This document discusses link prediction in homogeneous and heterogeneous social networks. It begins by introducing the problem of link prediction and its applications. It then discusses various unsupervised and supervised methods for link prediction in homogeneous networks. Next, it covers relationship prediction and collective link prediction in heterogeneous networks. It also discusses link prediction in aligned heterogeneous networks using link transfer and anchor link inference. Finally, it outlines future work on this topic.















![44 DMLLink Prediction DMLDMLLink Prediction44
References
[1] L. Lü and T. Zhou, "Link prediction in complex networks: A survey," Physica A:
Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, vol. 390, pp. 1150-1170, 2011.
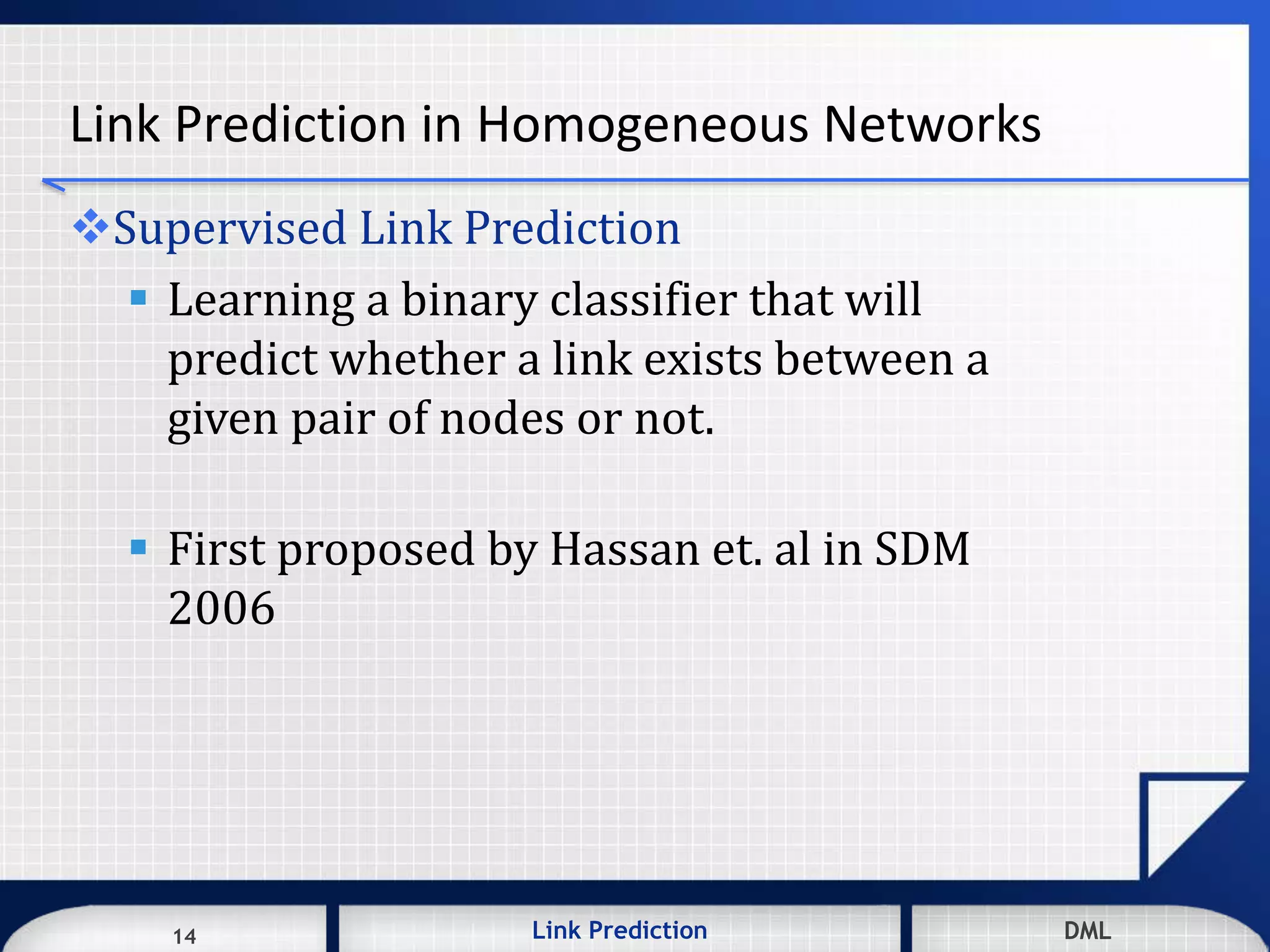
[2] M. Al Hasan, V. Chaoji, S. Salem, and M. Zaki, "Link prediction using supervised
learning," in SDM’06: Workshop on Link Analysis, Counter-terrorism and Security,
2006.
[3] J. Zhang and S. Y. Philip, "Link Prediction across Heterogeneous Social
Networks: A Survey," 2014.
[4] Y. Sun, R. Barber, M. Gupta, C. C. Aggarwal, and J. Han, "Co-author relationship
prediction in heterogeneous bibliographic networks," in Advances in Social
Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), 2011 International Conference on, 2011,
pp. 121-128.
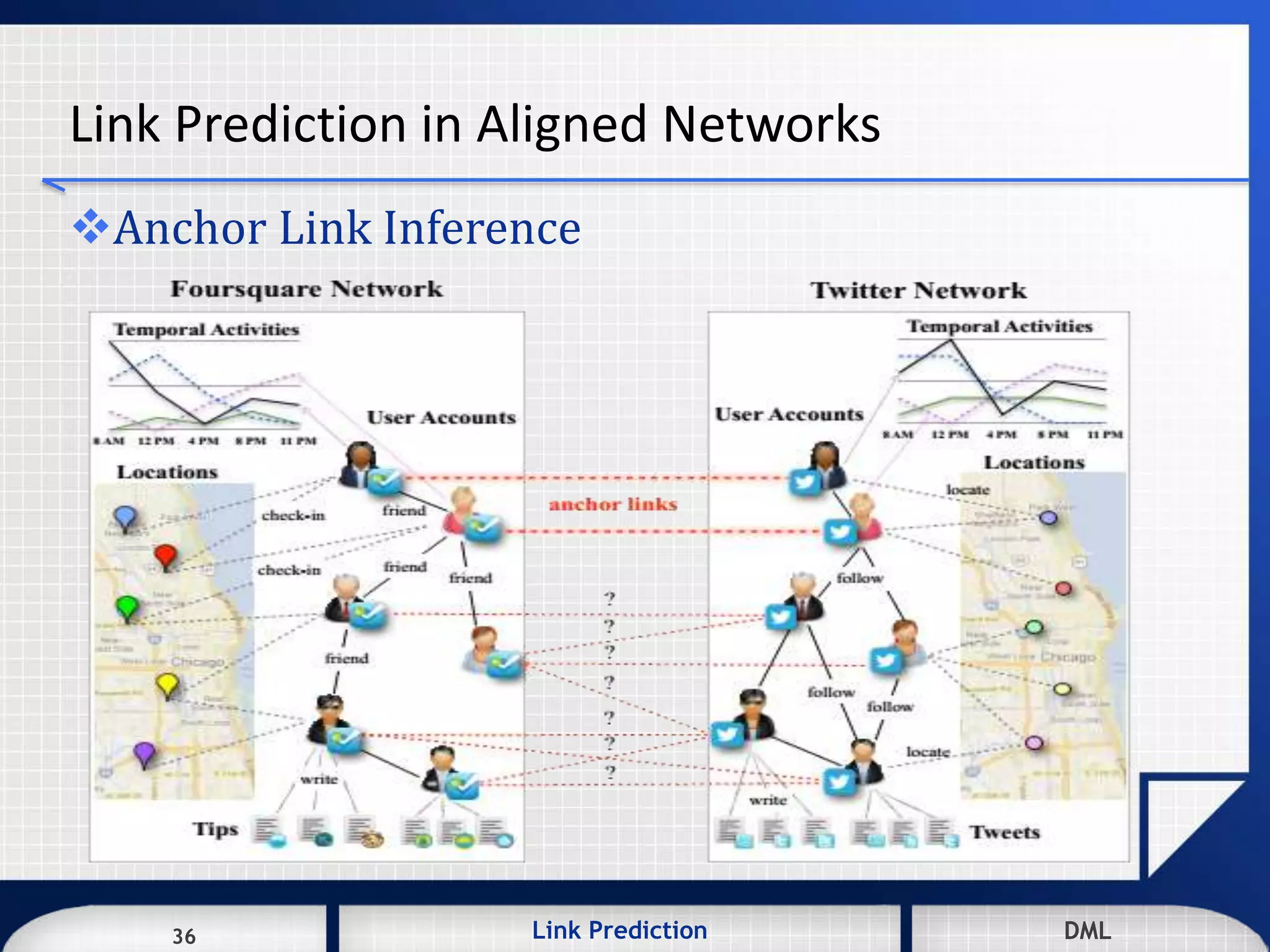
[5] X. Kong, J. Zhang, and P. S. Yu, "Inferring anchor links across multiple
heterogeneous social networks," in Proceedings of the 22nd ACM international
conference on Conference on information & knowledge management, 2013, pp. 179-
188.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e38d2aca-e267-4c55-8493-45e77ac39ac3-160513074657/75/Link-Prediction-in-Partially-Aligned-Heterogeneous-Social-Networks-44-2048.jpg)
