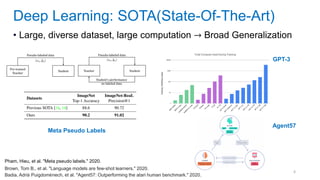
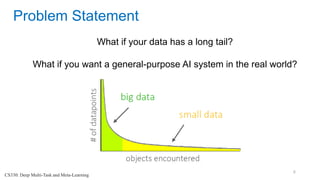
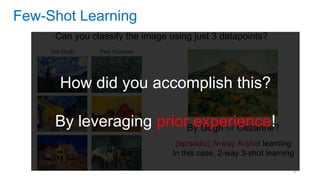
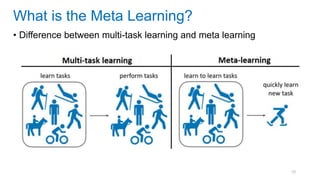
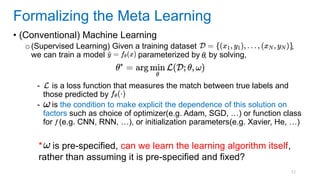
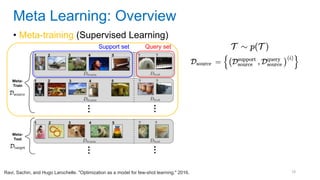
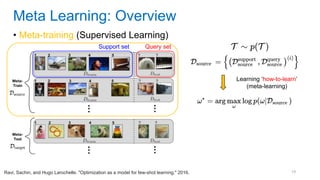
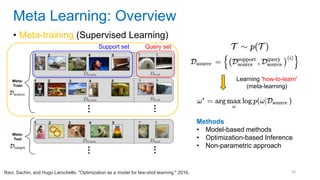
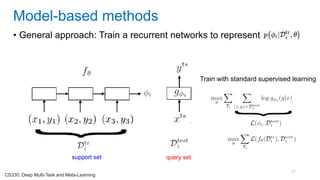
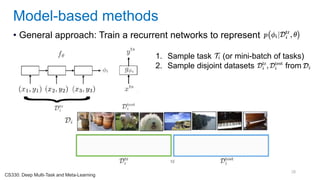
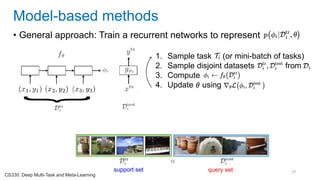
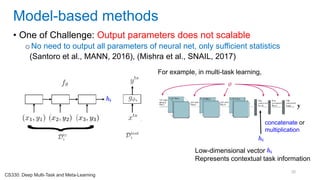
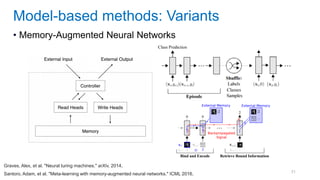
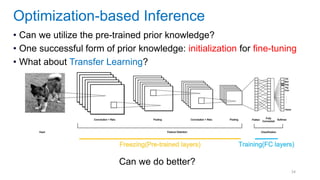
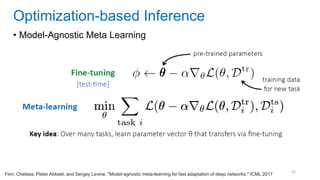
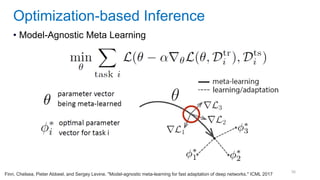
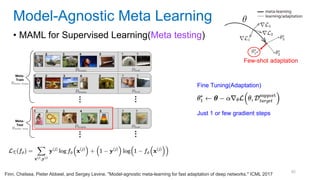
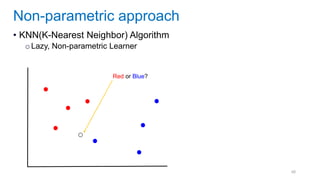
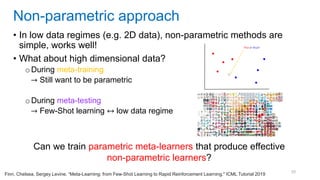
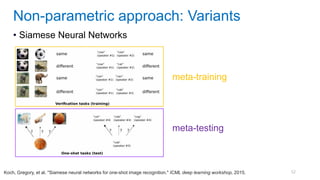
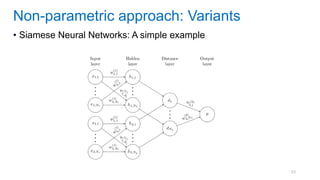
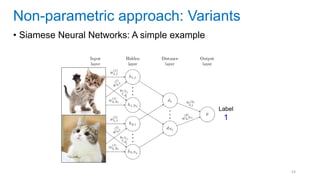
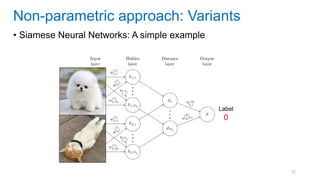
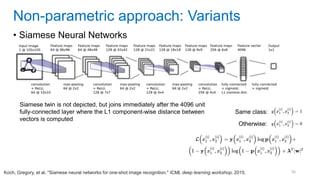
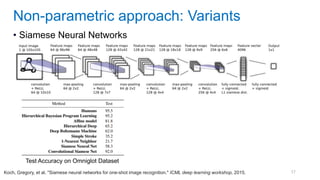
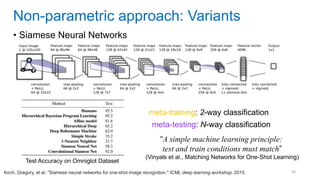
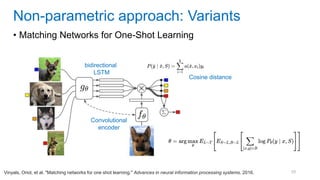
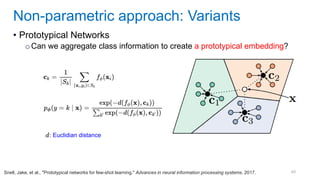
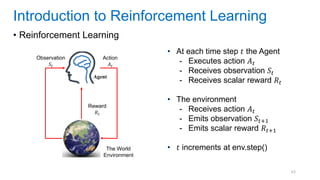
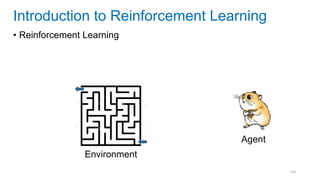
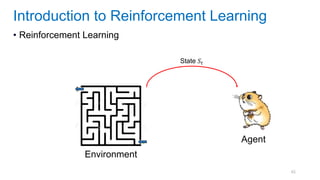
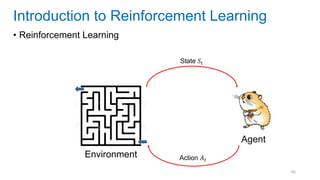
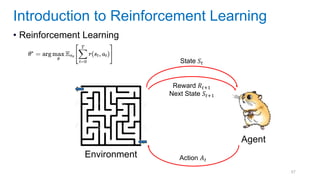
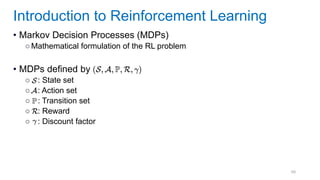
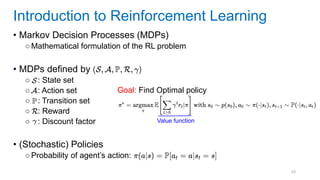
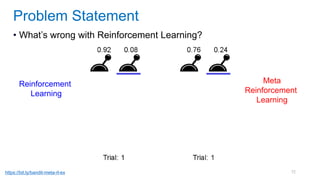
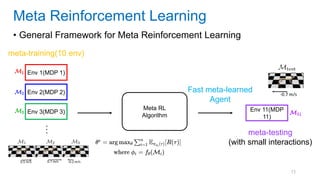
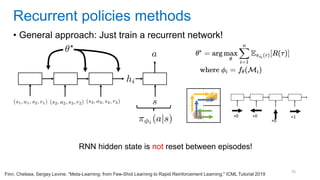
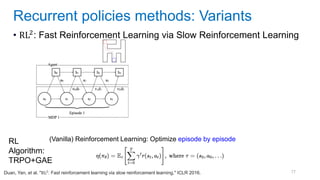
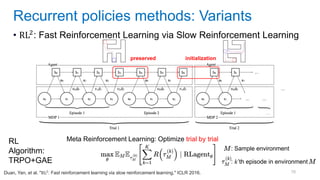
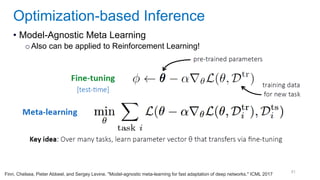
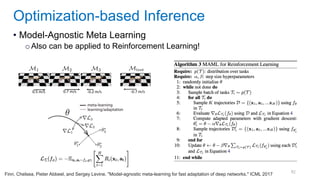
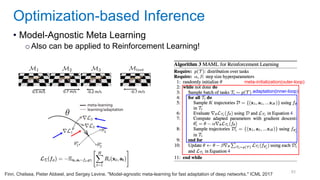
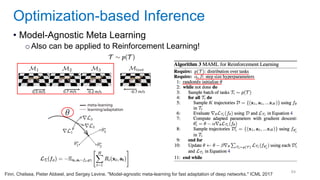
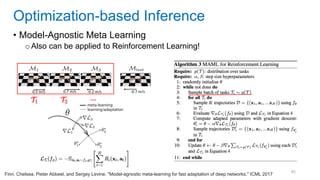
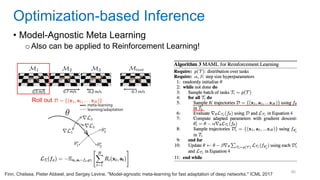
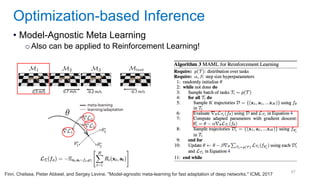
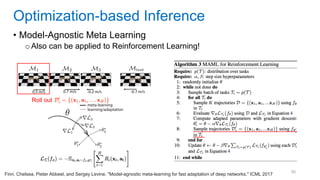
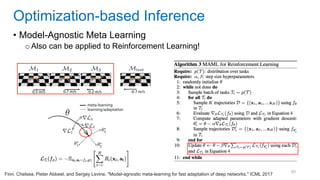
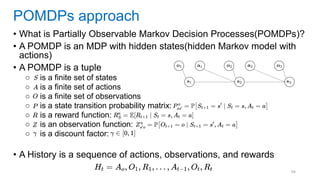
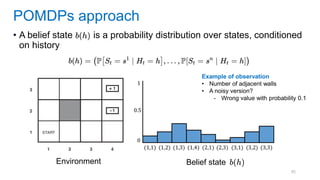
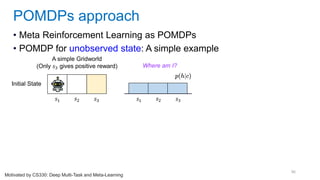
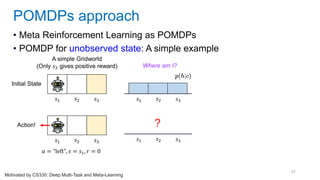
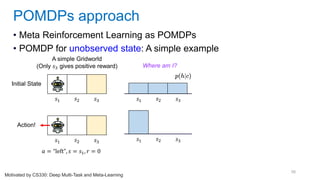
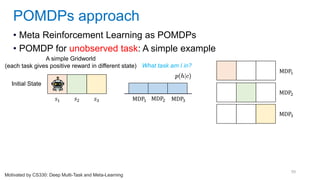
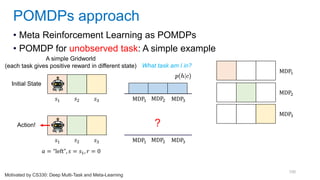
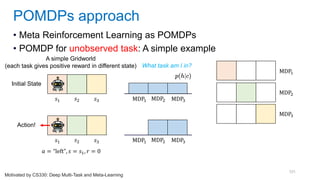
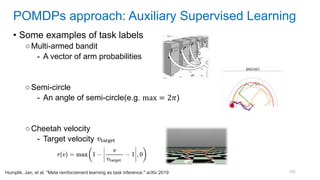
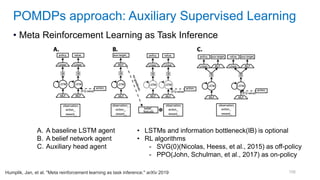
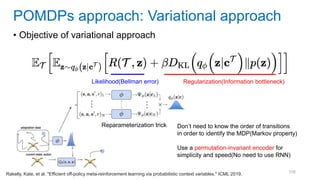
This document discusses deep meta learning and learning-to-learn in neural networks. It provides an agenda that covers an overview of meta learning, meta supervised learning approaches including model-based methods, optimization-based inference, and non-parametric approaches. It also briefly discusses meta reinforcement learning and recurrent policy, optimization-based inference, and POMDP approaches. The document seeks to explain what meta learning is, how to formalize and solve meta learning problems, common meta learning algorithms, and benchmark datasets for evaluating meta supervised learning.