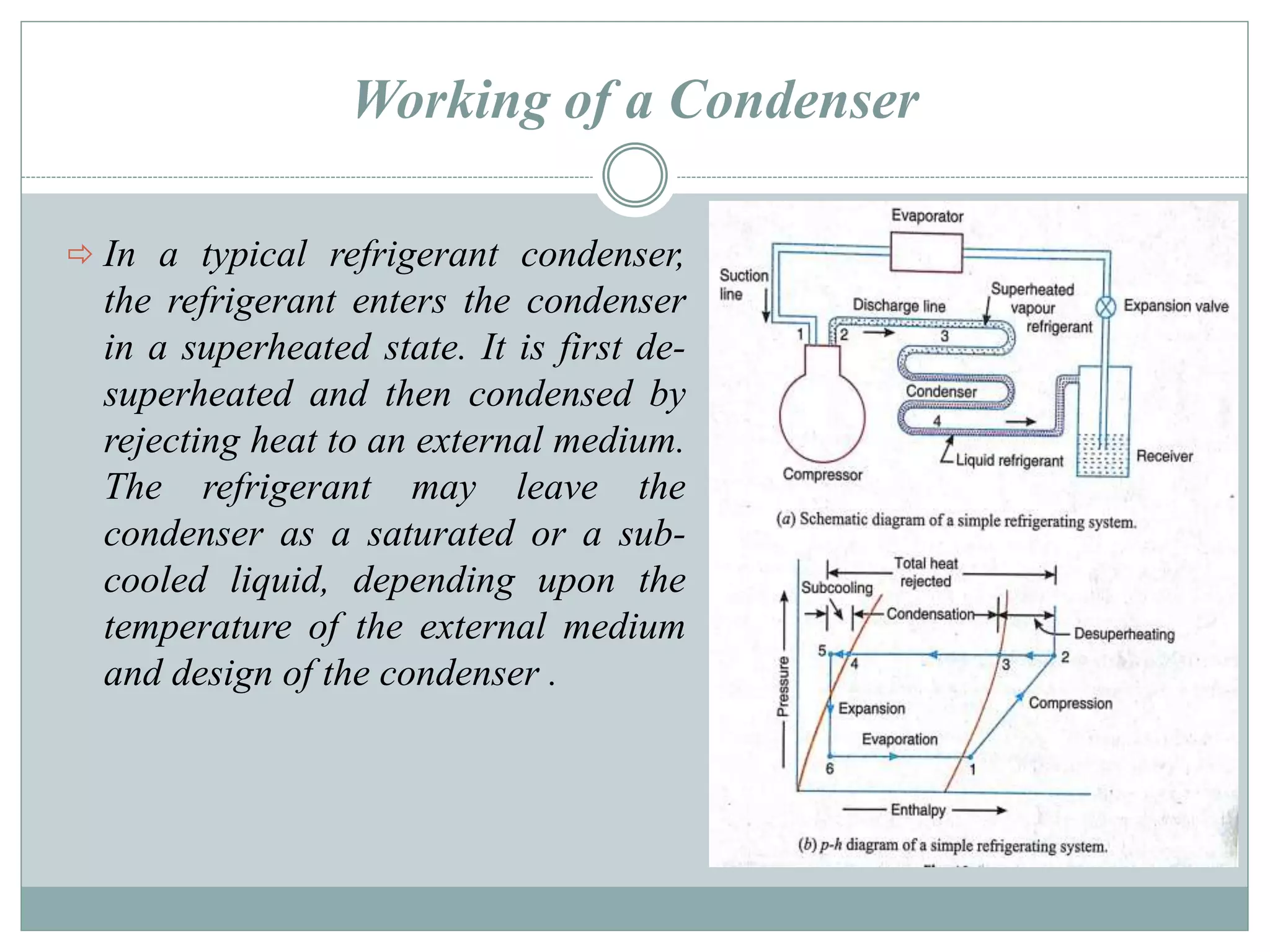
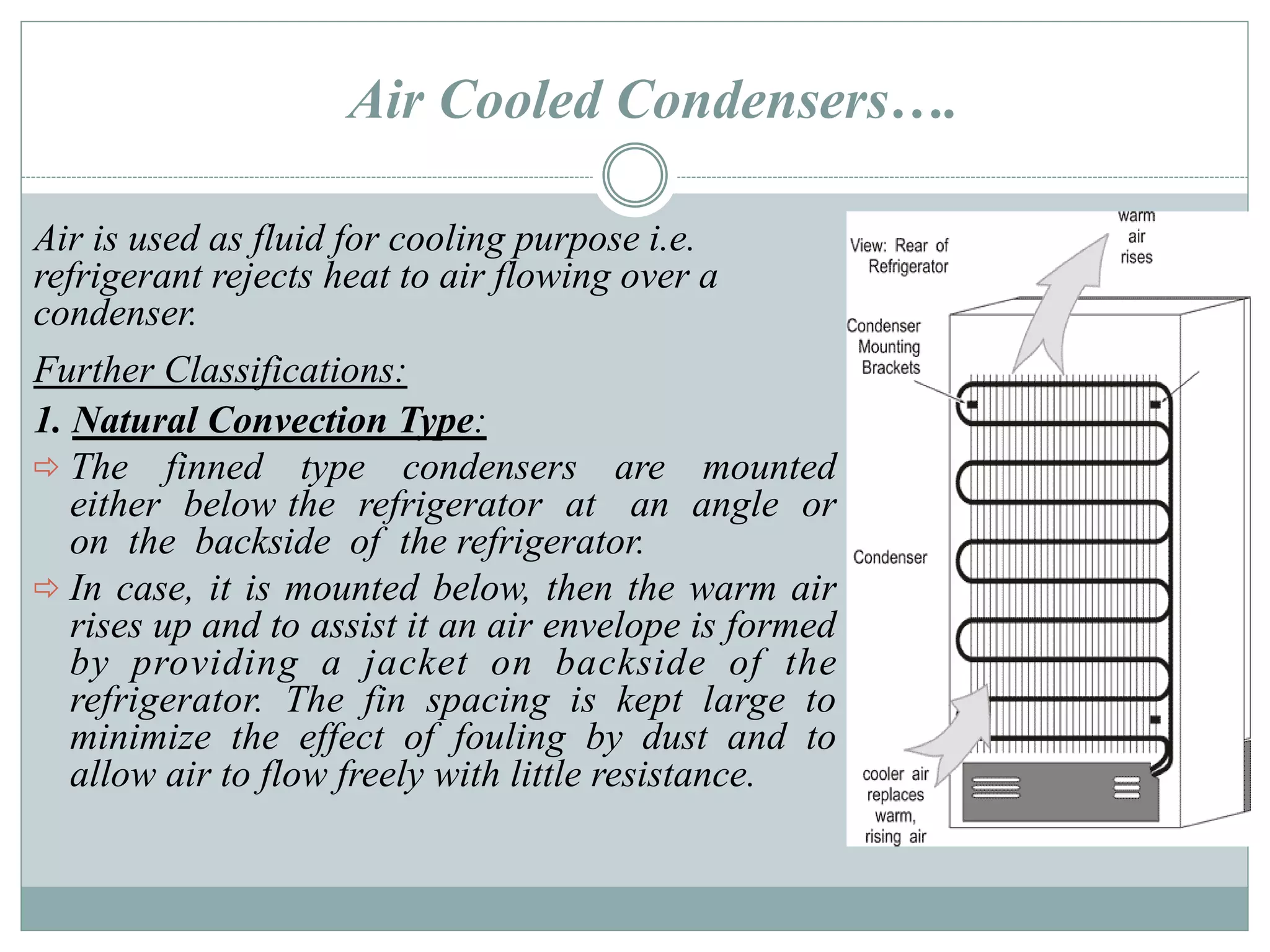
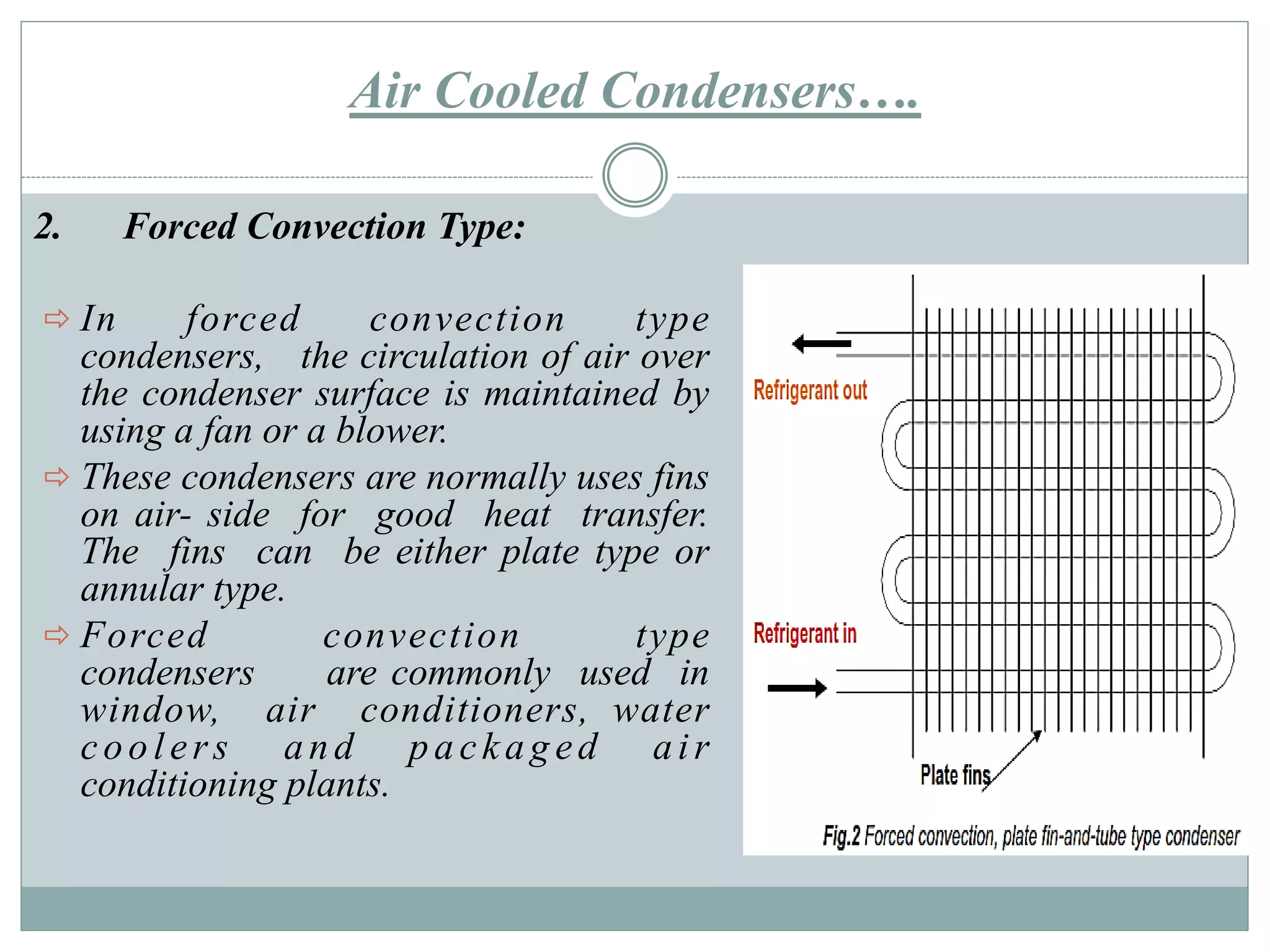
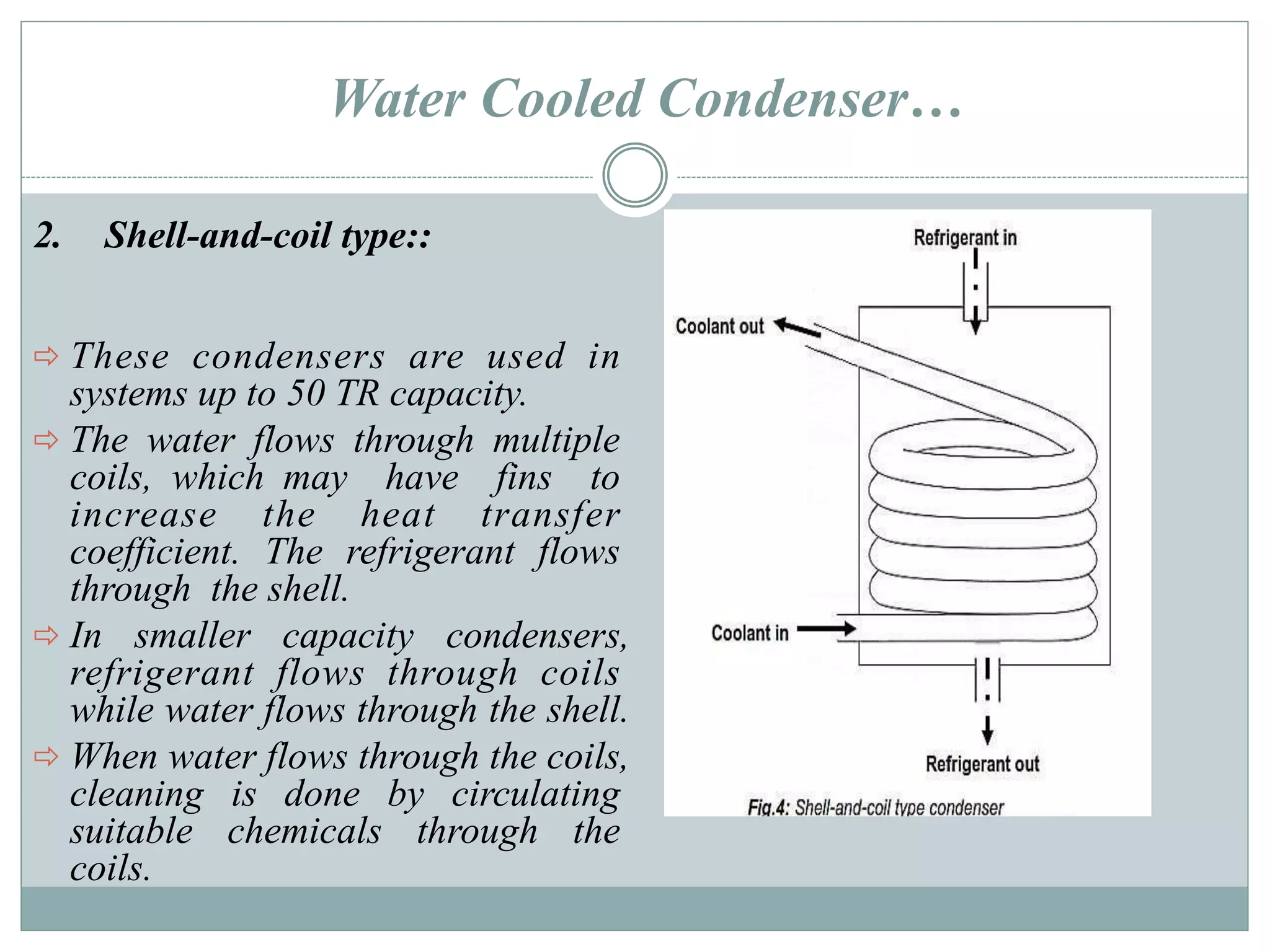
Condensers are heat exchangers that condense refrigerant vapor by rejecting heat to an external medium such as air or water. There are several types of condensers including air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative condensers. Air-cooled condensers use air as the external medium and can be natural or forced convection. Water-cooled condensers include tube-in-tube, shell-and-coil, and shell-and-tube designs with water flowing inside tubes or a shell. Evaporative condensers combine features of cooling towers and water-cooled condensers using both air and water to extract heat from the condensing refrigerant.