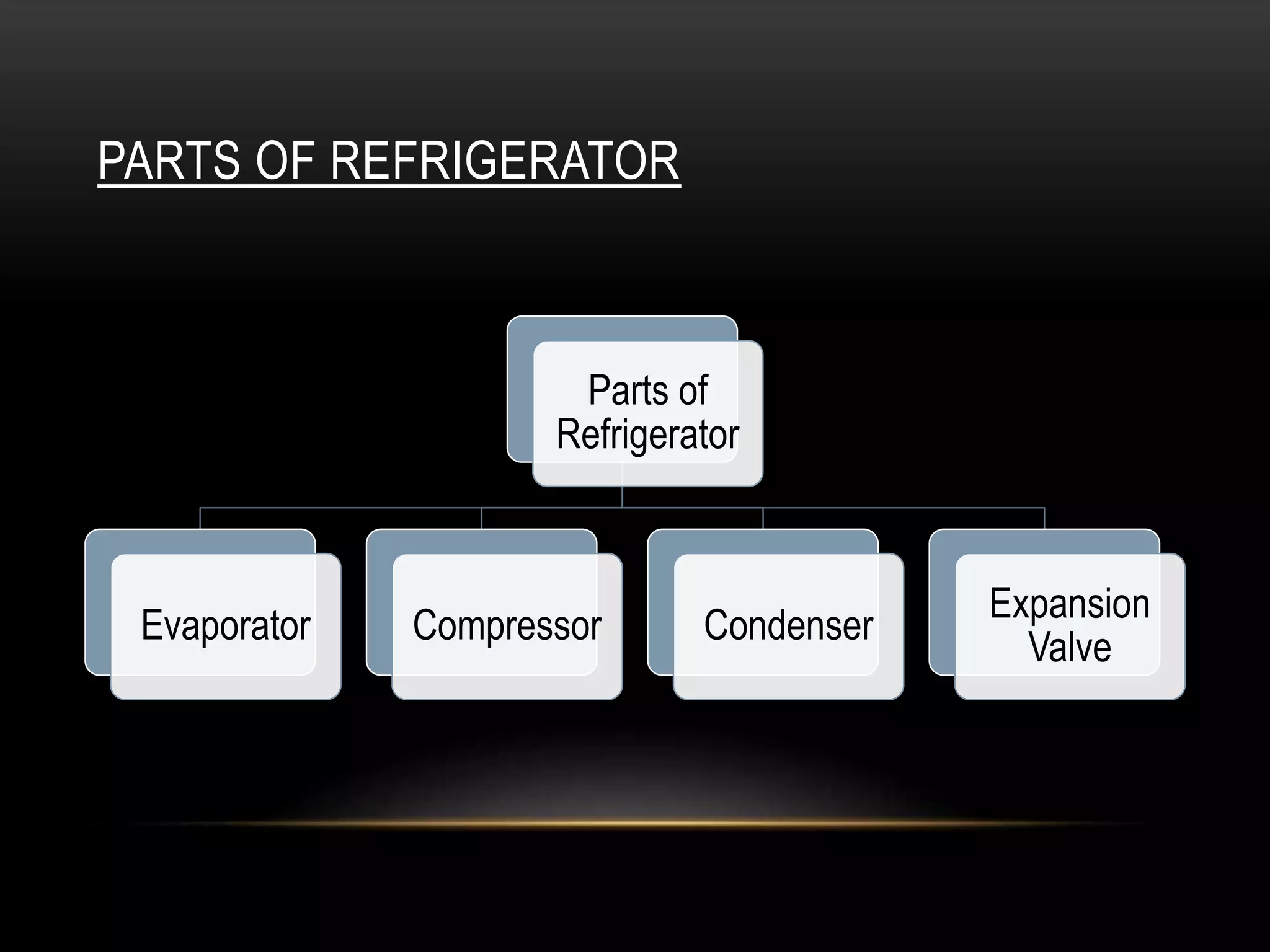
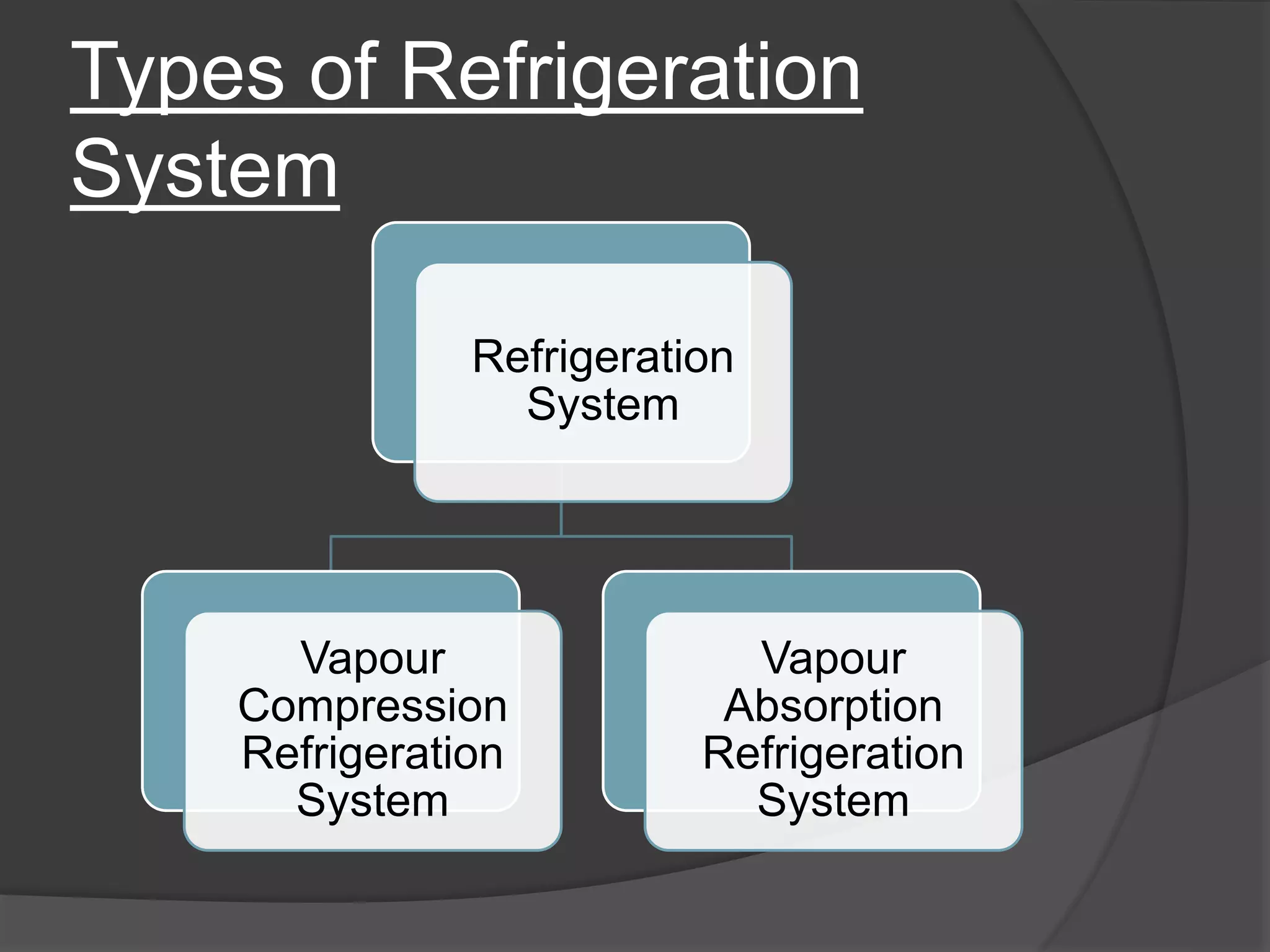
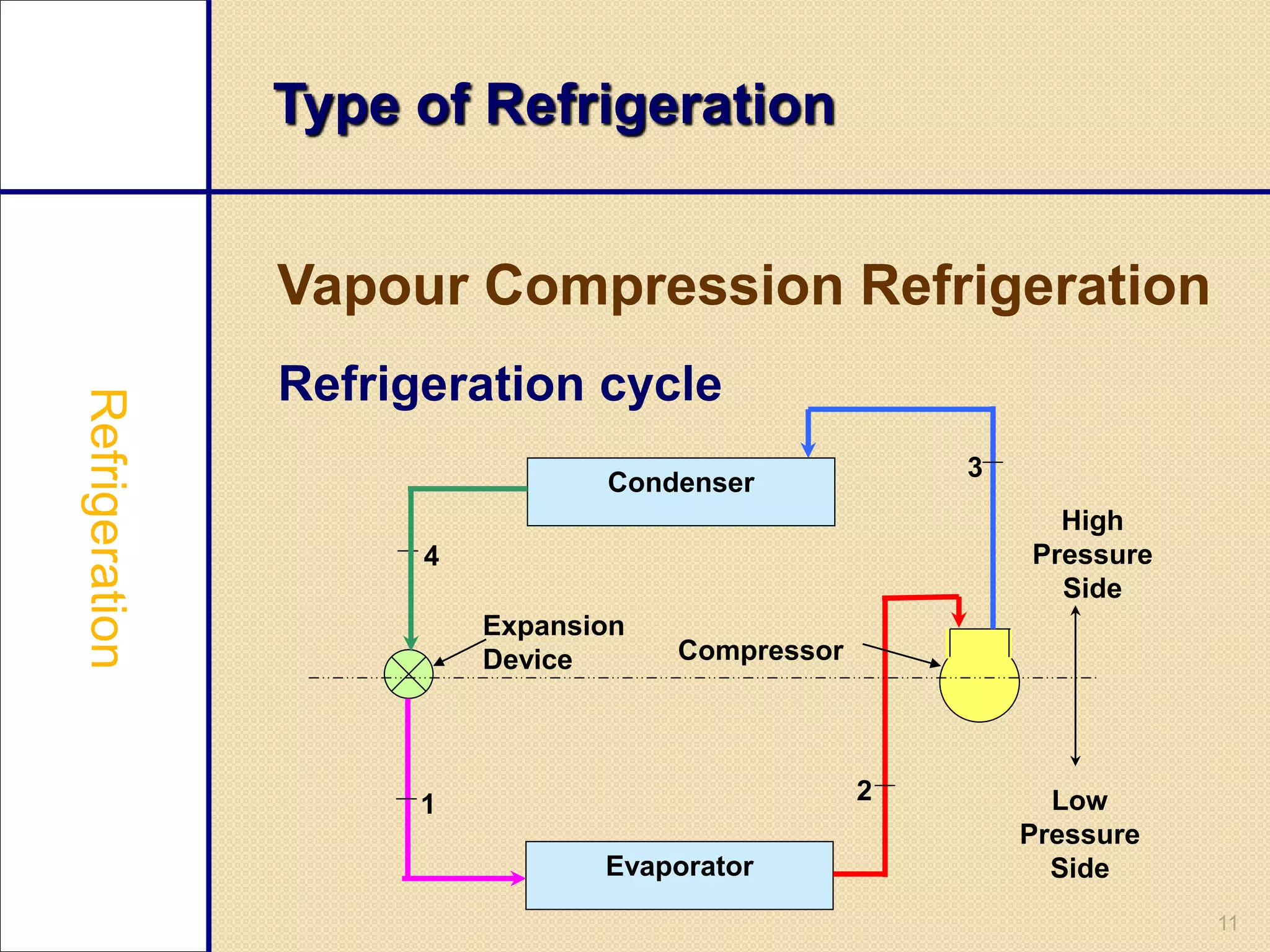
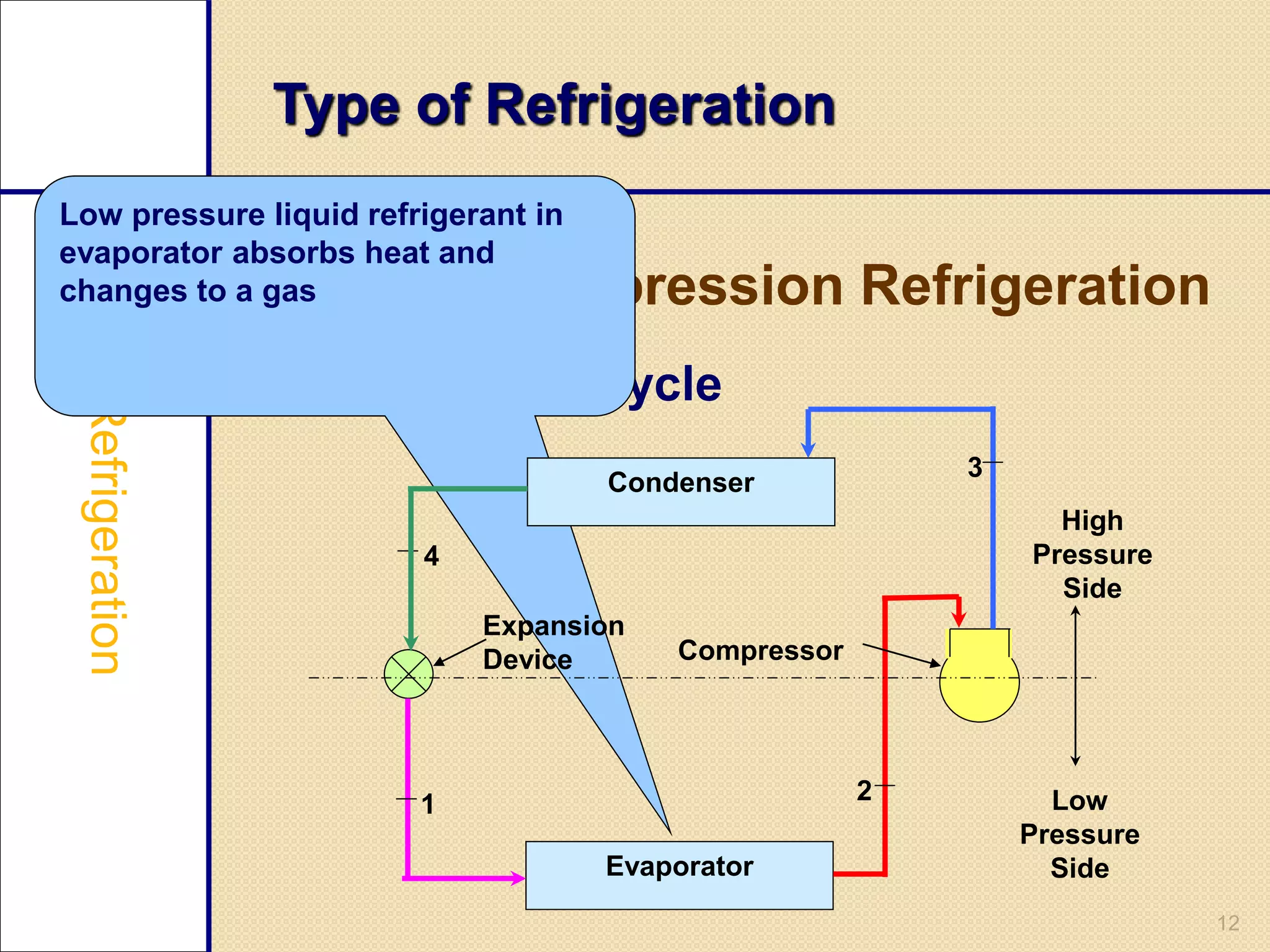
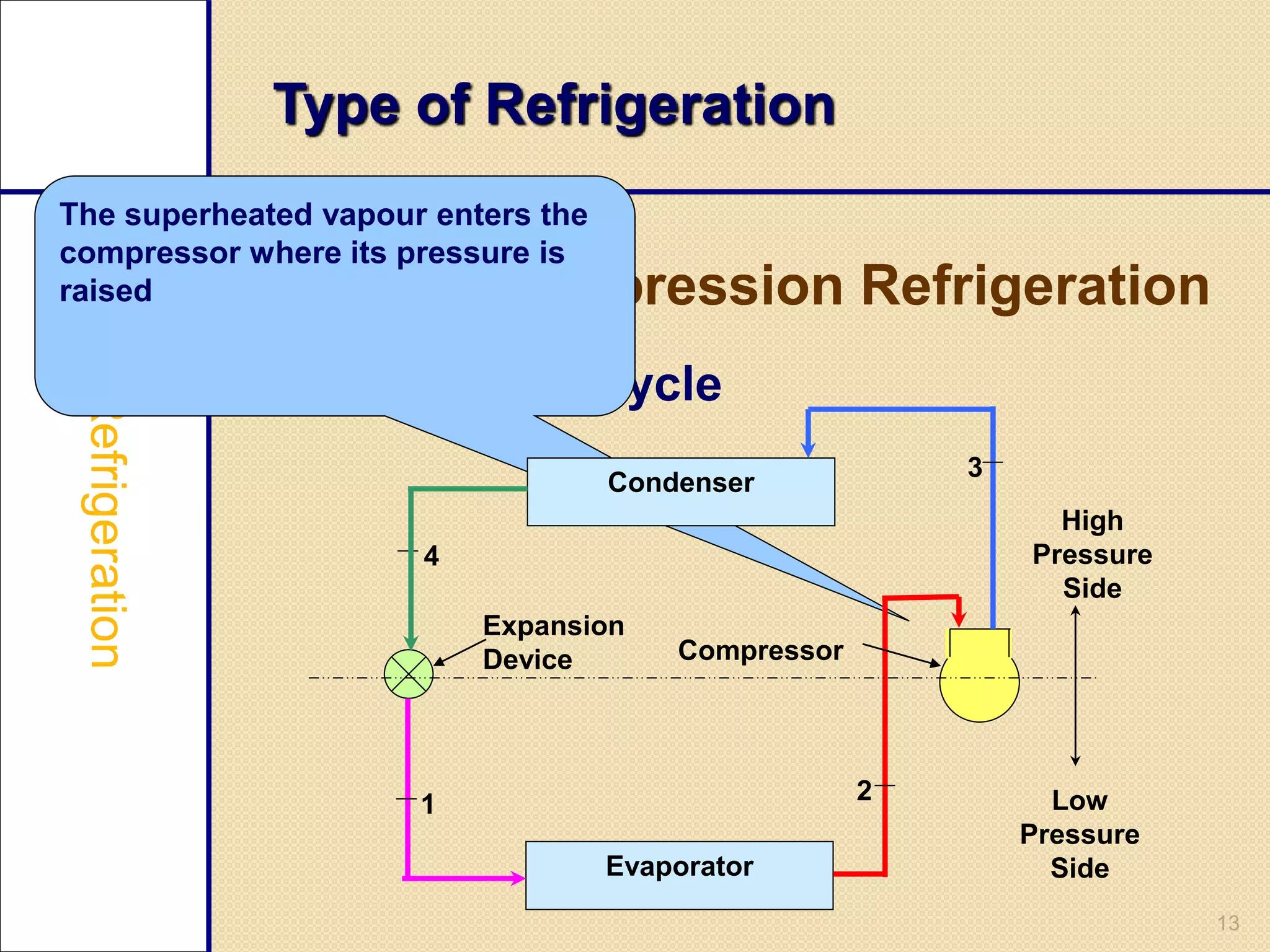
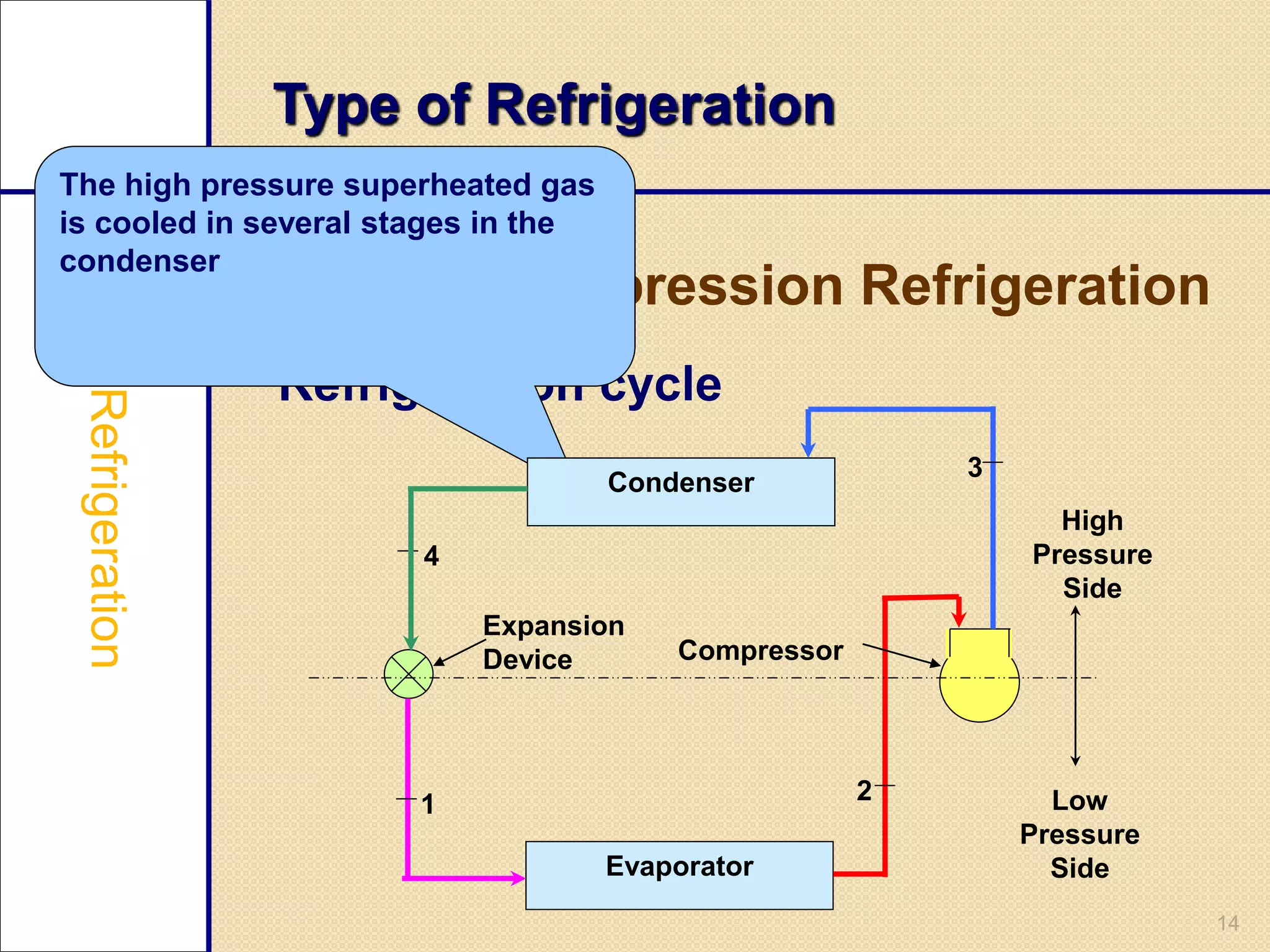
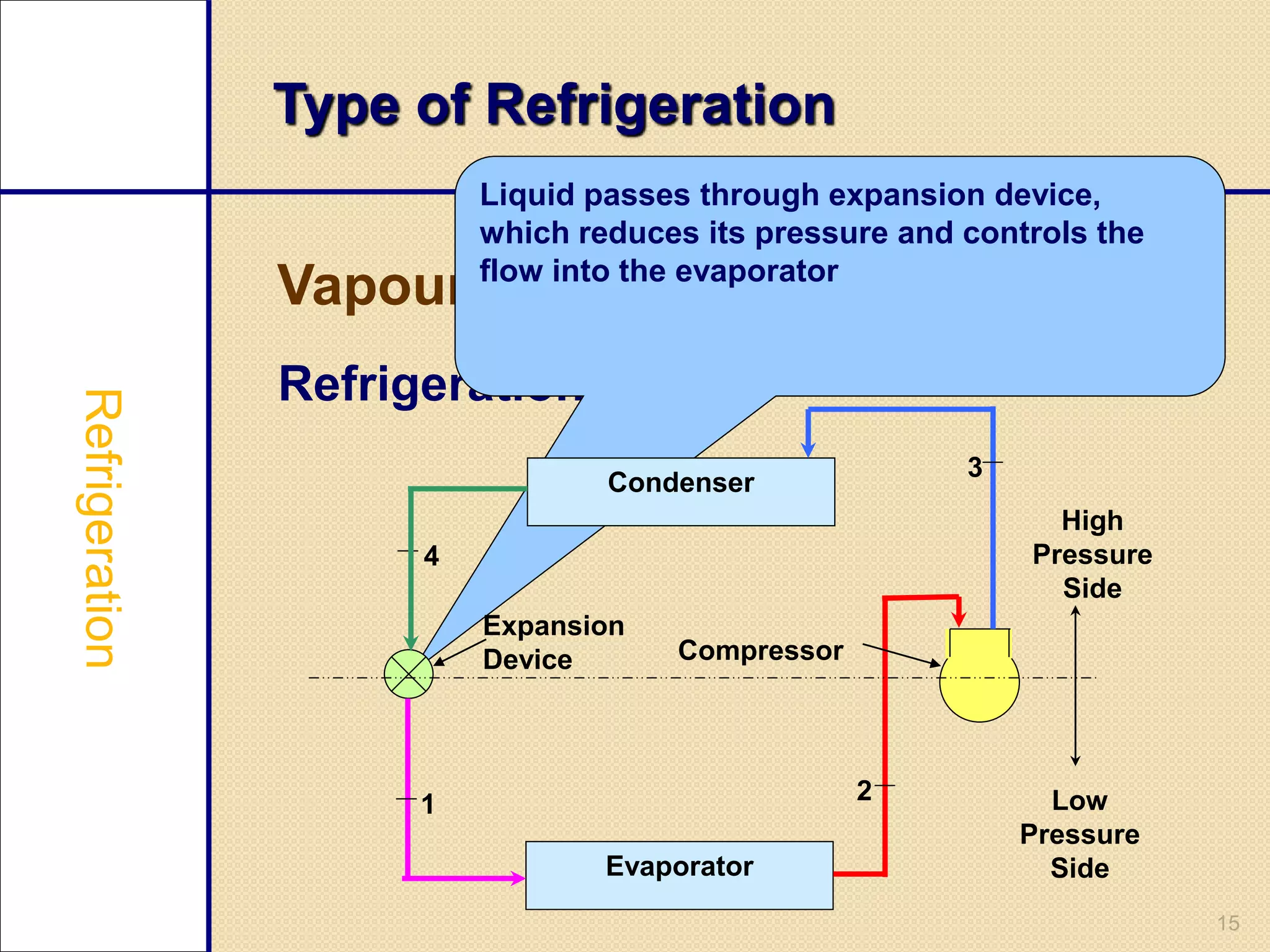
This document provides an overview of a seminar on vapour compression refrigeration. The seminar was guided by Mr. Devendra Bhandari and prepared by Ujjwal Nautiyal. It discusses the basic principles of refrigeration including how refrigerants are used to extract heat from refrigerators and reject it to the atmosphere. It then describes the key components of a refrigeration system including the evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve. The document outlines the refrigeration cycle process and concludes by discussing advantages like high efficiency and disadvantages like use of ozone depleting refrigerants.