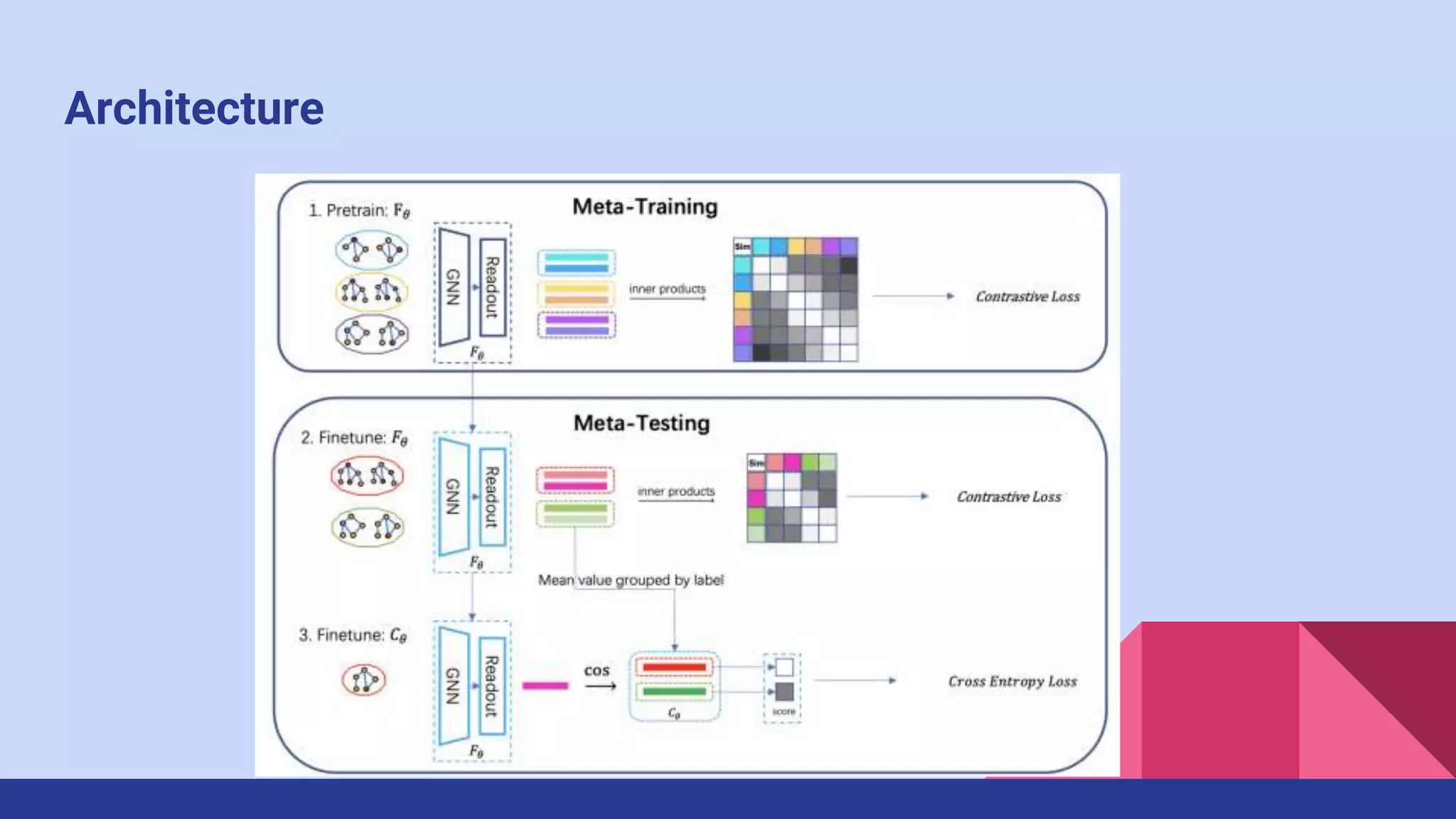
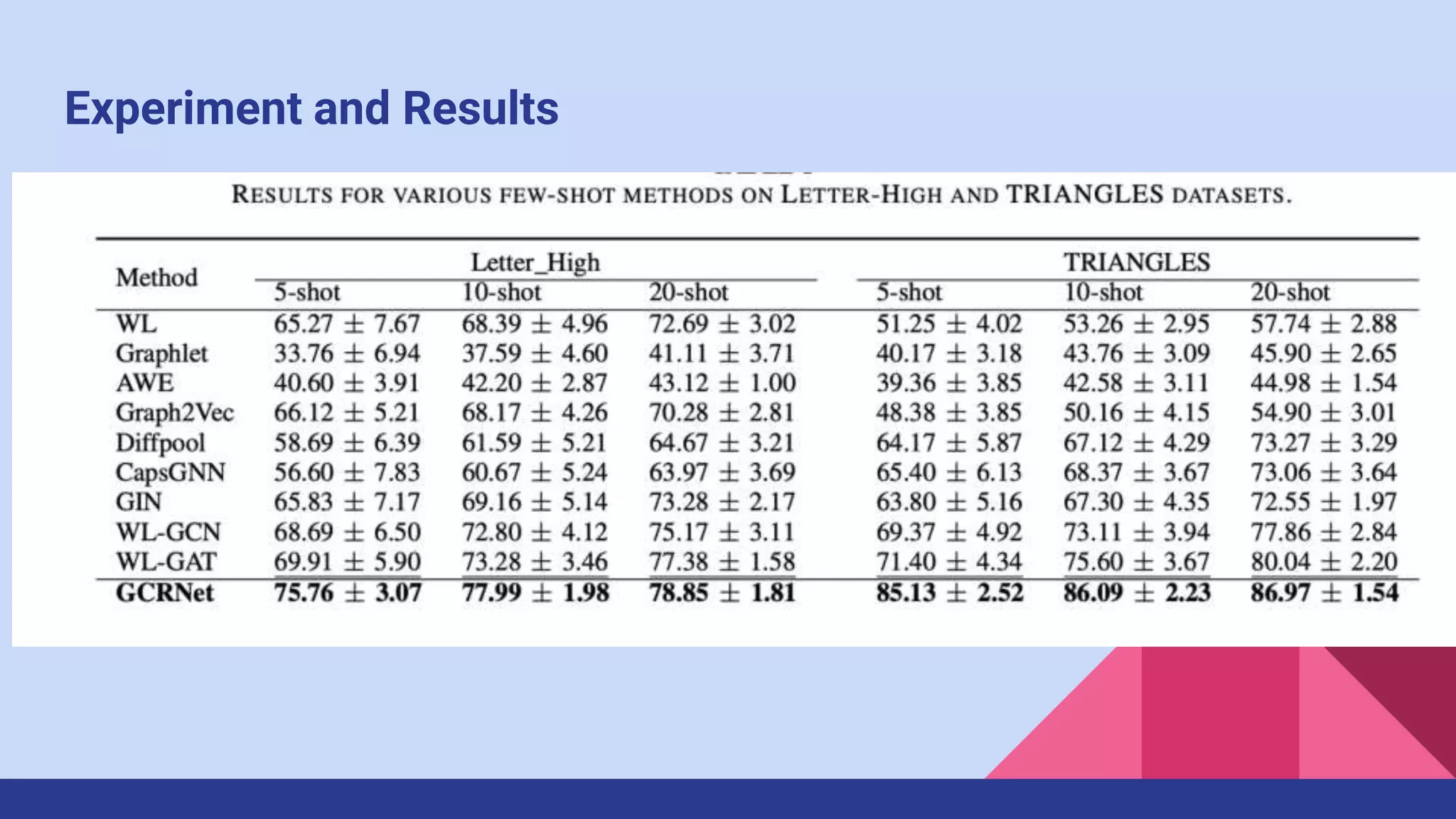
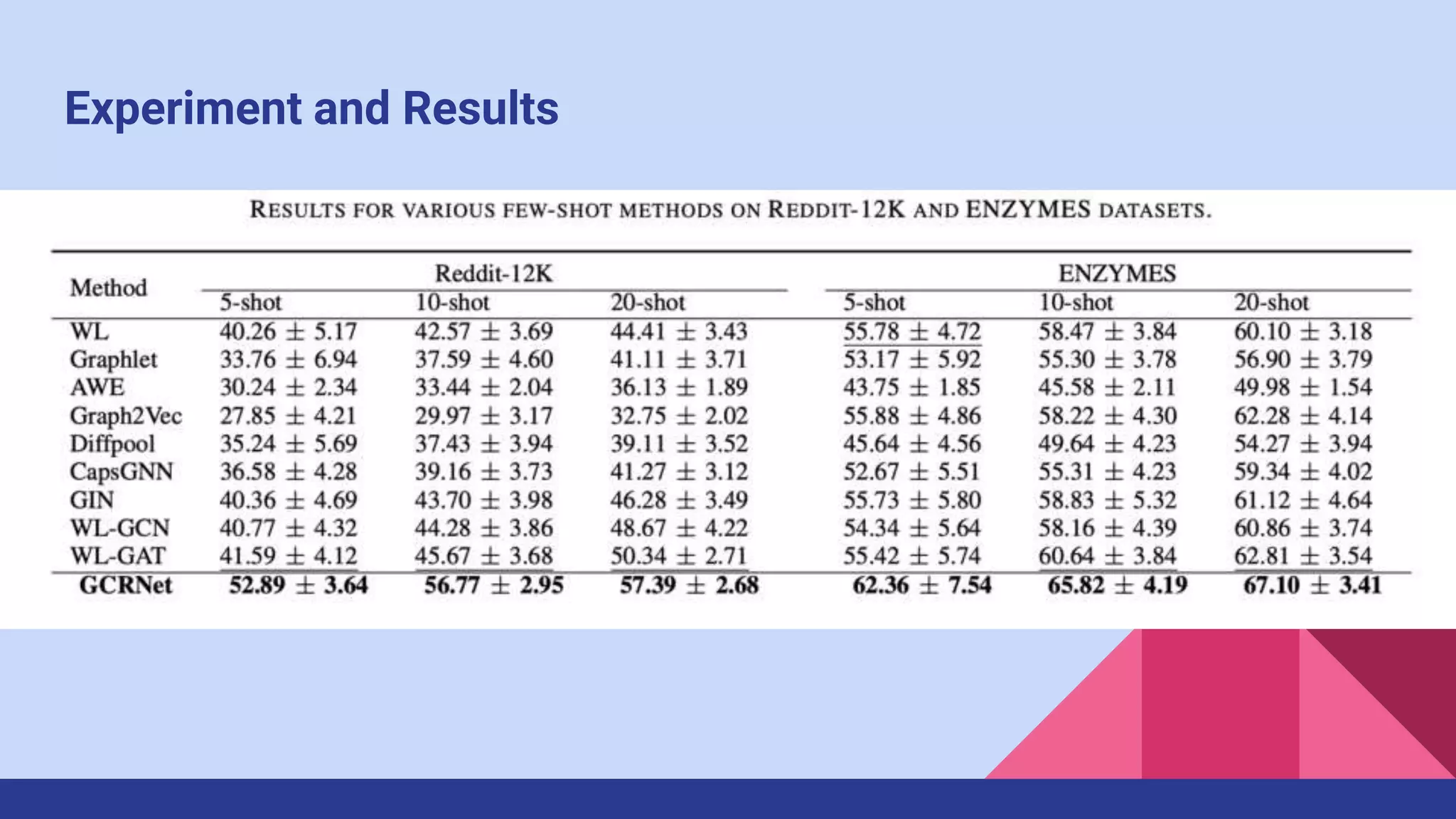
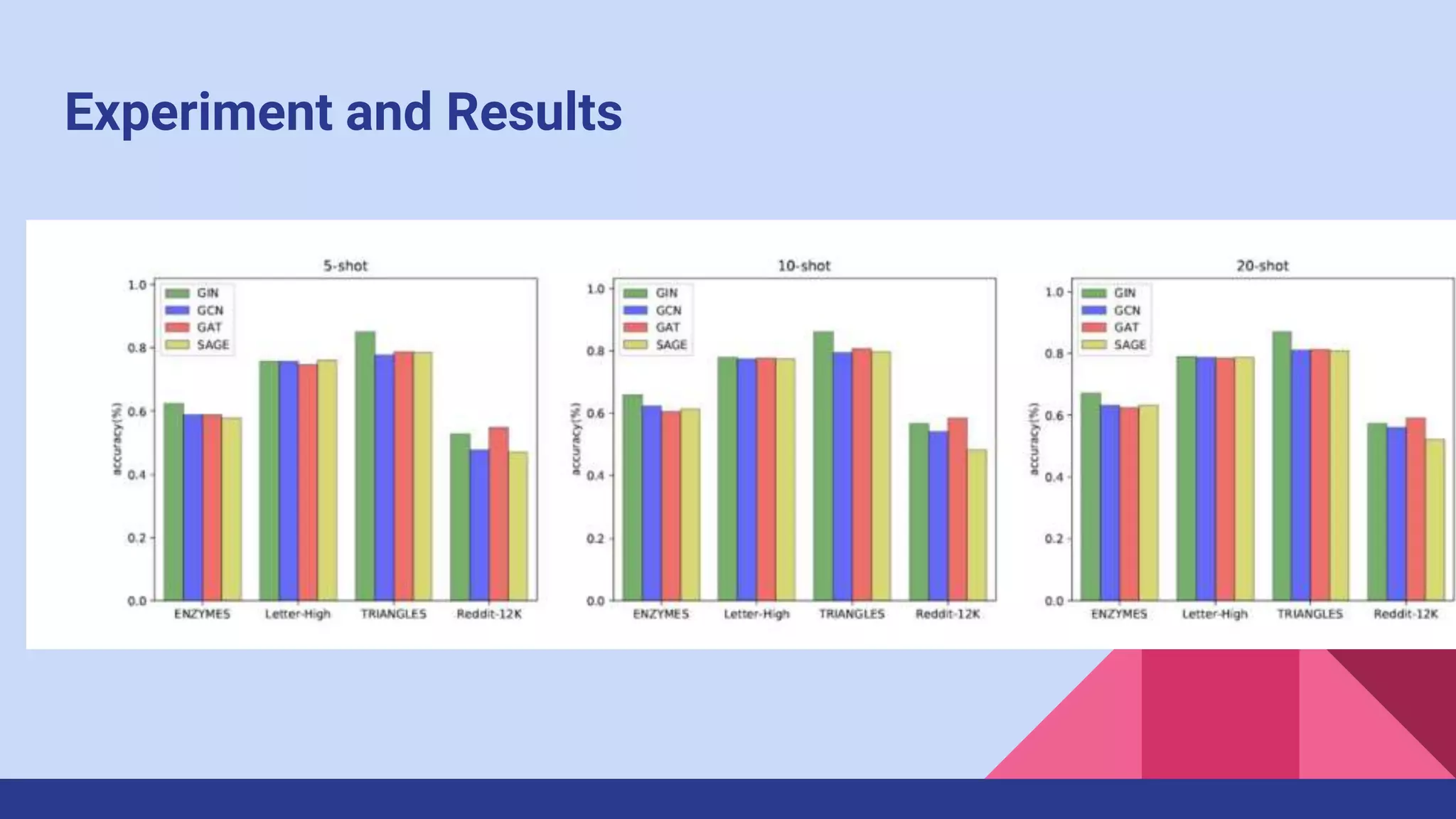
The paper presents a novel method for few-shot graph classification called GCRNet, which leverages contrastive loss and a meta-classifier to enhance performance with limited labeled graphs. It demonstrates superior results on four datasets, outperforming the state-of-the-art method by 10% even with small support sets. The approach involves a graph neural network architecture and emphasizes the role of contrastive learning in improving classification accuracy.